Question
ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS CAREFULLY Section A Operating Systems As nicely as storage and retrieval of facts, the capabilities of a submitting machine consist of:
ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS CAREFULLY
Section A
Operating Systems As nicely as storage and retrieval of facts, the capabilities of a submitting machine consist of: ? naming and call resolution ? get right of entry to manage ? lifestyles manipulate ? concurrency manage For every of the above (a) Briefly outline the function. [1 mark each] (b) Discuss how, and wherein submitting system factor, the feature may be furnished. Use examples from one or extra real operating systems to illustrate your solution. [4 marks each] 6 CST.Ninety eight.1.7 12 Operating Systems What is supposed with the aid of the term demand paging in a virtual memory control system, and how is it implemented? [5 marks] List 5 strategies which the running gadget can use to enhance the efficiency of demand paging. [5 marks] Suppose the page desk for the currently executing manner is as follows. All values are decimal, and indexes are numbered from zero. Addresses are reminiscence byte addresses. The page offset is 10 bits. Virtual Page # Valid bit Reference bit Modify bit Page Frame # 0 1 1 zero four 1 1 1 1 7 2 0 zero 0 - three 1 zero zero 2 4 zero zero zero - 5 1 0 1 zero Describe precisely how, in general, a virtual deal with generated through the CPU is translated right into a bodily cope with, with the useful resource of a diagram. [4 marks] To what physical deal with (if any) would the subsequent digital addresses correspond? (a) 1052 (b) 2221 (c) 5499 [6 marks]Consider the own family of 1-dimensional Gabor wavelets, parameterised for place x0, size ?, and frequency 0. Their functional shape is: f(x) = e ?i0x e ?(x?x0) 2 /?2 and their Fourier Transform is: F() = e ?ix0 e ?(?0) 2? 2 (a) Explain the dualities of: (i) modulation and moving; and (ii) similarity (reciprocal scaling), in phrases of the behaviour of the parameters in the expressions above for f(x) and F(). [4 marks] (b) What can you are saying about the Fourier transform of the sum of any two Gabor wavelets? [4 marks] (c) What can you say about the Fourier transform of the made of any Gabor wavelets, and why? [4 marks] (d) What is the Fourier transform of f (n) (x), the n th-spinoff of a Gabor wavelet? [4 marks] (e) Show that the set of all Gabor wavelets is closed under convolution: i.E., that the convolution of any two Gabor wavelets is itself a unmarried Gabor wavelet. [4 marks] 1 [TURN OVER CST.98.4.2 2 Concurrent Systems In a device which allocates sources dynamically (a) What are the aid allocation rules that make it important to recall the possibility of impasse? [3 marks] (b) If there is one instance of every resource type what's the important and sufficient circumstance for impasse to exist? [2 marks] Using the notation ? for an instance of a aid R ? ? > P method P has an example of useful resource R R ? ?
}}
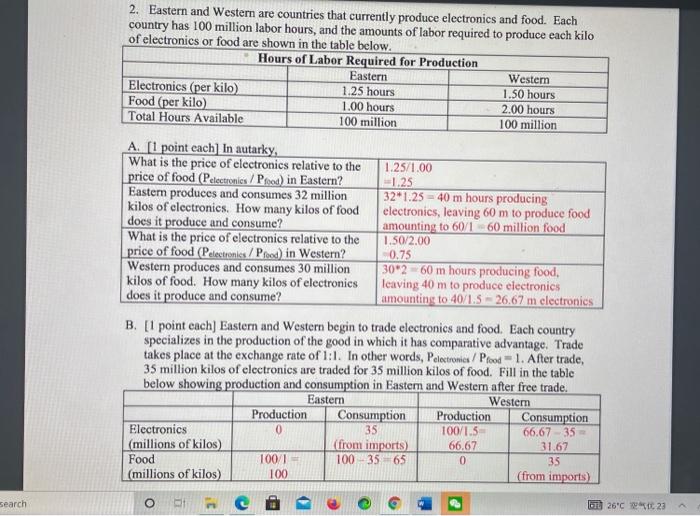

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


