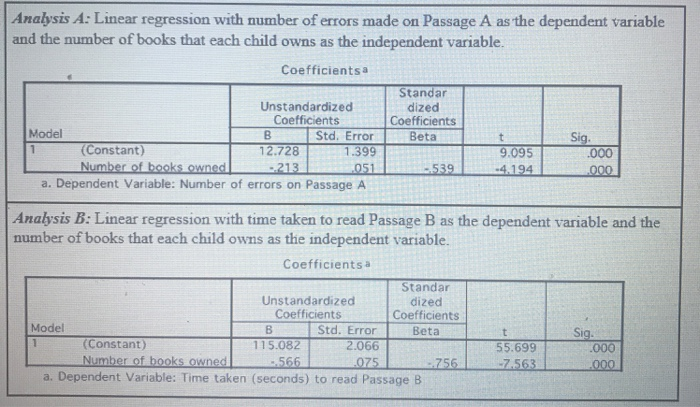
Analysis A: Linear regression with number of errors made on Passage A as the dependent variable and the number of books that each child owns as the independent variable. Coefficients a Standar Unstandardized dized Coefficients Coefficients Model B Std. Error Beta Sig. 1 (Constant) 72.728 1.399 9.095 .000 Number of books owned -213 051 539 -4.194 .000 a. Dependent Variable: Number of errors on Passage A t Analysis B: Linear regression with time taken to read Passage B as the dependent variable and the number of books that each child owns as the independent variable. Coefficients a Standar Unstandardized dized Coefficients Coefficients Model Std. Error Beta t Sig. (Constant) 115.082 2.066 55.699 .000 Number of books owned .075 .756 -7563 .000 a. Dependent Variable: Time taken (seconds) to read Passage B 1 $5.699 -566 (a) What is the Pearson correlation between the number of errors made on Passage A and the number of books that each child owns? (b) What percentage of variance in the time taken to read Passage B is accounted for by the number of books that each child owns? 6 According to the regression analyses, which measure of reading performance is better predicted by the number of books that a child owns? Select ONE measure by placing an X in the box provided. Number of errors on Passage A Time taken to read Passage B (i) Which values from the SPSS output on the previous page did you use to reach this conclusion? Please describe ONE of the values from the SPSS output for each analysis. From Analysis A, I used... From Analysis B. I used... Write down the equation for the regression line that allows you calculate the expected time taken to read Passage B from the number of books a child owns. Use the letter T to stand for the time taken in seconds, and use the letter B to stand for the number of books a child owns. You can omit ^ and other non-standard symbols. Equation: Analysis A: Linear regression with number of errors made on Passage A as the dependent variable and the number of books that each child owns as the independent variable. Coefficients a Standar Unstandardized dized Coefficients Coefficients Model B Std. Error Beta Sig. 1 (Constant) 72.728 1.399 9.095 .000 Number of books owned -213 051 539 -4.194 .000 a. Dependent Variable: Number of errors on Passage A t Analysis B: Linear regression with time taken to read Passage B as the dependent variable and the number of books that each child owns as the independent variable. Coefficients a Standar Unstandardized dized Coefficients Coefficients Model Std. Error Beta t Sig. (Constant) 115.082 2.066 55.699 .000 Number of books owned .075 .756 -7563 .000 a. Dependent Variable: Time taken (seconds) to read Passage B 1 $5.699 -566 (a) What is the Pearson correlation between the number of errors made on Passage A and the number of books that each child owns? (b) What percentage of variance in the time taken to read Passage B is accounted for by the number of books that each child owns? 6 According to the regression analyses, which measure of reading performance is better predicted by the number of books that a child owns? Select ONE measure by placing an X in the box provided. Number of errors on Passage A Time taken to read Passage B (i) Which values from the SPSS output on the previous page did you use to reach this conclusion? Please describe ONE of the values from the SPSS output for each analysis. From Analysis A, I used... From Analysis B. I used... Write down the equation for the regression line that allows you calculate the expected time taken to read Passage B from the number of books a child owns. Use the letter T to stand for the time taken in seconds, and use the letter B to stand for the number of books a child owns. You can omit ^ and other non-standard symbols. Equation