Answer sheets

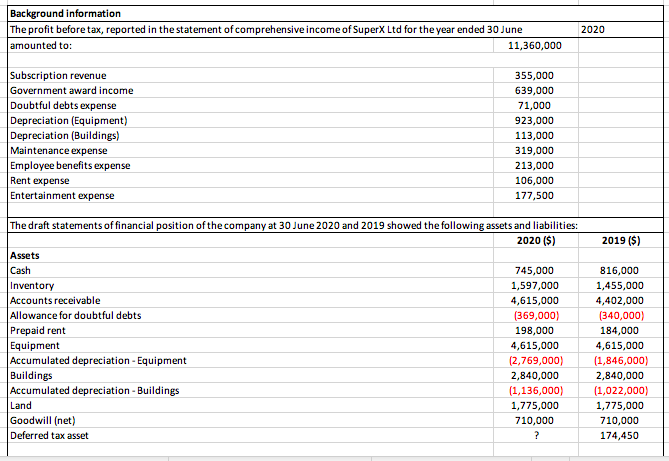
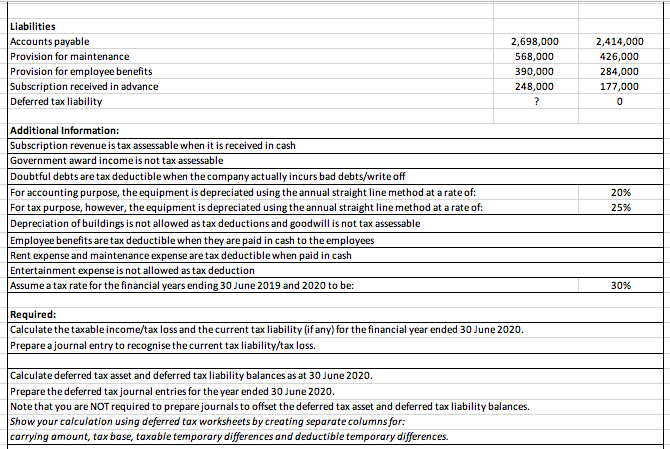
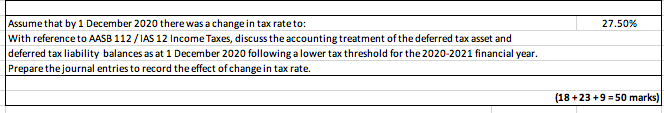
Background information The profit before tax, reported in the statement of comprehensive income of SuperX Ltd for the year ended 30 June amounted to: 11,360,000 2020 2019 ($) Subscription revenue 355,000 Government award income 639,000 Doubtful debts expense 71,000 Depreciation (Equipment) 923,000 Depreciation (Buildings) 113,000 Maintenance expense 319,000 Employee benefits expense 213,000 Rent expense 106,000 Entertainment expense 177,500 The draft statements of financial position of the company at 30 June 2020 and 2019 showed the following assets and liabilities: 2020 ($) Assets Cash 745,000 Inventory 1,597,000 Accounts receivable 4,615,000 Allowance for doubtful debts (369,000) Prepaid rent 198,000 Equipment 4,615,000 Accumulated depreciation - Equipment (2,769,000) Buildings 2,840,000 Accumulated depreciation - Buildings (1,136,000) Land 1,775,000 Goodwill (net) 710,000 Deferred tax asset ? 816,000 1,455,000 4,402,000 (340,000) 184,000 4,615,000 (1,846,000) 2,840,000 (1,022,000) 1,775,000 710,000 174,450 Liabilities Accounts payable Provision for maintenance Provision for employee benefits Subscription received in advance Deferred tax liability 2,698,000 568,000 390,000 248,000 ? 2,414,000 426,000 284,000 177,000 0 Additional Information: Subscription revenue is tax assessable when it is received in cash Government award income is not tax assessable Doubtful debts are tax deductible when the company actually incurs bad debts/write off For accounting purpose, the equipment is depreciated using the annual straight line method at a rate of: For tax purpose, however, the equipment is depreciated using the annual straight line method at a rate of: Depreciation of buildings is not allowed as tax deductions and goodwill is not tax assessable Employee benefits are tax deductible when they are paid in cash to the employees Rent expense and maintenance expense are tax deductible when paid in cash Entertainment expense is not allowed as tax deduction Assume a tax rate for the financial years ending 30 June 2019 and 2020 to be: 20% 25% 30% Required: Calculate the taxable income/tax loss and the current tax liability (if any) for the financial year ended 30 June 2020. Prepare a journal entry to recognise the current tax liability/tax loss. Calculate deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability balances as at 30 June 2020. Prepare the deferred tax journal entries for the year ended 30 June 2020. Note that you are NOT required to prepare journals to offset the deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability balances. Show your calculation using deferred tax worksheets by creating separate columns for: carrying amount, tax base, taxable temporary differences and deductible temporary differences. 27.50% Assume that by 1 December 2020 there was a change in tax rate to: With reference to AASB 112 / IAS 12 Income Taxes, discuss the accounting treatment of the deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability balances as at 1 December 2020 following a lower tax threshold for the 2020-2021 financial year. Prepare the journal entries to record the effect of change in tax rate. (18+23+9 = 50 marks) Calculate the taxable income/tax loss and the current tax liability (if any) for the financial year ended 30th June 2020. Prepare a journal entry to recognise the current tax liability/tax loss. $ Workings: Calculate delened tax asset and defe med tax liability balances as at 30 June 2020. Prepare the deemed Lux jouma envies for the year ended 30 June 2020. Journey 23 mars Assume that by 1 December 2020 there was a change in tax rate to: 27.50% With reference to AASB112 Income Taxes, discuss the accounting treatment of the deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability balances as at 1 December 2020 following a lower tax threshold for the financial year 2020-2021. Prepare the journal entries to record the effect of change in tax rate. Journal entry: Dr Cr 9 marks Background information The profit before tax, reported in the statement of comprehensive income of SuperX Ltd for the year ended 30 June amounted to: 11,360,000 2020 2019 ($) Subscription revenue 355,000 Government award income 639,000 Doubtful debts expense 71,000 Depreciation (Equipment) 923,000 Depreciation (Buildings) 113,000 Maintenance expense 319,000 Employee benefits expense 213,000 Rent expense 106,000 Entertainment expense 177,500 The draft statements of financial position of the company at 30 June 2020 and 2019 showed the following assets and liabilities: 2020 ($) Assets Cash 745,000 Inventory 1,597,000 Accounts receivable 4,615,000 Allowance for doubtful debts (369,000) Prepaid rent 198,000 Equipment 4,615,000 Accumulated depreciation - Equipment (2,769,000) Buildings 2,840,000 Accumulated depreciation - Buildings (1,136,000) Land 1,775,000 Goodwill (net) 710,000 Deferred tax asset ? 816,000 1,455,000 4,402,000 (340,000) 184,000 4,615,000 (1,846,000) 2,840,000 (1,022,000) 1,775,000 710,000 174,450 Liabilities Accounts payable Provision for maintenance Provision for employee benefits Subscription received in advance Deferred tax liability 2,698,000 568,000 390,000 248,000 ? 2,414,000 426,000 284,000 177,000 0 Additional Information: Subscription revenue is tax assessable when it is received in cash Government award income is not tax assessable Doubtful debts are tax deductible when the company actually incurs bad debts/write off For accounting purpose, the equipment is depreciated using the annual straight line method at a rate of: For tax purpose, however, the equipment is depreciated using the annual straight line method at a rate of: Depreciation of buildings is not allowed as tax deductions and goodwill is not tax assessable Employee benefits are tax deductible when they are paid in cash to the employees Rent expense and maintenance expense are tax deductible when paid in cash Entertainment expense is not allowed as tax deduction Assume a tax rate for the financial years ending 30 June 2019 and 2020 to be: 20% 25% 30% Required: Calculate the taxable income/tax loss and the current tax liability (if any) for the financial year ended 30 June 2020. Prepare a journal entry to recognise the current tax liability/tax loss. Calculate deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability balances as at 30 June 2020. Prepare the deferred tax journal entries for the year ended 30 June 2020. Note that you are NOT required to prepare journals to offset the deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability balances. Show your calculation using deferred tax worksheets by creating separate columns for: carrying amount, tax base, taxable temporary differences and deductible temporary differences. 27.50% Assume that by 1 December 2020 there was a change in tax rate to: With reference to AASB 112 / IAS 12 Income Taxes, discuss the accounting treatment of the deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability balances as at 1 December 2020 following a lower tax threshold for the 2020-2021 financial year. Prepare the journal entries to record the effect of change in tax rate. (18+23+9 = 50 marks) Calculate the taxable income/tax loss and the current tax liability (if any) for the financial year ended 30th June 2020. Prepare a journal entry to recognise the current tax liability/tax loss. $ Workings: Calculate delened tax asset and defe med tax liability balances as at 30 June 2020. Prepare the deemed Lux jouma envies for the year ended 30 June 2020. Journey 23 mars Assume that by 1 December 2020 there was a change in tax rate to: 27.50% With reference to AASB112 Income Taxes, discuss the accounting treatment of the deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability balances as at 1 December 2020 following a lower tax threshold for the financial year 2020-2021. Prepare the journal entries to record the effect of change in tax rate. Journal entry: Dr Cr 9 marks












