
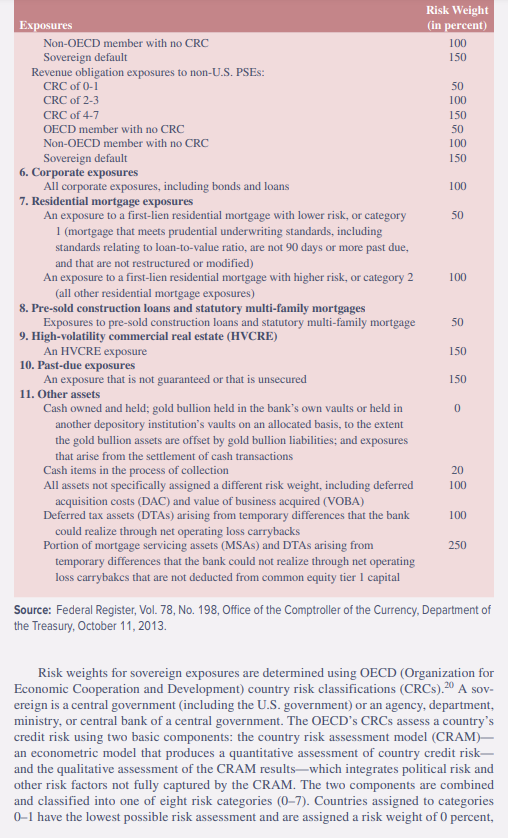

Appendix 13E calculating Risk-Based Capital Rolos Under the Basel III risk-based capital plan, each DI assigns its assets to one of several categories of credit risk exposure. Table 13-28 lists the key categories and assets in these categories. 0 20 a 20 100 150 150 TABLE 13-28 Risk Weights for Calculating Risk-Weighted Assets for On-Balance-Sheet Items under Basel III Risk Weight Exposures (in percent) 1. Exposures to sovereigns Exposures to the U.S. government: An exposure to the U.S. government, its central bank, or a U.S. government agency The portion of an exposure that is directly and unconditionally guaranteed by 0 the U.S. government, its central bank, or a U.S. government agency The portion of an exposure that is conditionally guaranteed by the U.S. government, its central bank, or a U.S. government agency Other sovereign exposures: CRC of 0-1 0 CRC of 2 CRC of 3 50 CRC of 4-6 CRC of 7 OECD member with no CRC 0 Non-OECD member with no CRC 100 Sovereign default 2. Exposures to certain supranational entities and multilateral development banks (MDB) An exposure to the BIS, the ECB, the European Commission, the IMF, or an MDB 3. Exposures to government-sponsored entities (GSE) An exposure to a GSE other than an equity exposure or preferred stock 20 An exposure to preferred stock issued by a GSE 100 4. Exposures to depository institutions, foreign banks, and credit unions Exposures to U.S. depository insitutions and credit unions Exposures to foreign banks: CRC of 0-1 20 CRC of 2 CRC of 3 CRC of 4-7 OECD member with no CRC Non-OECD member with no CRC 100 Sovereign default 5. Exposures to public sector entities (PSES): General obligation exposures to U.S. PSES 20 Revenue obligation exposures to U.S. PSE General obligation exposures to non-U.S. PSES: CRC of 0-1 CRC of 2 CRC of 3 CRC of 4-7 OECD member with no CRC 20 0 20 SO 100 150 20 150 50 20 SO 100 150 (continued) Risk Weight (in percent) 100 150 50 100 150 50 100 150 100 50 100 Exposures Non-OECD member with no CRC Sovereign default Revenue obligation exposures to non-U.S. PSES: CRC of 0-1 CRC of 2-3 CRC of 4-7 OECD member with no CRC Non-OECD member with no CRC Sovereign default 6. Corporate exposures All corporate exposures, including bonds and loans 7. Residential mortgage exposures An exposure to a first-lien residential mortgage with lower risk, or category 1 (mortgage that meets prudential underwriting standards, including standards relating to loan-to-value ratio, are not 90 days or more past due, and that are not restructured or modified) An exposure to a first-lien residential mortgage with higher risk, or category 2 (all other residential mortgage exposures) 8. Pre-sold construction loans and statutory multi-family mortgages Exposures to pre-sold construction loans and statutory multi-family mortgage 9. High-volatility commercial real estate (HVCRE) An HVCRE exposure 10. Past-due exposures An exposure that is not guaranteed or that is unsecured 11. Other assets Cash owned and held; gold bullion held in the bank's own vaults or held in another depository institution's vaults on an allocated basis, to the extent the gold bullion assets are offset by gold bullion liabilities, and exposures that arise from the settlement of cash transactions Cash items in the process of collection All assets not specifically assigned a different risk weight, including deferred acquisition costs (DAC) and value of business acquired (VOBA) Deferred tax assets (DTAS) arising from temporary differences that the bank could realize through net operating loss carrybacks Portion of mortgage servicing assets (MSAs) and DTAs arising from temporary differences that the bank could not realize through net operating loss carrybakcs that are not deducted from common equity tier 1 capital 50 150 150 0 20 100 100 250 Source: Federal Register, Vol. 78, No. 198, Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, Department of the Treasury, October 11, 2013. Risk weights for sovereign exposures are determined using OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) country risk classifications (CRCs).20 A sov- ereign is a central government (including the U.S. government) or an agency, department, ministry, or central bank of a central government. The OECD's CRCs assess a country's credit risk using two basic components: the country risk assessment model (CRAM)- an econometric model that produces a quantitative assessment of country credit risk- and the qualitative assessment of the CRAM resultswhich integrates political risk and other risk factors not fully captured by the CRAM. The two components are combined and classified into one of eight risk categories (0-7). Countries assigned to categories 0-1 have the lowest possible risk assessment and are assigned a risk weight of 0 percent, Refer to Table 1328. What is the contribution to the asset base of the following items under the Basel III requirements? (Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "o" wherever required. Enter your answers in dollars not in millions.) a. $10 million cash reserves. b. $40 million 91-day U.S. Treasury bills. c. $20 million cash items in the process of collection. d. $5 million UK government bonds, OECD CRD rated 1. e. $5 million French short-term government bonds, OECD CRD rated 2. 4. $1 million general obligation bonds. g. $50 million repurchase agreements (against U.S. Treasuries). h. $3 million loan to foreign bank, OECD rated 3. 1. $400 million 1-4 family home mortgages, category 1, loan-to-value ratio 80%. J. $10 million 1-4 family home mortgages, category 2, loan-to-value ratio 95%. k. $5 million 1-4 family home mortgages, 100 days past due. 1. $400 million commercial and industrial loans. AAA-rated. m. $400 million commercial and industrial loans. B-rated. n. $100,000 performance-related standby letters of credit to a AAA-rated corporation. o. $100.000 performance-related standby letters of credit to a municipality issuing general obligation bonds. p. $6 million commercial letter of credit to a foreign bank, OECD CRC rated 2. q. $2 million five-year loan commitment to a foreign government. OECD CRC rated 1. r. $5 million bankers' acceptance conveyed to a U.S. AA-rated corporation. s. $14 million three-year loan commitment to a private agent. t. $14 million three-month loan commitment to a private agent. u. $28 million standby letter of credit to back an A-rated corporate issue of commercial paper. v. $8 million five-year interest rate swap with no current exposure. w. $6 million two-year currency swap with $500,000 current exposure. Basel III Asset Base a. b. c. d. f. 9 h. i. j k. 1. m. n. 0. p. 9. r. S. t. U V. W. Appendix 13E calculating Risk-Based Capital Rolos Under the Basel III risk-based capital plan, each DI assigns its assets to one of several categories of credit risk exposure. Table 13-28 lists the key categories and assets in these categories. 0 20 a 20 100 150 150 TABLE 13-28 Risk Weights for Calculating Risk-Weighted Assets for On-Balance-Sheet Items under Basel III Risk Weight Exposures (in percent) 1. Exposures to sovereigns Exposures to the U.S. government: An exposure to the U.S. government, its central bank, or a U.S. government agency The portion of an exposure that is directly and unconditionally guaranteed by 0 the U.S. government, its central bank, or a U.S. government agency The portion of an exposure that is conditionally guaranteed by the U.S. government, its central bank, or a U.S. government agency Other sovereign exposures: CRC of 0-1 0 CRC of 2 CRC of 3 50 CRC of 4-6 CRC of 7 OECD member with no CRC 0 Non-OECD member with no CRC 100 Sovereign default 2. Exposures to certain supranational entities and multilateral development banks (MDB) An exposure to the BIS, the ECB, the European Commission, the IMF, or an MDB 3. Exposures to government-sponsored entities (GSE) An exposure to a GSE other than an equity exposure or preferred stock 20 An exposure to preferred stock issued by a GSE 100 4. Exposures to depository institutions, foreign banks, and credit unions Exposures to U.S. depository insitutions and credit unions Exposures to foreign banks: CRC of 0-1 20 CRC of 2 CRC of 3 CRC of 4-7 OECD member with no CRC Non-OECD member with no CRC 100 Sovereign default 5. Exposures to public sector entities (PSES): General obligation exposures to U.S. PSES 20 Revenue obligation exposures to U.S. PSE General obligation exposures to non-U.S. PSES: CRC of 0-1 CRC of 2 CRC of 3 CRC of 4-7 OECD member with no CRC 20 0 20 SO 100 150 20 150 50 20 SO 100 150 (continued) Risk Weight (in percent) 100 150 50 100 150 50 100 150 100 50 100 Exposures Non-OECD member with no CRC Sovereign default Revenue obligation exposures to non-U.S. PSES: CRC of 0-1 CRC of 2-3 CRC of 4-7 OECD member with no CRC Non-OECD member with no CRC Sovereign default 6. Corporate exposures All corporate exposures, including bonds and loans 7. Residential mortgage exposures An exposure to a first-lien residential mortgage with lower risk, or category 1 (mortgage that meets prudential underwriting standards, including standards relating to loan-to-value ratio, are not 90 days or more past due, and that are not restructured or modified) An exposure to a first-lien residential mortgage with higher risk, or category 2 (all other residential mortgage exposures) 8. Pre-sold construction loans and statutory multi-family mortgages Exposures to pre-sold construction loans and statutory multi-family mortgage 9. High-volatility commercial real estate (HVCRE) An HVCRE exposure 10. Past-due exposures An exposure that is not guaranteed or that is unsecured 11. Other assets Cash owned and held; gold bullion held in the bank's own vaults or held in another depository institution's vaults on an allocated basis, to the extent the gold bullion assets are offset by gold bullion liabilities, and exposures that arise from the settlement of cash transactions Cash items in the process of collection All assets not specifically assigned a different risk weight, including deferred acquisition costs (DAC) and value of business acquired (VOBA) Deferred tax assets (DTAS) arising from temporary differences that the bank could realize through net operating loss carrybacks Portion of mortgage servicing assets (MSAs) and DTAs arising from temporary differences that the bank could not realize through net operating loss carrybakcs that are not deducted from common equity tier 1 capital 50 150 150 0 20 100 100 250 Source: Federal Register, Vol. 78, No. 198, Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, Department of the Treasury, October 11, 2013. Risk weights for sovereign exposures are determined using OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) country risk classifications (CRCs).20 A sov- ereign is a central government (including the U.S. government) or an agency, department, ministry, or central bank of a central government. The OECD's CRCs assess a country's credit risk using two basic components: the country risk assessment model (CRAM)- an econometric model that produces a quantitative assessment of country credit risk- and the qualitative assessment of the CRAM resultswhich integrates political risk and other risk factors not fully captured by the CRAM. The two components are combined and classified into one of eight risk categories (0-7). Countries assigned to categories 0-1 have the lowest possible risk assessment and are assigned a risk weight of 0 percent, Refer to Table 1328. What is the contribution to the asset base of the following items under the Basel III requirements? (Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "o" wherever required. Enter your answers in dollars not in millions.) a. $10 million cash reserves. b. $40 million 91-day U.S. Treasury bills. c. $20 million cash items in the process of collection. d. $5 million UK government bonds, OECD CRD rated 1. e. $5 million French short-term government bonds, OECD CRD rated 2. 4. $1 million general obligation bonds. g. $50 million repurchase agreements (against U.S. Treasuries). h. $3 million loan to foreign bank, OECD rated 3. 1. $400 million 1-4 family home mortgages, category 1, loan-to-value ratio 80%. J. $10 million 1-4 family home mortgages, category 2, loan-to-value ratio 95%. k. $5 million 1-4 family home mortgages, 100 days past due. 1. $400 million commercial and industrial loans. AAA-rated. m. $400 million commercial and industrial loans. B-rated. n. $100,000 performance-related standby letters of credit to a AAA-rated corporation. o. $100.000 performance-related standby letters of credit to a municipality issuing general obligation bonds. p. $6 million commercial letter of credit to a foreign bank, OECD CRC rated 2. q. $2 million five-year loan commitment to a foreign government. OECD CRC rated 1. r. $5 million bankers' acceptance conveyed to a U.S. AA-rated corporation. s. $14 million three-year loan commitment to a private agent. t. $14 million three-month loan commitment to a private agent. u. $28 million standby letter of credit to back an A-rated corporate issue of commercial paper. v. $8 million five-year interest rate swap with no current exposure. w. $6 million two-year currency swap with $500,000 current exposure. Basel III Asset Base a. b. c. d. f. 9 h. i. j k. 1. m. n. 0. p. 9. r. S. t. U V. W









