Question
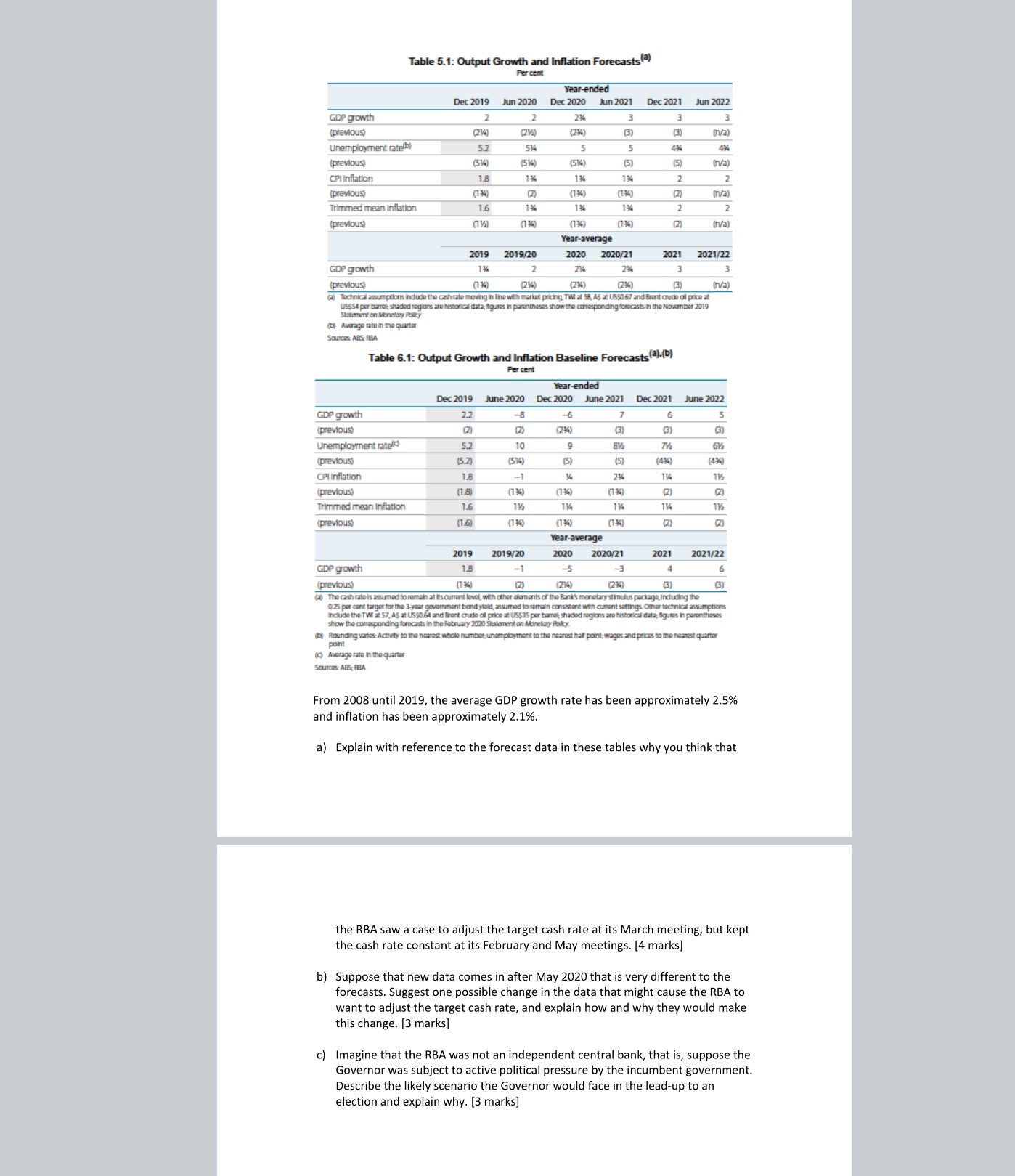
Anyone help me solve this From 2008 until 2019, the average GDP growth rate has been approximately 2.5% and inflation has been approximately 2.1%.a) Explain
Anyone help me solve this From 2008 until 2019, the average GDP growth rate has been approximately 2.5% and inflation has been approximately 2.1%.a) Explain with reference to the forecast data in these tables why you think that the RBA saw a case to adjust the target cash rate at its March meeting, but kept the cash rate constant at its February and May meetings. [4 marks]b) Suppose that new data comes in after May 2020 that is very different to the forecasts. Suggest one possible change in the data that might cause the RBA to want to adjust the target cash rate, and explain how and why they would make this change. [3 marks]c) Imagine that the RBA was not an independent central bank, that is, suppose the Governor was subject to active political pressure by the incumbent government. Describe the likely scenario the Governor would face in the lead-up to an election and explain why. [3 marks
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


