Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Analyze the data and fill in the table below [4] Mass Mean 0.1 kg Acceleration a (m/s) SEOM Result reported as 1 kg ii.
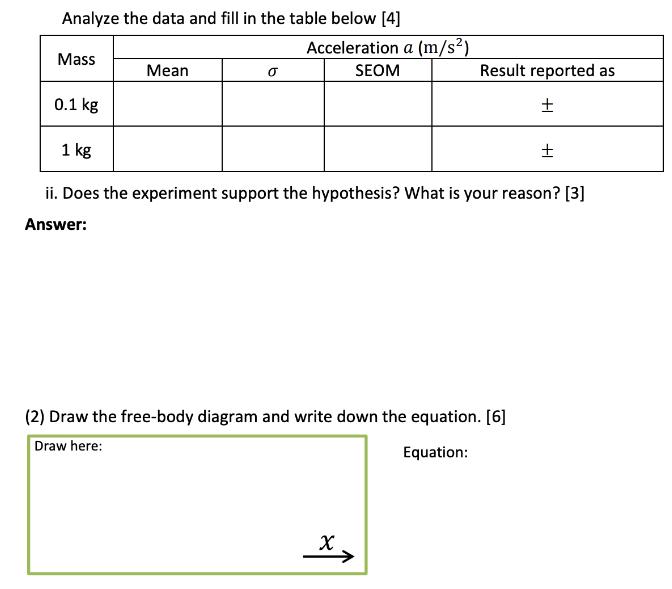


Analyze the data and fill in the table below [4] Mass Mean 0.1 kg Acceleration a (m/s) SEOM Result reported as 1 kg ii. Does the experiment support the hypothesis? What is your reason? [3] Answer: (2) Draw the free-body diagram and write down the equation. [6] Draw here: X Equation: (3) Draw the free-body diagram and write down the equation. (Pay attention to the given x-direction.) [6] Draw here: (4) Why can one assume Answer: * atg? [3] = = -Wa Equation: (5) Show that |W|- || = (matg + Mn) ax. [4] Answer: (6) What do the graph's slope and the y-intercept mean? [4] Answer: Question (write down the answers on Pre-lab) (1) Below are measurements on the acceleration of 0.10 kg and 1.0 kg freely falling objects. Acceleration a (m/s) Mass Trial 1 Trial 2 0.1 kg 9.532 9.113 1 kg 9.524 9.551 Trial 3 9.821 9.499 Trial 4 Trial 5 9.201 9.113 9.463 9.097 i. Follow the steps below to analyze the data in EXCEL and record in Pre-lab. (If you are not familiar with the statistical analysis, review Lab 1. If you do not have access to a computer, follow the method in Lab 1 to do calculations.) a. Key in the N data points in A1, ..., AN, respectively. b. In B1, type "AVERAGE(A1:AN)" and press ENTER. B1 shows the mean. c. In C1, type "=STDEV(A1:AN)" and press ENTER. C1 shows the standard deviation . d. SEOM can be directly calculated as /N. ii. From your analysis, does the experiment support the hypothesis a more massive object falls faster than a less massive one"? What is your reason? (Hint: your reason should be based on a comparison between the mean and SEOM of the two cases. It is helpful to re- view the content about comparison of two measurement values in Lab 1 Manual, page 4.) (2) Considering the airtrack system in Figure 1, draw the free-body diagram of the glider (pay attention to the given x direction). Write down the Newton's 2nd law for the glider's motion in the x direction, in terms of |T|, |, ||, |Watg|, matg, and ax. (Some quantities might not appear in the equation.) (3) Draw the free-body diagram of the hanger in Figure 1 (pay attention to the given x direction). In terms of |7|, |W|, m, and , write down the Newton's 2nd law for the hanger's mo- tion in the x direction. (4) Why can one assume N = -W atg when the glider is moving on the airtrack? (5) Using the results of Questions (2) and (3), show that || || = (matg + Mn) ax- - (6) In the experiment, if one plots |W| vs. ax, what do the graph's slope and y-intercept mean?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


