Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
answer all. for The stoichiometry of the radical halogenation reaction should include mutliple equivalents of the halogen to be correct. True False Question 7 0
answer all. for 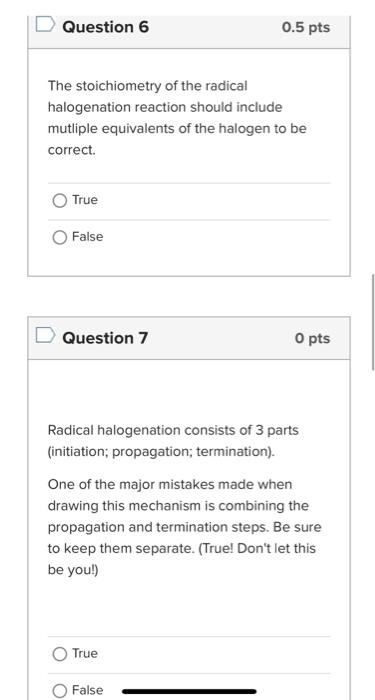

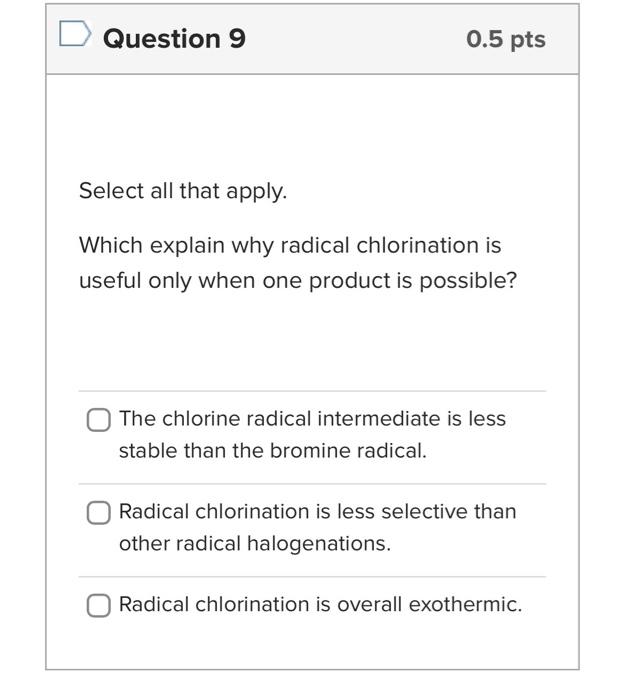
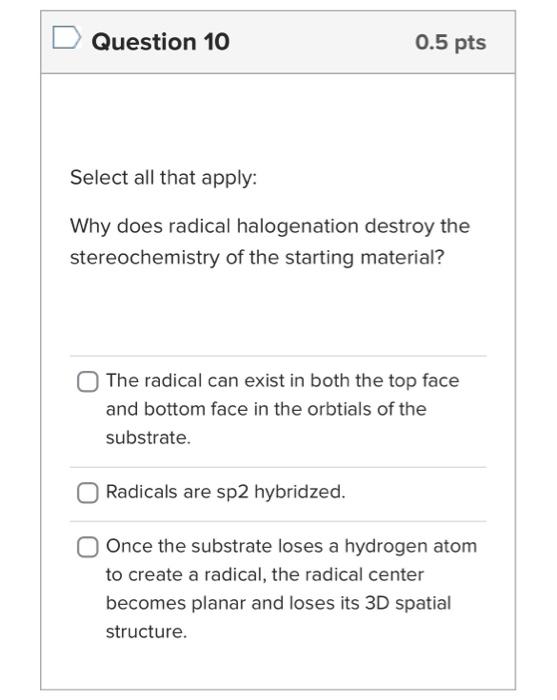

The stoichiometry of the radical halogenation reaction should include mutliple equivalents of the halogen to be correct. True False Question 7 0 pts Radical halogenation consists of 3 parts (initiation; propagation; termination). One of the major mistakes made when drawing this mechanism is combining the propagation and termination steps. Be sure to keep them separate. (True! Don't let this be you!) True Question 8 0.5pts Select all that apply. How do you know which product would be the major product of radical bromination if you aren't sure at first glance? Take the time to calculate the percent yield of the individual products (as shown in the problem set). Draw out all of the possible radical intermediates to see which one would be most stable. See which position contains the most number of hydrogen atoms. Question 9 0.5pt Select all that apply. Which explain why radical chlorination is useful only when one product is possible? The chlorine radical intermediate is less stable than the bromine radical. Radical chlorination is less selective than other radical halogenations. Radical chlorination is overall exothermic. Question 10 0.5pts Select all that apply: Why does radical halogenation destroy the stereochemistry of the starting material? The radical can exist in both the top face and bottom face in the orbtials of the substrate. Radicals are sp2 hybridzed. Once the substrate loses a hydrogen atom to create a radical, the radical center becomes planar and loses its 3D spatial structure. Select the 2 that best describe the key points of handout 5.7. A reaction can create a chiral product if a chiral center remains for the entirety of the reaction or if the transition state is chiral. Radical reactions lead to chiral products because they have chiral transition states. Reactions with enantiomeric transition states always create optically active product mixtures. The transition state determines the stereochemistry of the products. Enantioselectivity/Diastereoselectivity can be obtained from all reactions with chiral starting materials in any reaction 




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


