Answer the following questions- for question 5 - there are 3 options for each drop down: (Positive, negative, or zero).
1.
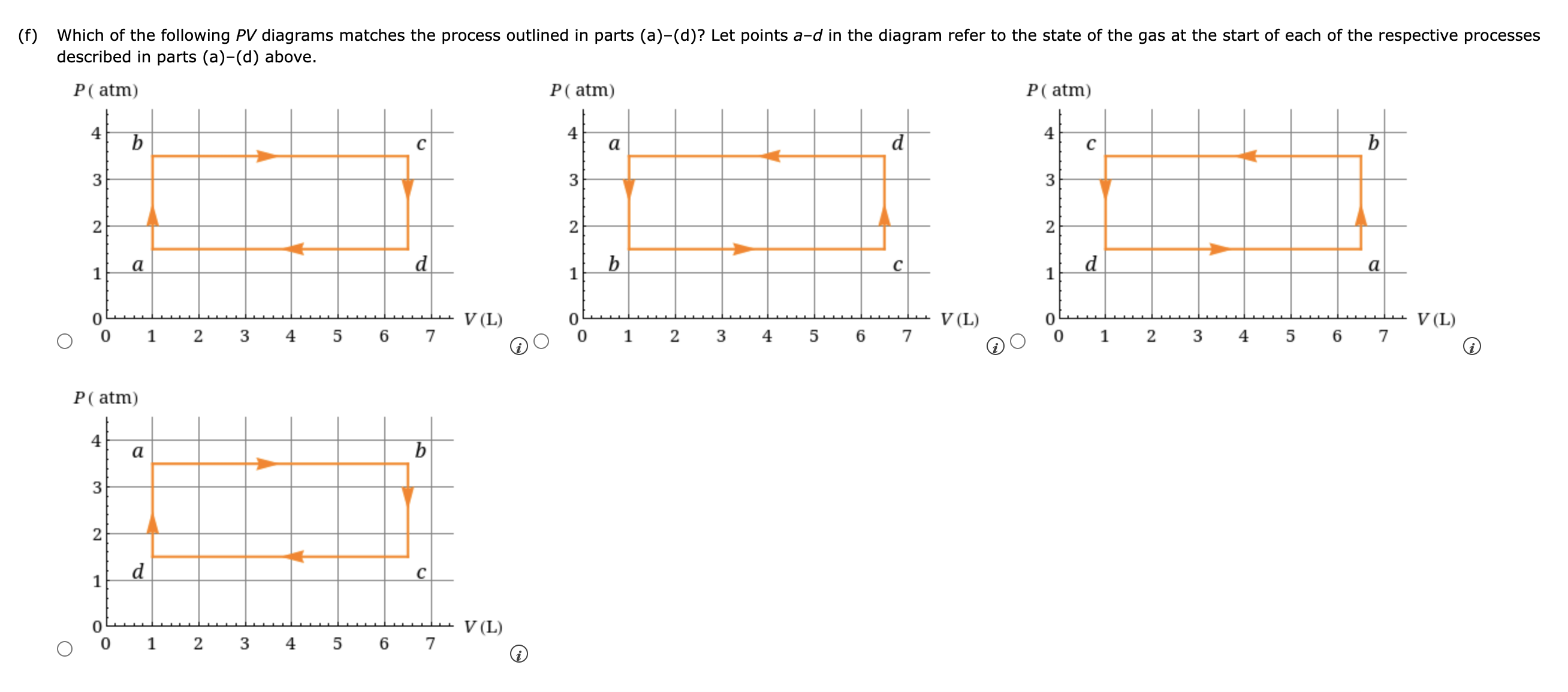
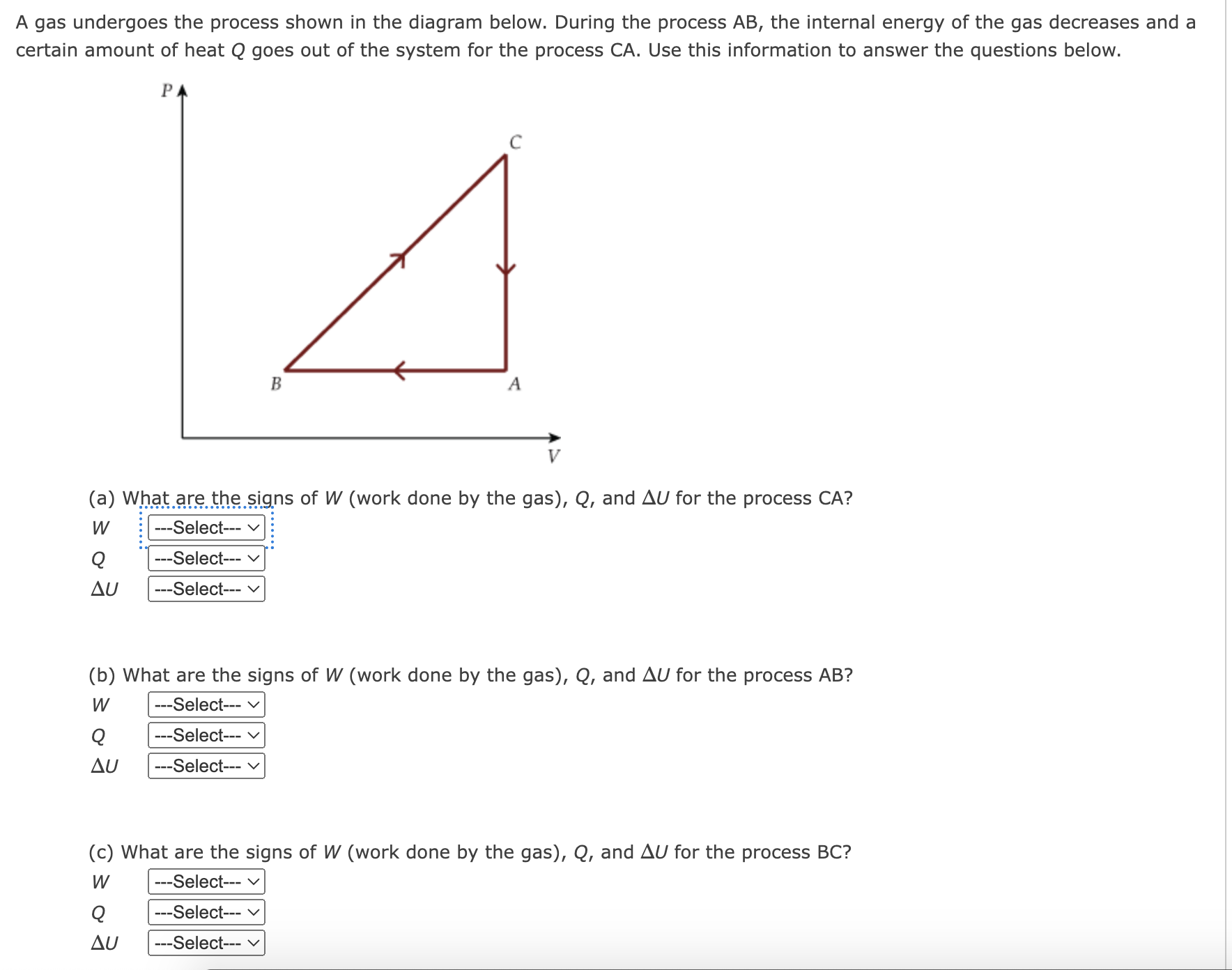
A sample of gas, initially with a volume of 1.0 L, undergoes a thermodynamic cycle. Find the work done by the gas on its environment during each stage of the cycle described below. (Enter your answers in J.) (a) First, the gas expands from a volume of 1.0 L to 6.5 L at a constant pressure of 3.5 atm. J (b) Second, the gas is cooled at constant volume until the pressure falls to 1.5 atm. J (c) Third, the gas is compressed at a constant pressure of 1.5 atm from a volume of 6.5 L to 1.0 L. (Note: Be careful of signs.) J (d) Finally, the gas is heated until its pressure increases from 1.5 atm to 3.5 atm at a constant volume. J (e) What is the net work done by the gas on its environment during the complete cycle described above? J (f) Which of the following PV diagrams matches the process outlined in parts (a)(d)? Let points ad in the diagram refer to the state of the gas at the start of each of the respective processes described in parts (a)(d) above. P( atm) n----- In a running event, a sprinter does 5.7 x 105 J of work and her internal energy decreases by 8.0 x 105 J. (a) Determine the heat transferred between her body and surroundings during this event. (Give the heat transferred to her body from the surroundings.) J (b) What does the sign of your answer to part (a) indicate? 0 Energy is transferred from the sprinter to the environment by heat. 0 There is no heat transferred between the sprinter and the environment. 0 Energy is transferred from the environment to the sprinter by heat. A gas is at a constant pressure of 2.1 x 105 N/mz. Its volume increases by 1.3 x 102 m3 the gas in the form of heat. Find the change in thermal energy of the gas. |:|J as 3700 J of energy is transferred to Nuclear fusion, the energy source of the sun and hydrogen bombs, occurs much more readily when the average kinetic energy of the atoms is high that is, at high temperatures. Suppose you want the atoms in your fusion experiment to have average kinetic energies of 3.10 x 10'14 J. What temperature is needed? |:]K A gas undergoes the process shown in the diagram below. During the process AB, the internal energy of the gas decreases and a certain amount of heat Q goes out of the system for the process CA. Use this information to answer the questions below. PA B (a) What are the signs of W (work done by the gas), Q, and AU for the process CA? W . . . . ... ---Select--- Q --Select--- AU --Select--- (b) What are the signs of W (work done by the gas), Q, and AU for the process AB? W --Select--- Q -Select--- AU ---Select--- (c) What are the signs of W (work done by the gas), Q, and AU for the process BC? W ---Select--- v Q --Select--- AU Select