Answer all. The prices of three commodities A, B and C are `x, `y and `z per unit respectively. P
purchases 4 units of C and sells 3 units of A and 5 units of B. Q purchases 3 units of B
and sells 2 units of A and 1 unit of C. R purchases 1 unit of A and sells 4 units of B and
6 units of C. In the process P, Q and R earn `6,000 , `5,000 and `13,000 respectively.
By using matrix inversion method, nd the prices per unit of A, B and C.
5. The sum of three numbers is 20. If we multiply the first by 2 and add the second
number and subtract the third we get 23. If we multiply the first by 3 and add second
and third to it, we get 46. By using matrix inversion method find the numbers.
6. Weekly expenditure in an office for three weeks is given as follows. Assuming that
the salary in all the three weeks of different categories of staff did not vary, calculate
the salary for each type of staff, using matrix inversion method method
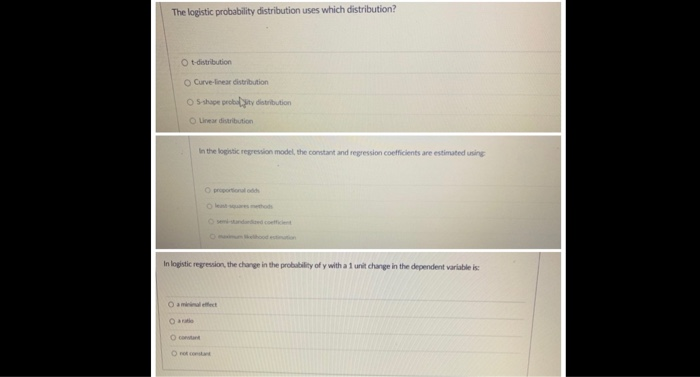
The logistic probability distribution uses which distribution? O t-distribution O Curve-Inear distribution Q 5-shape probulality distribution O Linear diveribution In the loghtic regression model, the comiant and regression corfficients are estimated sing In logistic regression, the change in the probability of y with a 1 unit change in the dependent variable is# 3 DISCRETE DISTRIBUTIONS. (25 pts) The literacy rate in Statistics in some US high schools is about 20%. Suppose 15 students in one high school selected at random are literate. a. In words, how the random variable X '2' Give its probability distribution function (Pd-f)- b. Calculate the (i) mean of X (ii) variance of X. c. Find the probability that more than ve students in the sample are literate. Level 2: Reviewing Concepts 321 LEVEL 2: REVIEWING CONCEPTS Chapter Overview Using the terms provided, correctly complete the chapter overview for the special senses. Unless otherwise noted, each term should be used once. internal car endolymph Boats modified neurons rotational planes gravity neurotransmitter salty olfactory cilia(a ). green semicircular ducts spiral organ open umami sterocilia oval window utricle and saccule tympanic membrane stimulates vestibule lose inhibits cochlear duct title receptors papillae cones textorial perilymph rods transJucin second messenger bleaching continually accessory structures FOUT depolarine (use twice) bipolar water distorts bitter olfactory epithelium( # ) OLFACTION Offactory receptor cells are found in the (1). in the nasal cavity. Odorant binding to receptor proteins on (2) activates a G protein complex, which converts ATP to CAMP CAMP, as a (3)_ . binds to and opens sodium channels to (4). the receptor membrane. Because olfactory receptor cells are (5)_ . olfaction does not display a synaptic delay in the transmission of sensory information. GUSTATION clustered in taste buds are found in epithelial (7) on the tongue. Also present are umami and water receptors Each taste bud can provide four primary taste ensations These include (8). and (9) in which a chemical binds directly to receptors and opens sodium channels to depolarize the membrane. The other taste sensa- tions include (10) and (11) in which a chemical binds to G protein- mediated receptors, called gustducins which activate a second messenger to stimulate the release of neurotransmitters. (12) receptors use a similar G protein-based mechanism, but the distribution of these receptors is not known in full detail. (13) receptors, found especially in the pharynx, have sensory output to the hypothalamus and play a role in fluid balance. VISION There are two types of photoreceptors in the retina of the eye: (14) do not discrim of which there are three types-red, (16) . and inate colors: (15) Sue -are semitive to specific wavelengths to allow for color discrimination. The basic mechanism of photoreception is the same for rods and cones. Differences in wavelength ensitivity depend on which type of opsin molecule is present. In darkness photoreceptors are tonically active. (17) secreting neurotransmit- ter to bipolar cells. Gated sodium channels are kept (18) by the presence of cGMP, and the transmembrane potential stays at about -40m V. When photons strike the photoreceptor, the bound retinal changes configuration, which then activates the opsin, which activates (19)_ - (a G protein), which activates phospho- diesterase to break down the cGMP holding the sodium gate open. As cGMP levels decline, the gated sodium channels (20) and the transmembrane potential hyperpolarizes