Question
Answer the analysis Part and answer the questions without skipping any questions. PHY-202 Lab#13: Ideal Gas Laws Purpose: To graphically verify the relationships given in
Answer the analysis Part and answer the questions without skipping any questions.
PHY-202
Lab#13: Ideal Gas Laws
Purpose:
- To graphically verify the relationships given in various gas laws
- To determine the amount of material in a sample
Equipment
- Simulation
Introduction
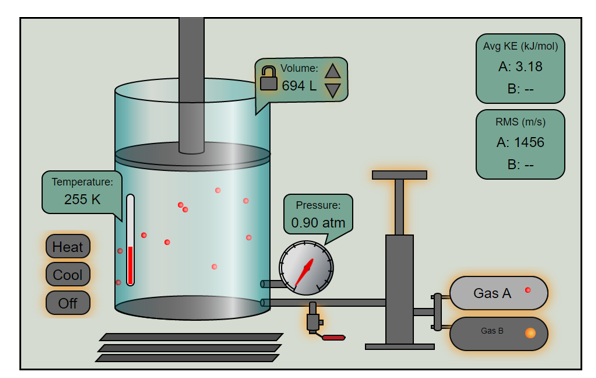
Gases have various properties which we can observe. These include the gas' pressure and temperature and the volumewhich contains the gas. We can also find the amount of gas in a sample, the KE of the molecules in a sample and the root mean-square velocity of the molecules. The values of these properties determine the state of the gas.
In the mid 1600's, Robert Boyle studied the relationship between the pressurePand the volumeVof a confined gas held at a constant temperature. Boyle observed that the product of the pressure and volume are observed to be nearly constant. The product of pressure and volume is exactly a constant for anideal gas.
P * V = constant
This relationship between pressure and volume is calledBoyle's Lawin his honor.
The relationship between temperature and volume, at a constant number of moles and pressure, is calledCharles and Gay-Lussac's Lawin honor of the two French scientists who first investigated this relationship. Charles did the original work, which was verified by Gay-Lussac. They observed that if the pressure is held constant, the volumeVis equal to a constant multiplied by the temperatureT:
V = constant * T
We generally separate the two laws and use the above as Charles' Law.
The version of Gay-Lussac's Law that we use states thatthe pressure of a given amount of gas held at constant volume is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature.
P = constant * T
Putting these laws together, we have the ideal gas law:
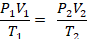
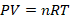
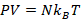
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


