Answer all Questions
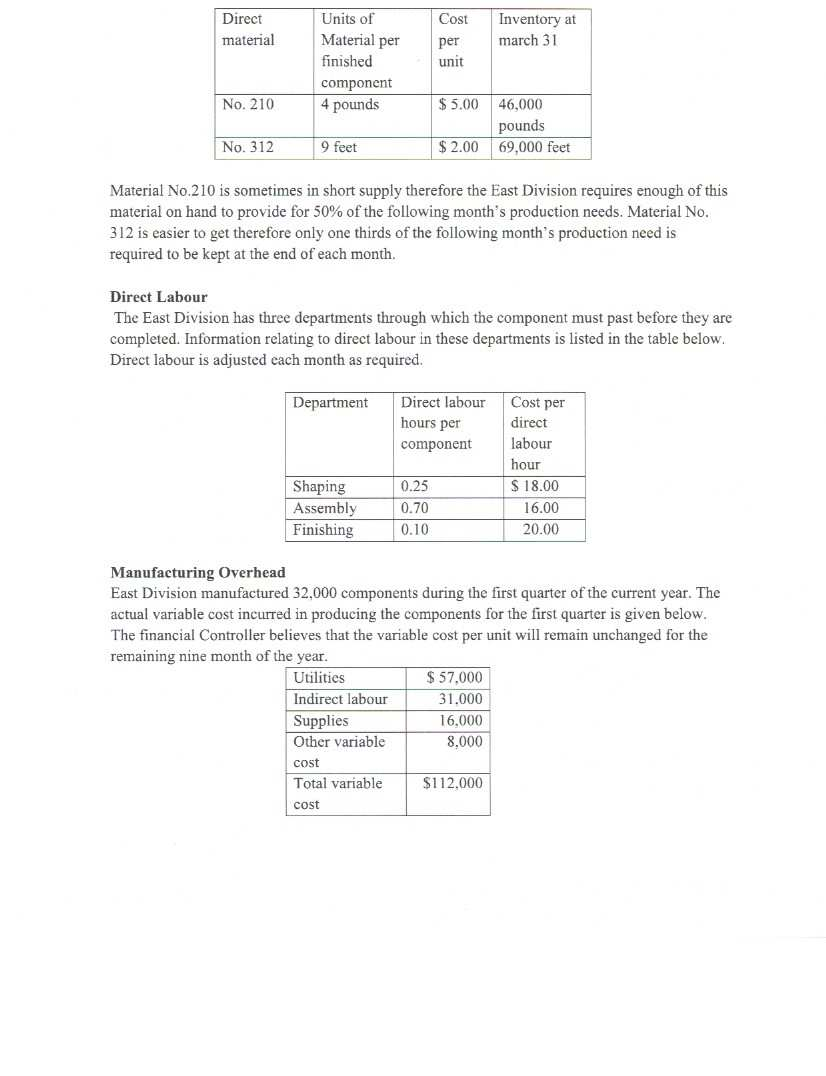
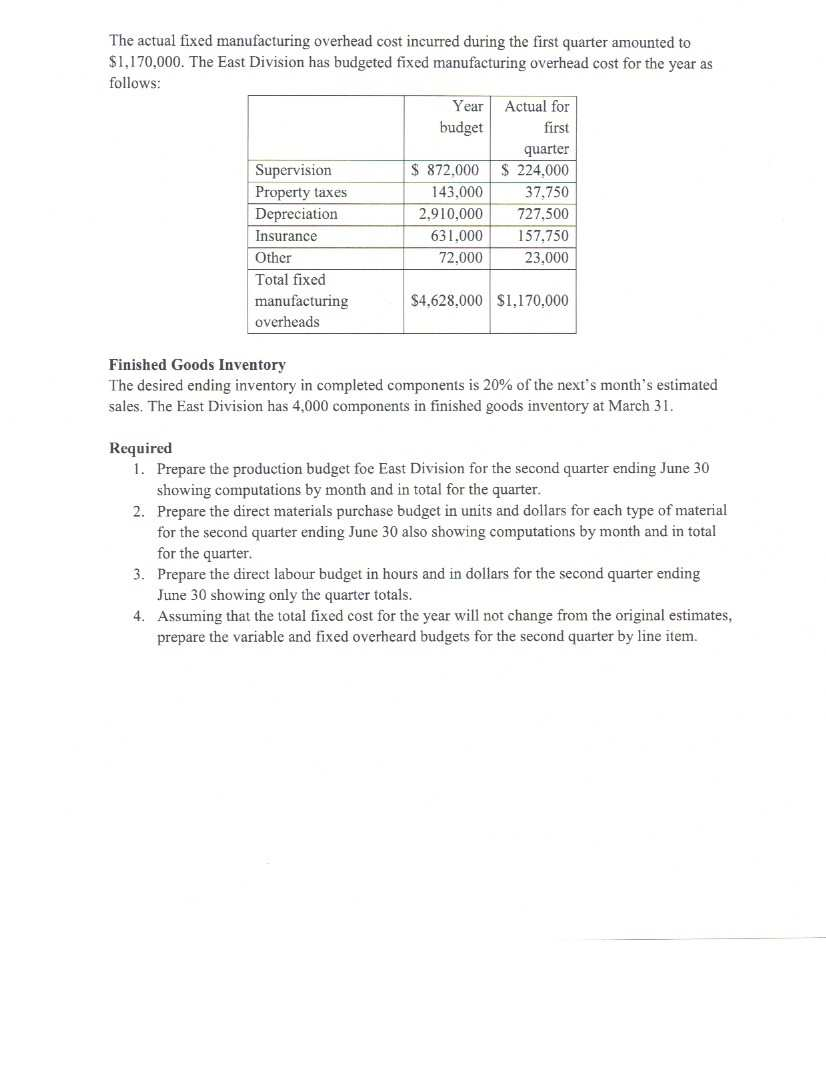
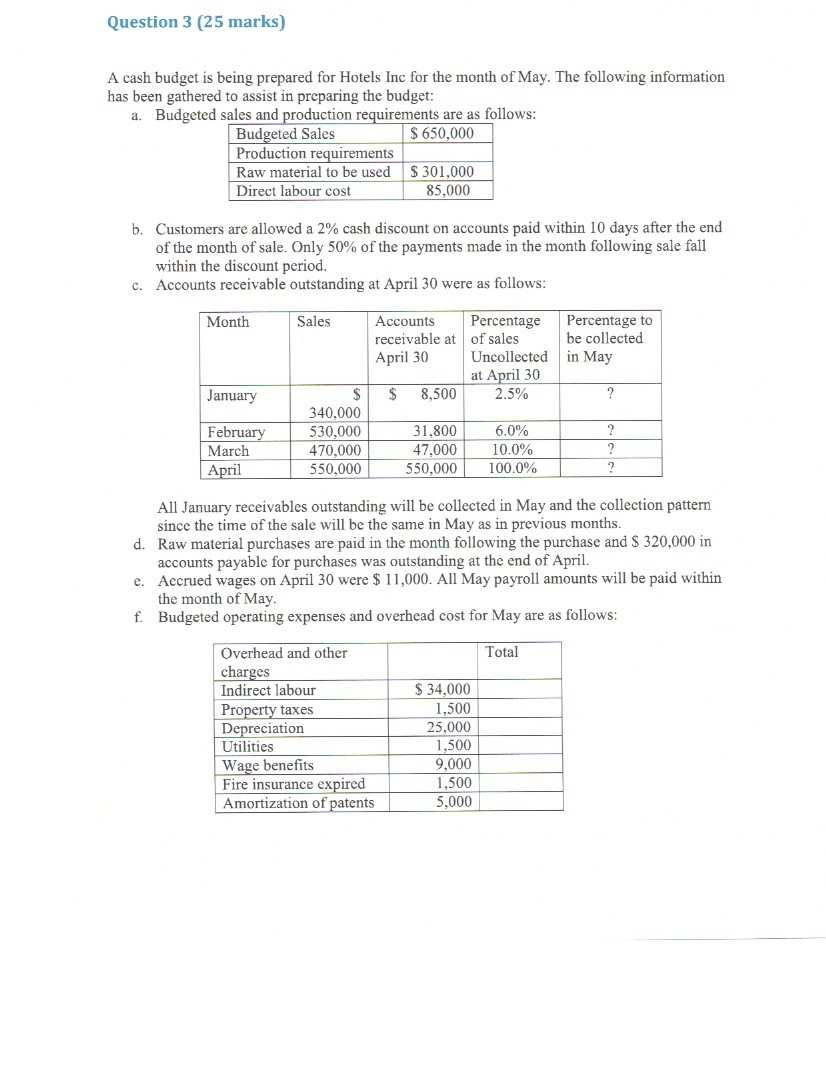




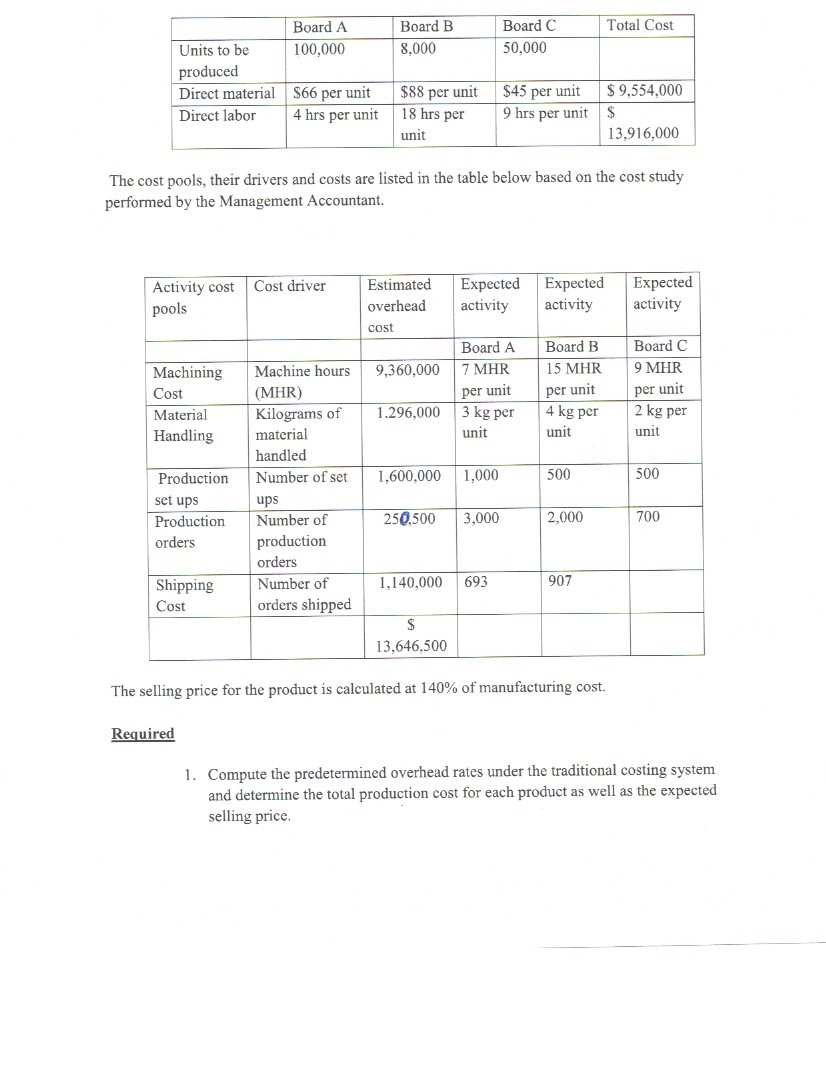

This individual project is worth 60% of your final grade. The assignment is due on May 15th, 2020. Question 1 (30 Marks) The concept of budgeting has been a long established management accounting concept though some managers view budget preparation as a waste of time which could be used more productively. This position has been suggested by the beyond budgeting roundtable. Critically review the budgeting concepts and the views suggested by the beyond budgeting round table to present your views on the methods which should be adopted in the future. Question 2 (50 Marks) The East Division of K Company manufactures a component that is vital to the health care Industry. This Division has been experiencing some problems in coordinating activities between various departments which resulted in acute and embarrassing shortages in the industry in the past. The divisions Manager in an effort to avoid future shortages has decided to reinforce the decision to have monthly budgets prepared to aid in the production process. To assist in preparing the second Quarter's budgets, the Financial Controller has provided the following actual and budgeted information. January (actual) February (actual) March (actual) April (Budget) May (budget) Junc(budget) July (budget) August (budget) 6.000 10,000 14.000 20,000 35,000 50,000 45,000 30,000 Direct Material Two different materials are used in the production of the component. Data related to these materials are given below: Direct material Units of Material per finished component 4 pounds Cost per unit Inventory at march 31 No. 210 $5.00 46,000 pounds 69,000 feet No. 312 9 feet $ 2.00 Material No.210 is sometimes in short supply therefore the East Division requires enough of this material on hand to provide for 50% of the following month's production needs. Material No. 312 is easier to get therefore only one thirds of the following month's production need is required to be kept at the end of each month. Direct Labour The East Division has three departments through which the component must past before they are completed. Information relating to direct labour in these departments is listed in the table below. Direct labour is adjusted each month as required. Department Direct labour Cost per hours per component direct labour hour $ 18.00 Shaping Assembly Finishing 0.25 0.70 0.10 16.00 20.00 Manufacturing Overhead East Division manufactured 32,000 components during the first quarter of the current year. The actual variable cost incurred in producing the components for the first quarter is given below. The financial Controller believes that the variable cost per unit will remain unchanged for the remaining nine month of the year. Utilities $ 57,000 Indirect labour 31.000 Supplies 16.000 Other variable 8,000 cost Total variable $112.000 cost The actual fixed manufacturing overhead cost incurred during the first quarter amounted to $1,170,000. The East Division has budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead cost for the year as follows: Year Actual for budget first quarter Supervision $ 872.000 $ 224.000 Property taxes 143,000 37,750 Depreciation 2,910,000 727,500 Insurance 631.000 157.750 Other 72.000 23,000 Total fixed manufacturing $4.628.000 $1.170.000 overheads Finished Goods Inventory The desired ending inventory in completed components is 20% of the next's month's estimated sales. The East Division has 4,000 components in finished goods inventory at March 31. Required 1. Prepare the production budget foe East Division for the second quarter ending June 30 showing computations by month and in total for the quarter. 2. Prepare the direct materials purchase budget in units and dollars for each type of material for the second quarter ending June 30 also showing computations by month and in total for the quarter. 3. Prepare the direct labour budget in hours and in dollars for the second quarter ending June 30 showing only the quarter totals. 4. Assuming that the total fixed cost for the year will not change from the original estimates, prepare the variable and fixed overheard budgets for the second quarter by line item. Question 3 (25 marks) A cash budget is being prepared for Hotels Inc for the month of May. The following information has been gathered to assist in preparing the budget: a. Budgeted sales and production requirements are as follows: Budgeted Sales $ 650,000 Production requirements Raw material to be used $ 301,000 Direct labour cost 85,000 b. Customers are allowed a 2% cash discount on accounts paid within 10 days after the end of the month of sale. Only 50% of the payments made in the month following sale fall within the discount period. C. Accounts receivable outstanding at April 30 were as follows: Month Sales Accounts Percentage Percentage to receivable at of sales be collected April 30 Uncollected in May at April 30 $ 8,500 2.5% ? January February March April $ 340.000 530,000 470.000 550,000 31.800 47.000 550.000 6.0% 10.0% 100.0% 2 ? ? All January receivables outstanding will be collected in May and the collection pattern since the time of the sale will be the same in May as in previous months. d. Raw material purchases are paid in the month following the purchase and S 320,000 in accounts payable for purchases was outstanding at the end of April. e. Accrued wages on April 30 were $ 11,000. All May payroll amounts will be paid within the month of May. f Budgeted operating expenses and overhead cost for May are as follows: Total Overhead and other charges Indirect labour Property taxes Depreciation Utilities Wage benefits Fire insurance expired Amortization of patents $ 34.000 1,500 25.000 1.500 9.000 1,500 5,000 Spoilage of materials in 1,500 $ 79000 the ware house Sales Salaries 45.000 Administrative salaries 15,000 g. Property taxes are paid in July of each year. h. Utilities are billed and paid within the month. i. Shipping cost for May will be $1,000 all payable in the month. The cash balance at April 30th was $5,750. J. Required 1. Prepare a Cash collections schedule for the month of May. 2. Prepare a cash budget for May in good form. Hotels Inc require a minimum cash balance of $5,500 at the end of each month and therefore a line of credit is set up to allow for borrowings to cover any deficiency in the ending cash balance. Question 4(20 Marks) Northwood Company manufactures basketballs. The company has a ball that sells for $25. At present, the ball is manufactured in a small plant that relies heavily on direct labor workers. Thus, variable costs are high, totaling $15 per ball. Last year, the company sold 30,000 of these balls, with the following results: Sales (30.000 balls. Less variable expenses... $750,000 450,000 Contribution margin. Less fixed expenses. 300,000 210,000 Net operating income. $ 90,000 Required: 1. Compute (a) the CM ratio and the break-even point in balls, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year's sales level. 2. Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that variable costs will increase by S2.75 per ball next year. If this change takes place and the selling price per ball remains constant at $25, what will be the new CM ratio and break-even point in balls? 3. Refer to the data in (2) above. If the expected change in variable costs takes place, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income ($70,000) as last year? 4. Refer again to the data in (2) above. The president feels that the company must raise the selling price of its basketballs. If Northwood Company wants to maintain the same CM ratio as last year, what selling price per ball must it charge next year to cover the increased labor costs? 5. Refer to the original data. The company is discussing the construction of a new automated manufacturing plant. The new plant would slash variable costs per ball by 40%, but it would cause fixed costs per year to double. If the new plant is built, what would be the company's new CM ratio and new break-even point in balls? 6. Refer to the data in (5) above. a. If the new plant is built, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income ($90,000) as last year? b. Assume the new plant is built and the next year the company manufactures and sells 30,000 balls (the same number as sold last year). Prepare a contribution income statement and compute the degree of operating leverage. c. If you were a member of top management, would you have been in favor of constructing the new plant? Explain. Question 5(20 rks) HD Corporation manufactures vehicles parts. When its production facilities are fully utilized it uses external sub-contractors to complete some orders. Management is reconsidering the uses of its manufacturing facilities for the coming year. The following table details the cost of producing a motor called the WB 13 used in the cooling system. Total cost for 60,000 units $ 480,000 360,000 180,000 Direct Materials Direct Labour Variable production overheads Fixed production overheads Total manufacturing cost 360,000 $1,380,000 One of the external producers has offered to supply HD Corporation with the same part for $ 21 cach. If the part is purchased externally, related fixed cost to the production of this part of $120,000 will be avoided. Required: a. b. What is the relevant per unit cost for the original part it assumed that the capacity now used to manufacture this part will become idle and should the part be made or bought? Assume that the capacity now being used to manufacture this part can be either (a) rented to carn $ 75,000 per or (b) be used to make oil filters that will yield a profit contribution of S 240,000. What is the best decision for HD Corporation management to propose? Question 6 (25 Marks) Matterson Electronics has just developed a new solar device that will be targeted to the green economy to provide charging capabilities using the power of the sun for electronic devices especially in third world countries where electricity supplies are unstable and expensive. Market research and cost studies have provided the following information. a. New equipment will be purchased at a cost of $ 515,000 and will have a 10 useful life. The salvage value at the end of the useful life is $15,000. b. Sales for the next 10 years is as follows 1 Year Sales in units 12.000 2 18,000 3 26,000 4-10 29,000 c. Production and sales of the device will require working capital of $ 60,000 to finance accounts receivable, inventories and day to day cash needs. This working capital is released at the end of the project's life. The machine will have to be refurbished in year 6 for $125,500 to maintain production efficiencies for the final 4 year of operations. This refurbishment will be expensed in the year it occurs. d. The devise will sell for $50 per unit. The variable cost for production, administration and sales would be $ 25 per unit. e. Fixed cost for salaries, maintenance property taxes and other miscellaneous operating cost inclusive of depreciation on the totals $182,300 per year. (Depreciation on the project is calculated using the straight line method) f. To gain rapid entry into the market, the company will advertise intensely. The projected advertising cost will be as follows: Year Amount of yearly advertising 1 $220,000 2 200,000 3 150,000 4-10 120.000 3. Matterson Electronics board of directors has specified a required rate of return of 14% on all new projects Required 1. Compute the net cash flows anticipated from the sale of the devices for each year over the next 10 years. 2. Using the information above compute the Net Present Value of the proposed investment. Would you recommend that Matterson Electronics accept the device as a new project? Question 7 (30 Marks) Electronic Inc (ET) produces three types of circuit boards, A, B and C for the Computer Manufacturers and after sales maintenance industries. The cost system used by EI until 2013 was classified as the traditional where all cost except direct material and direct labour were allocated to each board based on the direct labour hours used to produce them, (i.e direct labour was the cost driver). The new Management accountant undertook a cost study to improve the costing and pricing of the boards and it was determined that they were six clearly identifiable cost pools which could be used to implement an ABC costing system. The following table details the budgeted information for the year 2015. Total Indirect Production cost for the year is budgeted to be $ 13,646,500. Total Cost Board A 100,000 Board B 8,000 Board C 50,000 Units to be produced Direct material Direct labor $88 per unit S66 per unit 4 hrs per unit $45 per unit 9 hrs per unit 18 hrs per $ 9,554.000 $ 13.916,000 unit The cost pools, their drivers and costs are listed in the table below based on the cost study performed by the Management Accountant. Cost driver Activity cost pools Estimated overhead cost Expected activity Expected activity Expected activity Board A 7 MHR Board B 15 MHR 9,360,000 Board C 9 MHR per unit per unit per unit Machining Cost Material Handling 1.296,000 3 kg per 4 kg per 2 kg per unit unit unit 1,600,000 1,000 500 500 Production set ups Production orders Machine hours (MHR) Kilograms of material handled Number of set ups Number of production orders Number of orders shipped 250.500 3,000 2,000 700 1.140,000 693 907 Shipping Cost $ 13,646.500 The selling price for the product is calculated at 140% of manufacturing cost. Required 1. Compute the predetermined overhead rates under the traditional costing system and determine the total production cost for each product as well as the expected selling price 2. Compute the ABC overhead cost for each product and determine the total production cost for each product and the expected selling price. 3. Discuss the effect to the organization of changing the costing method. This individual project is worth 60% of your final grade. The assignment is due on May 15th, 2020. Question 1 (30 Marks) The concept of budgeting has been a long established management accounting concept though some managers view budget preparation as a waste of time which could be used more productively. This position has been suggested by the beyond budgeting roundtable. Critically review the budgeting concepts and the views suggested by the beyond budgeting round table to present your views on the methods which should be adopted in the future. Question 2 (50 Marks) The East Division of K Company manufactures a component that is vital to the health care Industry. This Division has been experiencing some problems in coordinating activities between various departments which resulted in acute and embarrassing shortages in the industry in the past. The divisions Manager in an effort to avoid future shortages has decided to reinforce the decision to have monthly budgets prepared to aid in the production process. To assist in preparing the second Quarter's budgets, the Financial Controller has provided the following actual and budgeted information. January (actual) February (actual) March (actual) April (Budget) May (budget) Junc(budget) July (budget) August (budget) 6.000 10,000 14.000 20,000 35,000 50,000 45,000 30,000 Direct Material Two different materials are used in the production of the component. Data related to these materials are given below: Direct material Units of Material per finished component 4 pounds Cost per unit Inventory at march 31 No. 210 $5.00 46,000 pounds 69,000 feet No. 312 9 feet $ 2.00 Material No.210 is sometimes in short supply therefore the East Division requires enough of this material on hand to provide for 50% of the following month's production needs. Material No. 312 is easier to get therefore only one thirds of the following month's production need is required to be kept at the end of each month. Direct Labour The East Division has three departments through which the component must past before they are completed. Information relating to direct labour in these departments is listed in the table below. Direct labour is adjusted each month as required. Department Direct labour Cost per hours per component direct labour hour $ 18.00 Shaping Assembly Finishing 0.25 0.70 0.10 16.00 20.00 Manufacturing Overhead East Division manufactured 32,000 components during the first quarter of the current year. The actual variable cost incurred in producing the components for the first quarter is given below. The financial Controller believes that the variable cost per unit will remain unchanged for the remaining nine month of the year. Utilities $ 57,000 Indirect labour 31.000 Supplies 16.000 Other variable 8,000 cost Total variable $112.000 cost The actual fixed manufacturing overhead cost incurred during the first quarter amounted to $1,170,000. The East Division has budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead cost for the year as follows: Year Actual for budget first quarter Supervision $ 872.000 $ 224.000 Property taxes 143,000 37,750 Depreciation 2,910,000 727,500 Insurance 631.000 157.750 Other 72.000 23,000 Total fixed manufacturing $4.628.000 $1.170.000 overheads Finished Goods Inventory The desired ending inventory in completed components is 20% of the next's month's estimated sales. The East Division has 4,000 components in finished goods inventory at March 31. Required 1. Prepare the production budget foe East Division for the second quarter ending June 30 showing computations by month and in total for the quarter. 2. Prepare the direct materials purchase budget in units and dollars for each type of material for the second quarter ending June 30 also showing computations by month and in total for the quarter. 3. Prepare the direct labour budget in hours and in dollars for the second quarter ending June 30 showing only the quarter totals. 4. Assuming that the total fixed cost for the year will not change from the original estimates, prepare the variable and fixed overheard budgets for the second quarter by line item. Question 3 (25 marks) A cash budget is being prepared for Hotels Inc for the month of May. The following information has been gathered to assist in preparing the budget: a. Budgeted sales and production requirements are as follows: Budgeted Sales $ 650,000 Production requirements Raw material to be used $ 301,000 Direct labour cost 85,000 b. Customers are allowed a 2% cash discount on accounts paid within 10 days after the end of the month of sale. Only 50% of the payments made in the month following sale fall within the discount period. C. Accounts receivable outstanding at April 30 were as follows: Month Sales Accounts Percentage Percentage to receivable at of sales be collected April 30 Uncollected in May at April 30 $ 8,500 2.5% ? January February March April $ 340.000 530,000 470.000 550,000 31.800 47.000 550.000 6.0% 10.0% 100.0% 2 ? ? All January receivables outstanding will be collected in May and the collection pattern since the time of the sale will be the same in May as in previous months. d. Raw material purchases are paid in the month following the purchase and S 320,000 in accounts payable for purchases was outstanding at the end of April. e. Accrued wages on April 30 were $ 11,000. All May payroll amounts will be paid within the month of May. f Budgeted operating expenses and overhead cost for May are as follows: Total Overhead and other charges Indirect labour Property taxes Depreciation Utilities Wage benefits Fire insurance expired Amortization of patents $ 34.000 1,500 25.000 1.500 9.000 1,500 5,000 Spoilage of materials in 1,500 $ 79000 the ware house Sales Salaries 45.000 Administrative salaries 15,000 g. Property taxes are paid in July of each year. h. Utilities are billed and paid within the month. i. Shipping cost for May will be $1,000 all payable in the month. The cash balance at April 30th was $5,750. J. Required 1. Prepare a Cash collections schedule for the month of May. 2. Prepare a cash budget for May in good form. Hotels Inc require a minimum cash balance of $5,500 at the end of each month and therefore a line of credit is set up to allow for borrowings to cover any deficiency in the ending cash balance. Question 4(20 Marks) Northwood Company manufactures basketballs. The company has a ball that sells for $25. At present, the ball is manufactured in a small plant that relies heavily on direct labor workers. Thus, variable costs are high, totaling $15 per ball. Last year, the company sold 30,000 of these balls, with the following results: Sales (30.000 balls. Less variable expenses... $750,000 450,000 Contribution margin. Less fixed expenses. 300,000 210,000 Net operating income. $ 90,000 Required: 1. Compute (a) the CM ratio and the break-even point in balls, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year's sales level. 2. Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that variable costs will increase by S2.75 per ball next year. If this change takes place and the selling price per ball remains constant at $25, what will be the new CM ratio and break-even point in balls? 3. Refer to the data in (2) above. If the expected change in variable costs takes place, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income ($70,000) as last year? 4. Refer again to the data in (2) above. The president feels that the company must raise the selling price of its basketballs. If Northwood Company wants to maintain the same CM ratio as last year, what selling price per ball must it charge next year to cover the increased labor costs? 5. Refer to the original data. The company is discussing the construction of a new automated manufacturing plant. The new plant would slash variable costs per ball by 40%, but it would cause fixed costs per year to double. If the new plant is built, what would be the company's new CM ratio and new break-even point in balls? 6. Refer to the data in (5) above. a. If the new plant is built, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income ($90,000) as last year? b. Assume the new plant is built and the next year the company manufactures and sells 30,000 balls (the same number as sold last year). Prepare a contribution income statement and compute the degree of operating leverage. c. If you were a member of top management, would you have been in favor of constructing the new plant? Explain. Question 5(20 rks) HD Corporation manufactures vehicles parts. When its production facilities are fully utilized it uses external sub-contractors to complete some orders. Management is reconsidering the uses of its manufacturing facilities for the coming year. The following table details the cost of producing a motor called the WB 13 used in the cooling system. Total cost for 60,000 units $ 480,000 360,000 180,000 Direct Materials Direct Labour Variable production overheads Fixed production overheads Total manufacturing cost 360,000 $1,380,000 One of the external producers has offered to supply HD Corporation with the same part for $ 21 cach. If the part is purchased externally, related fixed cost to the production of this part of $120,000 will be avoided. Required: a. b. What is the relevant per unit cost for the original part it assumed that the capacity now used to manufacture this part will become idle and should the part be made or bought? Assume that the capacity now being used to manufacture this part can be either (a) rented to carn $ 75,000 per or (b) be used to make oil filters that will yield a profit contribution of S 240,000. What is the best decision for HD Corporation management to propose? Question 6 (25 Marks) Matterson Electronics has just developed a new solar device that will be targeted to the green economy to provide charging capabilities using the power of the sun for electronic devices especially in third world countries where electricity supplies are unstable and expensive. Market research and cost studies have provided the following information. a. New equipment will be purchased at a cost of $ 515,000 and will have a 10 useful life. The salvage value at the end of the useful life is $15,000. b. Sales for the next 10 years is as follows 1 Year Sales in units 12.000 2 18,000 3 26,000 4-10 29,000 c. Production and sales of the device will require working capital of $ 60,000 to finance accounts receivable, inventories and day to day cash needs. This working capital is released at the end of the project's life. The machine will have to be refurbished in year 6 for $125,500 to maintain production efficiencies for the final 4 year of operations. This refurbishment will be expensed in the year it occurs. d. The devise will sell for $50 per unit. The variable cost for production, administration and sales would be $ 25 per unit. e. Fixed cost for salaries, maintenance property taxes and other miscellaneous operating cost inclusive of depreciation on the totals $182,300 per year. (Depreciation on the project is calculated using the straight line method) f. To gain rapid entry into the market, the company will advertise intensely. The projected advertising cost will be as follows: Year Amount of yearly advertising 1 $220,000 2 200,000 3 150,000 4-10 120.000 3. Matterson Electronics board of directors has specified a required rate of return of 14% on all new projects Required 1. Compute the net cash flows anticipated from the sale of the devices for each year over the next 10 years. 2. Using the information above compute the Net Present Value of the proposed investment. Would you recommend that Matterson Electronics accept the device as a new project? Question 7 (30 Marks) Electronic Inc (ET) produces three types of circuit boards, A, B and C for the Computer Manufacturers and after sales maintenance industries. The cost system used by EI until 2013 was classified as the traditional where all cost except direct material and direct labour were allocated to each board based on the direct labour hours used to produce them, (i.e direct labour was the cost driver). The new Management accountant undertook a cost study to improve the costing and pricing of the boards and it was determined that they were six clearly identifiable cost pools which could be used to implement an ABC costing system. The following table details the budgeted information for the year 2015. Total Indirect Production cost for the year is budgeted to be $ 13,646,500. Total Cost Board A 100,000 Board B 8,000 Board C 50,000 Units to be produced Direct material Direct labor $88 per unit S66 per unit 4 hrs per unit $45 per unit 9 hrs per unit 18 hrs per $ 9,554.000 $ 13.916,000 unit The cost pools, their drivers and costs are listed in the table below based on the cost study performed by the Management Accountant. Cost driver Activity cost pools Estimated overhead cost Expected activity Expected activity Expected activity Board A 7 MHR Board B 15 MHR 9,360,000 Board C 9 MHR per unit per unit per unit Machining Cost Material Handling 1.296,000 3 kg per 4 kg per 2 kg per unit unit unit 1,600,000 1,000 500 500 Production set ups Production orders Machine hours (MHR) Kilograms of material handled Number of set ups Number of production orders Number of orders shipped 250.500 3,000 2,000 700 1.140,000 693 907 Shipping Cost $ 13,646.500 The selling price for the product is calculated at 140% of manufacturing cost. Required 1. Compute the predetermined overhead rates under the traditional costing system and determine the total production cost for each product as well as the expected selling price 2. Compute the ABC overhead cost for each product and determine the total production cost for each product and the expected selling price. 3. Discuss the effect to the organization of changing the costing method
















