Question
answer asap please and thank you! Corp. is a small public company with a December 31 fiscal year-end. At the end of 2016, the company
answer asap please and thank you!
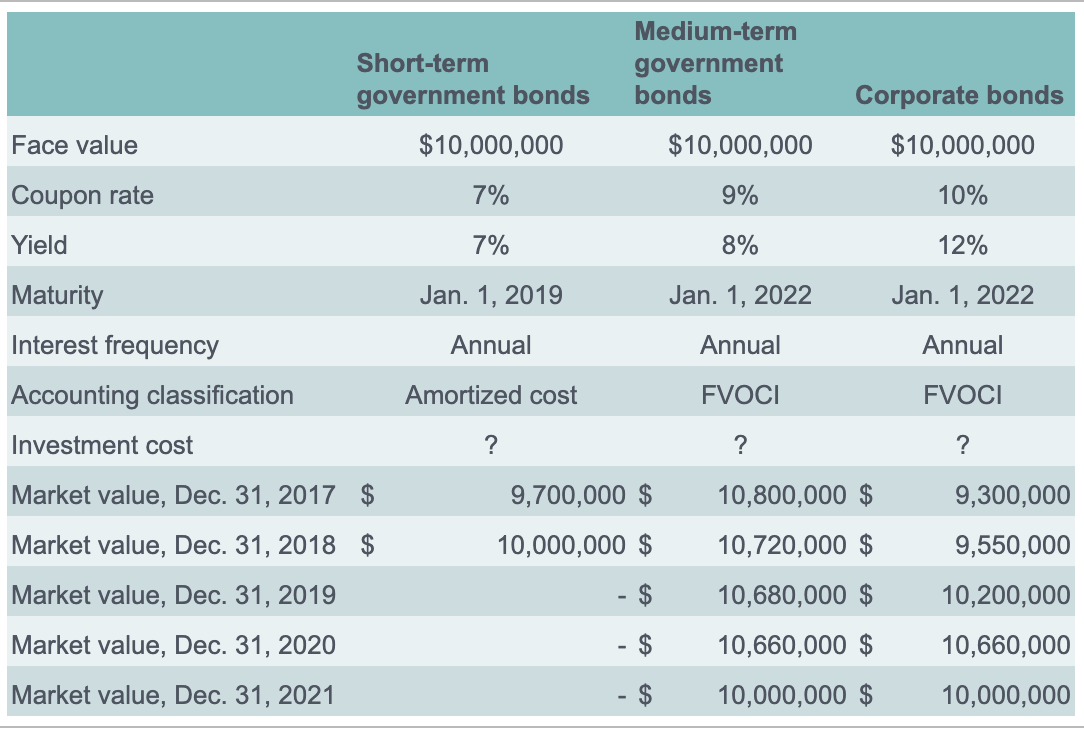
Corp. is a small public company with a December 31 fiscal year-end. At the end of 2016, the company had $30 million of excess cash. The board of directors decided that the company should hold the funds until the right business opportunity appeared, rather than pay out the funds to its shareholders and then have to issue shares to obtain the financing later. The board directed management to invest the funds in a diversified portfolio of debt instruments. As a result, on January 1, 2017, management purchased $10 million of short-term government bonds, $10 million of medium-term government bonds, and $10 million of high-quality corporate bonds. (The amounts are face values, not investment cost.) The following table provides additional information about these investments.
REQUIREMENTS:
a) Determine the investment cost of the three investments on January 1, 2017.
b) Prepare amortization schedules for the medium-term government bonds and the corporate bonds.
c) For each of the three investments, determine the following amounts for each fiscal year:
- balance sheet asset
- income
- other comprehensive income
- accumulated other comprehensive income component of equity.
d) Had Gate classified the medium-term government bonds and the corporate bonds as amortized cost financial assets, how much would have been the total amount of income over the five years for each of the type of bonds?
e) Had Gate classified the medium-term government bonds and the corporate bonds as FVPL financial assets, how much would have been the total amount of income over the five years for each of the type of bonds? What would be different under this scenario?
Short-term government bonds $10,000,000 Medium-term government bonds Corporate bonds $10,000,000 Face value $10,000,000 Coupon rate 7% 9% 10% Yield 7% 8% 12% Jan. 1, 2019 Jan. 1, 2022 Jan. 1, 2022 Maturity Interest frequency Annual Annual Annual Accounting classification Amortized cost FVOCI FVOCI Investment cost ? ? ? 9,700,000 $ 10,800,000 $ Market value, Dec. 31, 2017 $ Market value, Dec. 31, 2018 $ 9,300,000 9,550,000 10,000,000 $ 10,720,000 $ 10,680,000 $ 10,660,000 $ Market value, Dec. 31, 2019 Market value, Dec. 31, 2020 10,200,000 10,660,000 Market value, Dec. 31, 2021 10,000,000 $ 10,000,000
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


