Question
Answer questions based on table 1. Convert the rotation per minutes to rotation per seconds and record the results in Data Table 11.1.2. Use equation
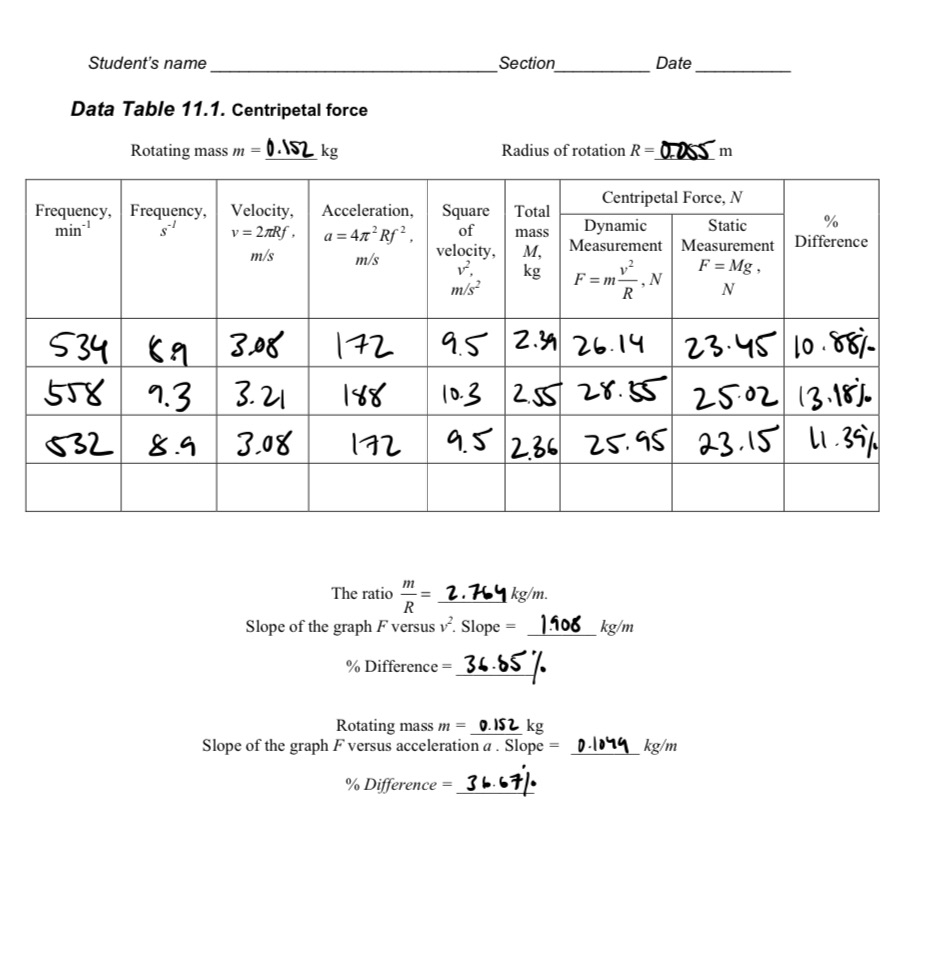
Answer questions based on table 1. Convert the rotation per minutes to rotation per seconds and record the results in Data Table 11.1.2. Use equation (11.6) v = 2?Rf and find the circular velocity for each rotation and square of the velocity. Record yourresult in Data Table 11.1.3. Use equation (11.3) and calculate the centripetal force acting on the rotating mass obtained through the dynamicmeasurement.4. Use the magnitude of the total mass M (the hanging mass plus the rotating mass m) and find the magnitude of thecentripetal force F = Mg , obtained through the static measurements. The magnitude of the centripetal force is equal tothe magnitude of the weight of the total mass.5. Compare the magnitudes of the centripetal force from step 3, obtained by dynamic measurement, and step 4, obtained bystatic measurement, by computing the percent difference.6. We can rewrite equation (11.3) in the following form: F = m v 2 . This shows that the centripetal force is directlyRproportional to the square of the velocity and the coefficient of proportionality is mR . Plot a graph for the centripetal force obtained by the static measurement versus the square of the velocity. Determine the slope of the graph. Find the ratio of the rotating mass to the radius of the rotation mR . Compare the slope of the graph with this ratio by computingthe percent difference.7. Use equation (11.7) and find the acceleration. Record your result in Data Table 11.1. To verify Newton's second law,plot a graph for the centripetal force obtained by the static measurement versus the acceleration. Determine the slope of the graph. The slope of the graph equal to the rotated mass m. Compare the slope of the graph with the rotated mass m by computing the percent difference.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


