Question: Apologies. Last time I posted it wrong. However, the code was still incorrect at first. I am still getting errors: #include #include using namespace std;
Apologies. Last time I posted it wrong. However, the code was still incorrect at first. I am still getting errors:
#include
using namespace std;
/****************************************************************************** * Node class declaration. * DO NOT modify. ******************************************************************************/
class Node { public: int data; Node* next; };
/****************************************************************************** * Functions you have to implement ******************************************************************************/
//Problem A: Remove part of a linked list. void Remove(Node* &llist, unsigned startIndex, unsigned endIndex) { //Write your solution here... // Check if the linked list is empty if (llist == nullptr) { return; }
// Create a dummy node to simplify the removal process Node dummyNode; dummyNode.data = 0; dummyNode.next = llist;
// Find the start node of the removal range Node* prev = &dummyNode; for (unsigned i = 0; i next != nullptr; i++) { prev = prev->next; }
// Find the end node of the removal range Node* curr = prev->next; for (unsigned i = startIndex; i next; }
// Update the pointers of the previous and next nodes prev->next = curr;
// Free the removed nodes while (prev->next != nullptr) { Node* temp = prev->next; prev->next = prev->next->next; delete temp; }
// Update the head of the linked list llist = dummyNode.next; }
//Problem B: Reversing a linked list. void ReverseList(Node* &llist) { //Write your solution here...
// Check if the linked list is empty or has only one node if (llist == nullptr || llist->next == nullptr) { return; }
// Initialize pointers to the first two nodes Node* prevNode = nullptr; Node* currNode = llist;
// Reverse the pointers of each node while (currNode != nullptr) { Node* nextNode = currNode->next; currNode->next = prevNode; prevNode = currNode; currNode = nextNode; }
// Update the head of the linked list llist = prevNode;
}
//Problem C: Perform a right shift to a Linked List. void RightShift(Node* &llist, int k) { //Write your solution here... // Check if the linked list is empty or has only one node if (llist == nullptr || llist->next == nullptr) { return; }
// Find the tail and count the number of nodes int count = 1; Node* tail = llist; while (tail->next != nullptr) { tail = tail->next; count++; }
// Calculate the number of nodes to shift int shift = count - 1 - (k % count); if (shift == 0) { return; }
// Find the new tail and head Node* newTail = llist; for (int i = 1; i next; } Node* newHead = newTail->next;
// Update the pointers newTail->next = nullptr; tail->next = llist; llist = newHead; }
//Problem D: Test if a list is a palindrome. bool IsPalindrome(Node* llist) { //Write your solution here... if (llist == nullptr || llist->next == nullptr) { return true; // an empty or single-node list is always a palindrome }
// Find the middle node using the slow and fast pointer technique Node* slow = llist; Node* fast = llist; while (fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; }
// Reverse the second half of the linked list Node* prev = nullptr; Node* curr = slow; while (curr != nullptr) { Node* next = curr->next; curr->next = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; }
// Compare the first and second half of the linked list Node* p1 = llist; Node* p2 = prev; bool is_palindrome = true; while (p2 != nullptr) { if (p1->data != p2->data) { is_palindrome = false; break; } p1 = p1->next; p2 = p2->next; }
// Restore the original order of the linked list prev = nullptr; curr = slow; while (curr != nullptr) { Node* next = curr->next; curr->next = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } slow->next = prev;
return is_palindrome; }
/****************************************************************************** * Functions that used by the driver. * DO NOT modify these functions. ******************************************************************************/
Node* CreateList(int* arr, int len) { if (len data = arr[len - 1]; head->next = NULL; for (int i = 1; i next = head; temp->data = arr[len - i - 1]; head = temp; } return head; }
void RemoveAll(Node*& first) { Node* cur = first; while (cur != NULL) { Node* del = cur; cur = cur->next; delete del; } first = NULL; }
void ShowList(Node* llist) { Node* cur = llist; while (cur != NULL) { cout data next; } cout
/****************************************************************************** * Test driver main function. * DO NOT modify the main function. ******************************************************************************/
int main() {
cout
cout
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
RemoveAll(llistA); RemoveAll(llistB); llistA = CreateList(a, 5); llistB = CreateList(b, 7);
cout
cout
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
RemoveAll(llistA); RemoveAll(llistB); llistA = CreateList(a, 5); llistB = CreateList(b, 7);
cout
cout
//////////////////////////////////////////////////
cout
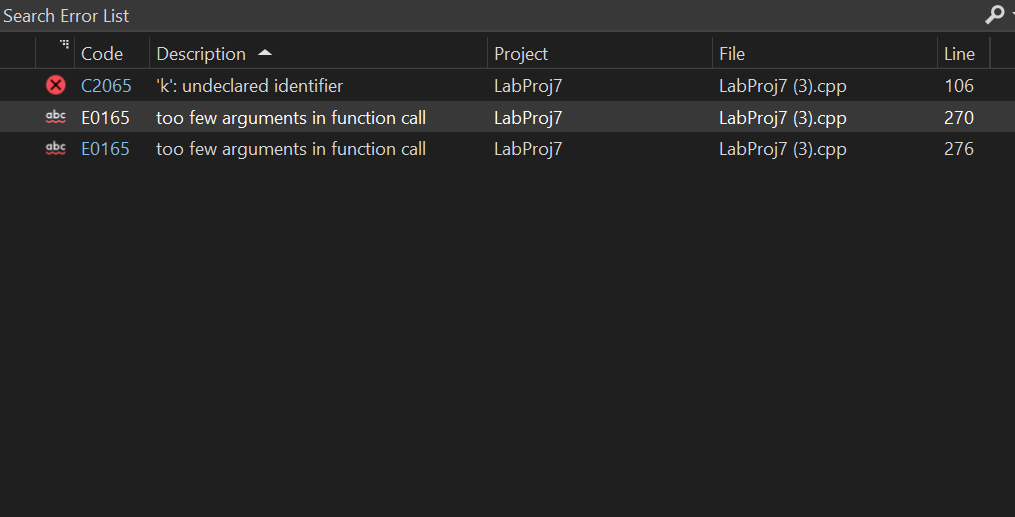
cout Search Error List
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


