Question
Analyze Note1 and Note2 and derive Your Own Utility Function of this note : Note 1 : People often face decision making under uncertainty. Popular
Analyze "Note1 and Note2 and derive Your Own Utility Function" of this note :
Note 1 : People often face decision making under uncertainty. Popular method to understand this behavior is the utility function and the expected utility theory. Suppose you face with the following three gambles with a combination of income and uncertainty. Assume you are an Individual 1 with Figure 1 utility function. Examine your mean value (MV) of each gamble based on probability and income you can earn (US$). First, you attempt to maximize the average income (MV) based on equation (1) MV = P1 X1 + P2 X2 (1) Second, you attempt to maximize utility associated with income you can earn. Under certain conditions, your expected utility (EU) is calculated as the following equation. EU = P1 U(X1) + P2 U(X2) (2) Based on expected utility, you will choose gamble 2, 1, and 3 in this order because the corresponding expected utility is higher in this order.
Note2 Risk Attitude; Risk Averse, Risk Neutral, and Risk Loving Based on expected utility theory, you can derive various utility function depending on individual risk attitude. Still in textbook, we use three types of utility function for educational purpose. They are risk averse, risk loving, and risk neutral utility function. Each of them are shown in the Figure
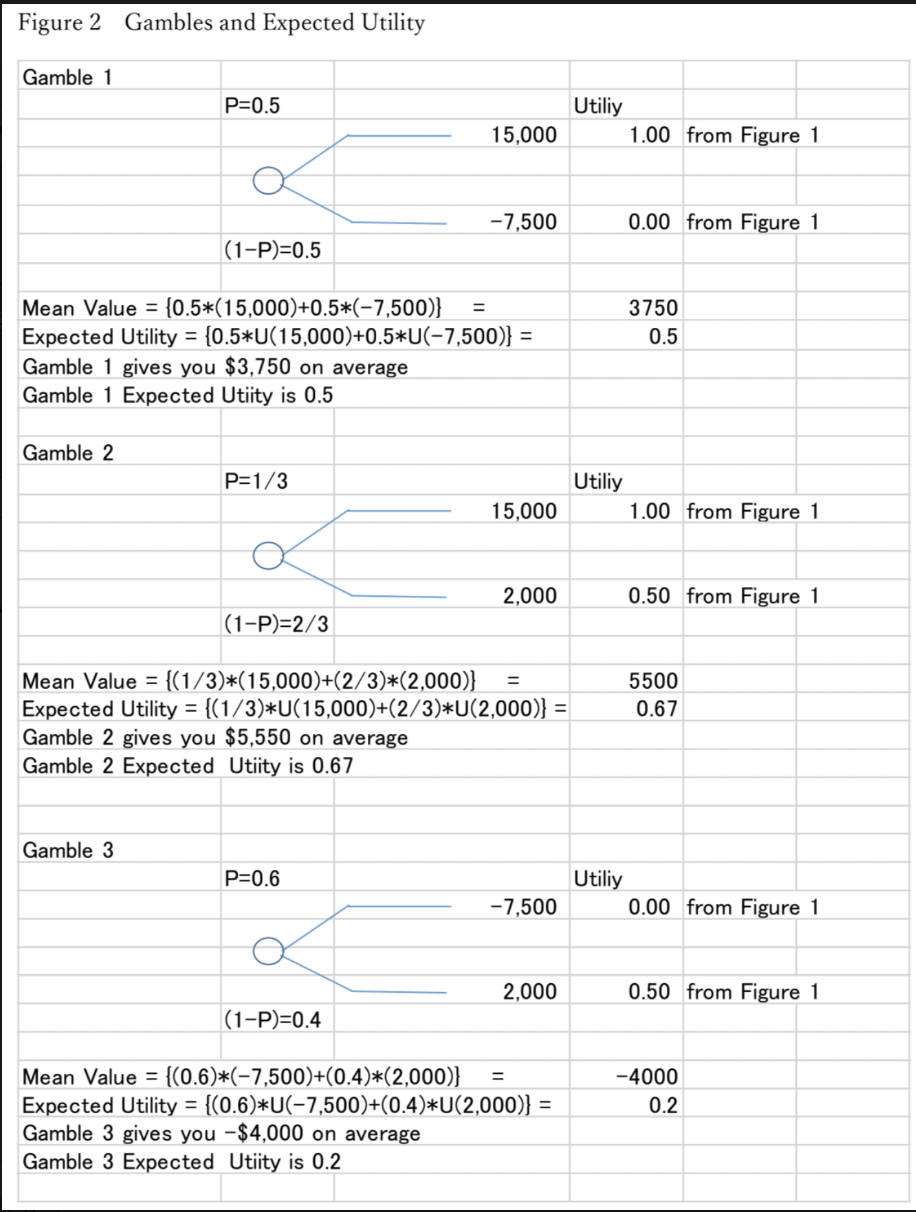
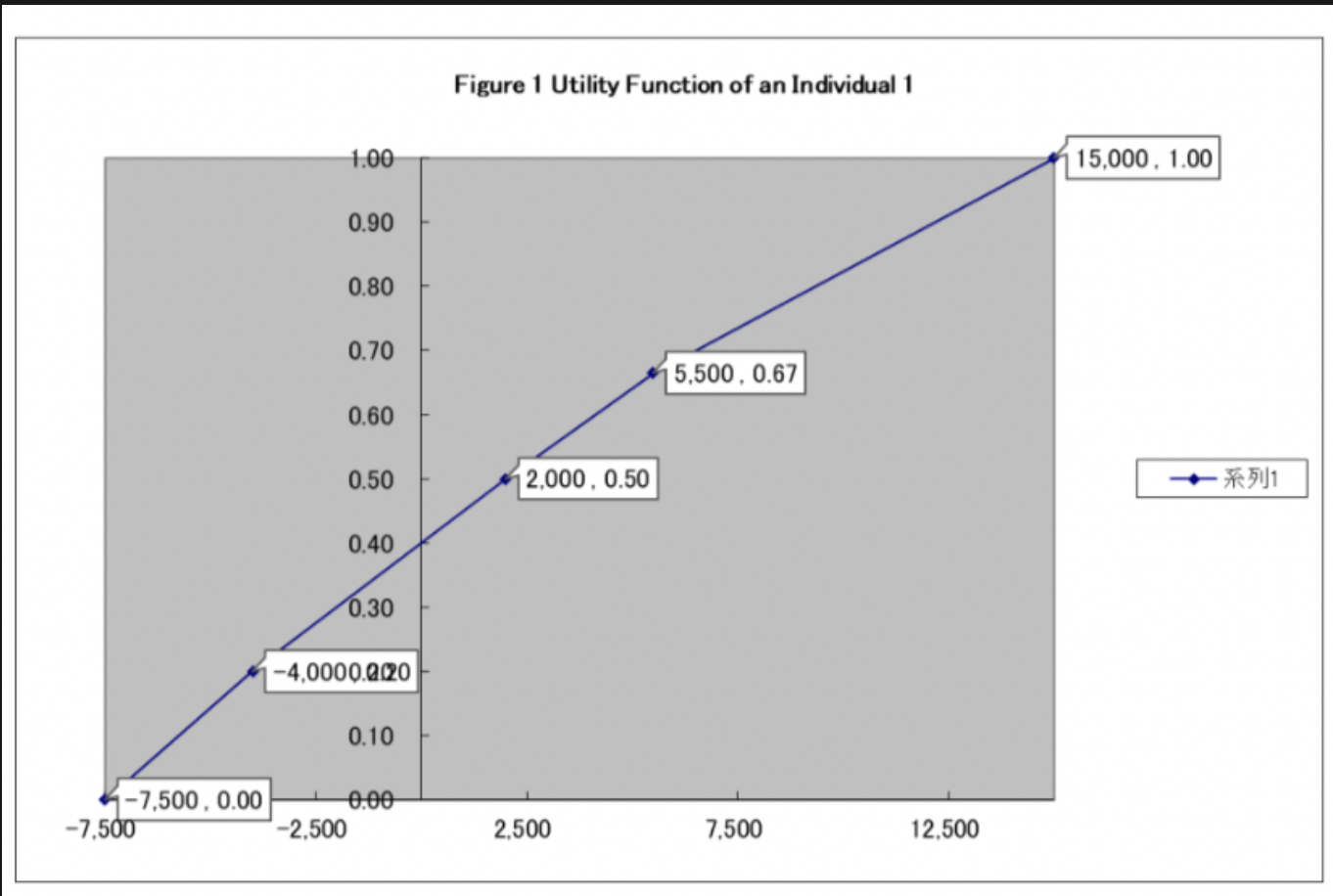
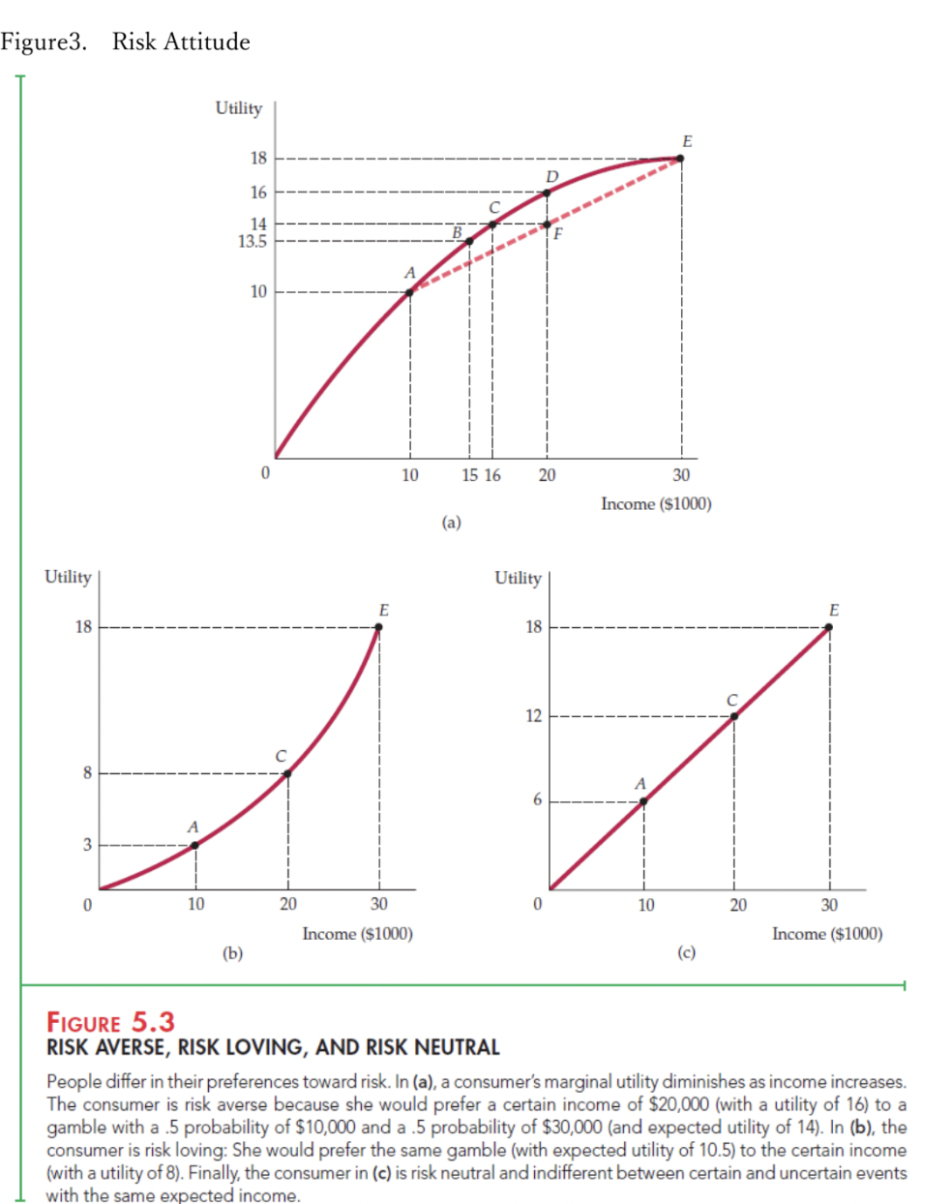
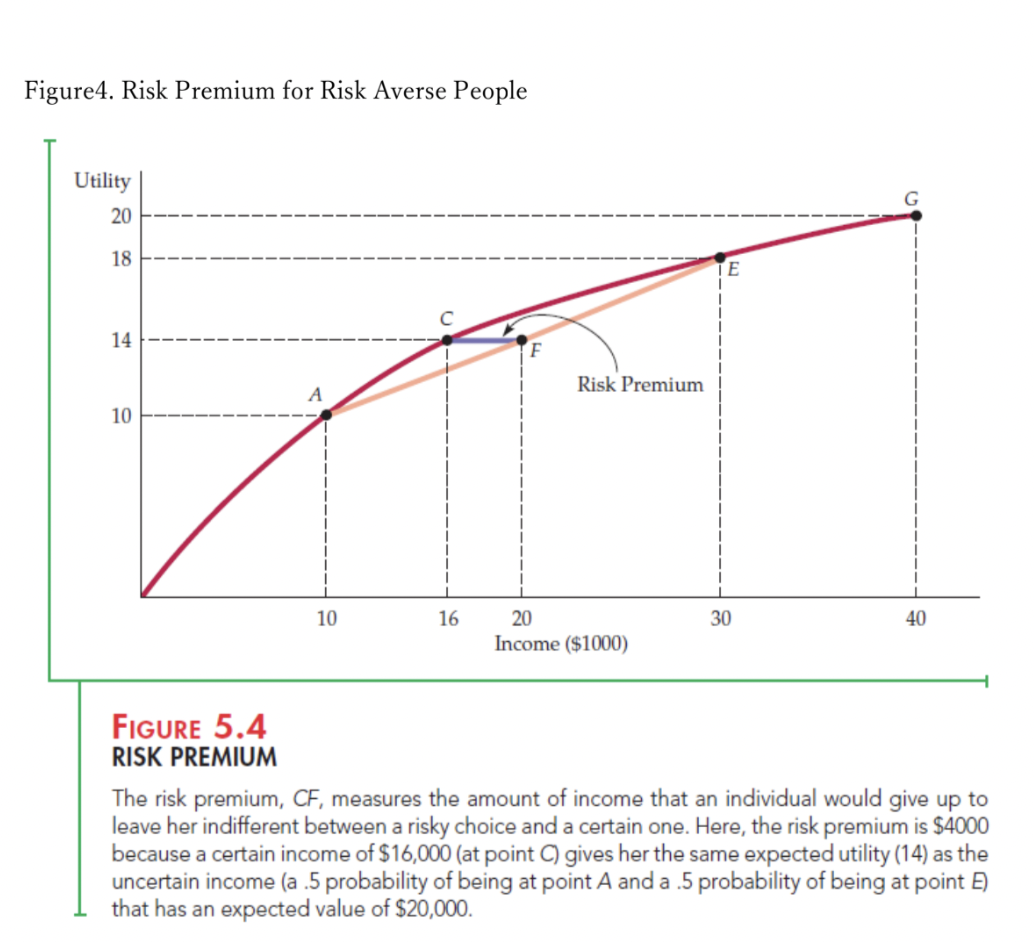
Figure 2 Gambles and Expected Utility Gamble 1 P=0.5 Utiliy 15,000 1.00 from Figure 1 -7,500 0.00 from Figure 1 (1-P)=0.5 = Mean Value = {0.5*(15,000)+0.5*(-7,500)} Expected Utility = {0.5*U(15,000)+0.5*U(-7,500)} = Gamble 1 gives you $3,750 on average Gamble 1 Expected Utiity is 0.5 Gamble 2 P=1/3 3750 0.5 Utiliy 15,000 1.00 from Figure 1 2,000 0.50 from Figure 1 (1-P)=2/3 Mean Value = {(1/3)*(15,000)+(2/3)*(2,000)} = Expected Utility = {(1/3)*U(15,000)+(2/3)*U(2,000)} = Gamble 2 gives you $5,550 on average Gamble 2 Expected Utiity is 0.67 5500 0.67 Gamble 3 P=0.6 Utiliy -7,500 0.00 from Figure 1 2,000 0.50 from Figure 1 (1-P)=0.4 Mean Value = {(0.6)*(-7,500)+(0.4)*(2,000)} = Expected Utility = {(0.6)*U(7,500)+(0.4)*U(2,000)} = Gamble 3 gives you -$4,000 on average Gamble 3 Expected Utiity is 0.2 -4000 0.2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access with AI-Powered Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started



