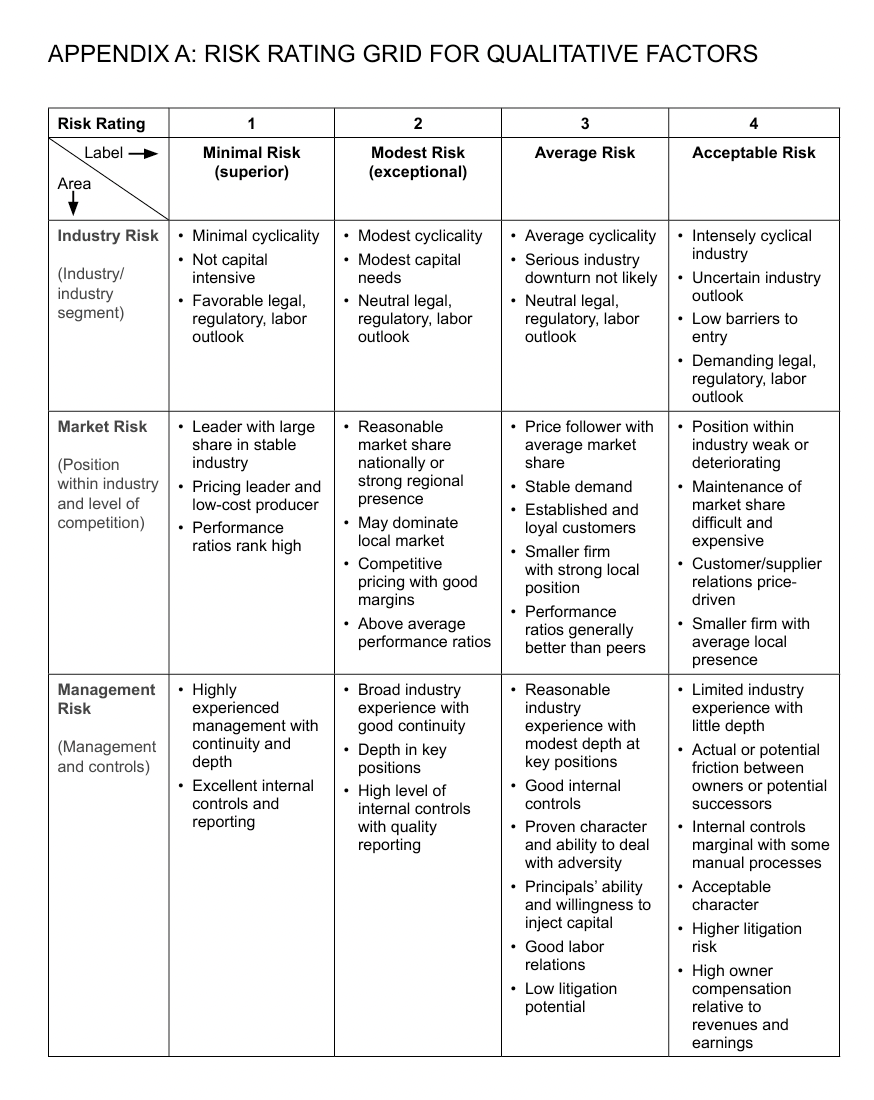
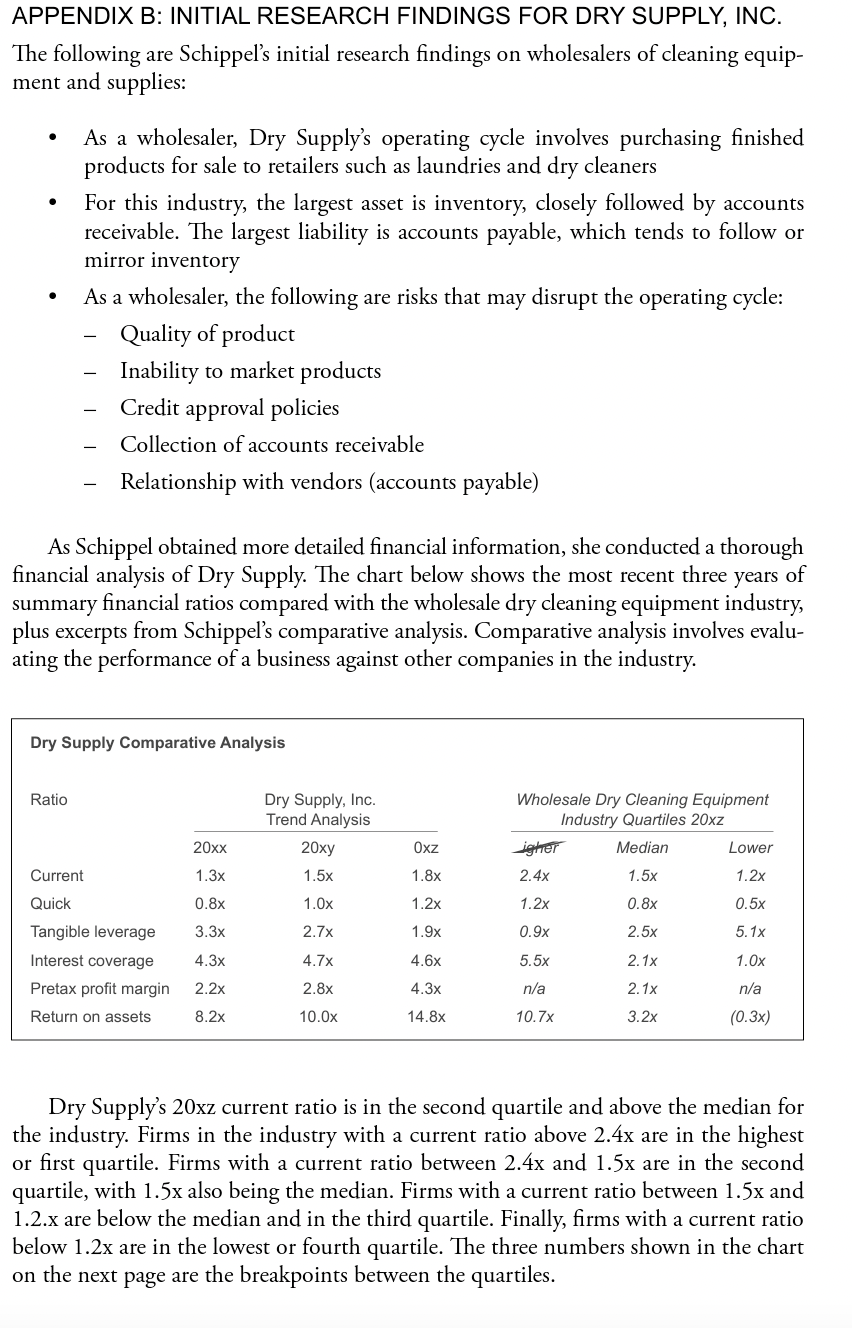


APPENDIX A: RISK RATING GRID FOR QUALITATIVE FACTORS 1 2 3 4 Risk Rating Label - Minimal Risk (superior) Modest Risk (exceptional) Average Risk Acceptable Risk Area Industry Risk (Industry industry segment) Minimal cyclicality Not capital intensive Favorable legal, regulatory, labor outlook Modest cyclicality Modest capital needs Neutral legal, regulatory, labor outlook Average cyclicality Serious industry downturn not likely Neutral legal, regulatory, labor outlook Intensely cyclical industry Uncertain industry outlook Low barriers to entry Demanding legal, regulatory, labor outlook Market Risk Price follower with average market share (Position within industry and level of competition) Leader with large share in stable industry Pricing leader and low-cost producer Performance ratios rank high Reasonable market share nationally or strong regional presence May dominate local market Competitive pricing with good margins . Above average performance ratios Stable demand Established and loyal customers Smaller firm with strong local position Performance ratios generally better than peers Management Risk Highly experienced management with continuity and depth Excellent internal controls and reporting (Management and controls) Broad industry experience with good continuity Depth in key positions High level of internal controls with quality reporting Position within industry weak or deteriorating Maintenance of market share difficult and expensive Customer/supplier relations price- driven Smaller firm with average local presence Limited industry experience with little depth Actual or potential friction between owners or potential successors Internal controls marginal with some manual processes Acceptable character Higher litigation risk High owner compensation relative to revenues and earnings Reasonable industry experience with modest depth at key positions Good internal controls Proven character and ability to deal with adversity Principals' ability and willingness to inject capital Good labor relations Low litigation potential APPENDIX B: INITIAL RESEARCH FINDINGS FOR DRY SUPPLY, INC. The following are Schippels initial research findings on wholesalers of cleaning equip- ment and supplies: . . As a wholesaler, Dry Supply's operating cycle involves purchasing finished products for sale to retailers such as laundries and dry cleaners For this industry, the largest asset is inventory, closely followed by accounts receivable. The largest liability is accounts payable, which tends to follow or mirror inventory As a wholesaler, the following are risks that may disrupt the operating cycle: Quality of product Inability to market products Credit approval policies Collection of accounts receivable Relationship with vendors (accounts payable) - As Schippel obtained more detailed financial information, she conducted a thorough financial analysis of Dry Supply. The chart below shows the most recent three years of summary financial ratios compared with the wholesale dry cleaning equipment industry, plus excerpts from Schippels comparative analysis. Comparative analysis involves evalu- ating the performance of a business against other companies in the industry. Dry Supply Comparative Analysis Ratio Dry Supply, Inc. Trend Analysis 20xy Wholesale Dry Cleaning Equipment Industry Quartiles 20xz igher Median Lower 2.4x 1.5x 1.2x 20xx Oxz Current 1.3x 1.5x 1.8x Quick 0.8x 1.Ox 1.2x 1.2x 0.8x 0.5x 3.3x 2.7x 1.9x 0.9x 2.5x 5. 1x 4.3x 4.7x 4.6x 5.5x 2.1x 1.0x Tangible leverage Interest coverage Pretax profit margin Return on assets 2.2x 2.8x 4.3x n/a 2. 1x n/a 8.2x 10.0x 14.8x 10.7x 3.2x (0.3x) Dry Supply's 20xz current ratio is in the second quartile and above the median for the industry. Firms in the industry with a current ratio above 2.4x are in the highest or first quartile. Firms with a current ratio between 2.4x and 1.5x are in the second quartile, with 1.5x also being the median. Firms with a current ratio between 1.5x and 1.2.x are below the median and in the third quartile. Finally, firms with a current ratio below 1.2x are in the lowest or fourth quartile. The three numbers shown in the chart on the next page are the breakpoints between the quartiles. Interpreting Industry Data Using the Current Ratio From Dry Supply Comparative Analysis Breakpoint Second Quartile Breakpoint First or Highest Quartile Third Quartile Breakpoint Fourth or Lowest Quartile 2.4x 1.5x 1.2x The current ratio of 1.8x suggests that, in liquidation, Dry Supply's current assets, even after discounts of almost 45 percent, would be sufficient to current liabilities. Moreover, its 20xz quick ratio is in the top quartile for its industry. An experienced business banker would recognize that Dry Supply's liquidity compares favorably to the industry. However, because the primary purpose of a ratio is to reflect trends, it is dif- ficult to be conclusive about any single ratio in isolation. This is why a business banker needs to understand the business and its industry. Dry Supply's tangible leverage ratio of 1.9x at 12/31/20xz indicates that creditors continue to have more risk than its owners. While this ratio has improved over the three years, it is still fairly high and may limit the company's ability to borrow addi- tional funds. At 12/31/20xz, this ratio is better than (lower than) the median, since it is below 2.5x, which means that, in general, Dry Supply has a lower (more favorable) tangible leverage ratio than most of its competitors. The coverage ratio available for the industry is interest coverage, which shows Dry Supply to be higher than the median for the industry. This is the result of having a lower leverage position than its peers, which likely includes having fewer borrowed funds to generate interest expense, together with favorable levels of profits as compared to the industry. Dry Supply's pretax profit margin for 20xz is well above the median for the in- dustry, with full quartiles not available from the industry data. A business banker should look further at the common-size income statement data for the industry to see which components cause the favorable position relative to the industry. Dry Supply could have a higher gross profit margin, lower operating expense levels, or a combination of both. The relatively high levels of profits contribute to Dry Supply being in the highest or first quartile for the return on assets (ROA) ratio for 20xz. This is because Dry Supply's ROA of 14.8 percent exceeds the 10.7 percent breakpoint between the first and second quartile. It is possible that Dry Supply uses its assets more efficiently than others in the industry to produce profits, but perhaps Dry Supply does not have as much new equipment as its competitors. If industry data for the sales to assets ratio is available, as well as the other efficiency ratios, a business banker can make better conclusions about this ratio. Instructions Review the Risk Rating Grid for Qualitative Factors and Schippel's financial review findings for Dry Supply in Appendix A and Appendix B in this chapter. Then answer these questions. 1. What are some initial risk rating conclusions you can make for the following: Industry risk? Market risk? Management risk? . APPENDIX A: RISK RATING GRID FOR QUALITATIVE FACTORS 1 2 3 4 Risk Rating Label - Minimal Risk (superior) Modest Risk (exceptional) Average Risk Acceptable Risk Area Industry Risk (Industry industry segment) Minimal cyclicality Not capital intensive Favorable legal, regulatory, labor outlook Modest cyclicality Modest capital needs Neutral legal, regulatory, labor outlook Average cyclicality Serious industry downturn not likely Neutral legal, regulatory, labor outlook Intensely cyclical industry Uncertain industry outlook Low barriers to entry Demanding legal, regulatory, labor outlook Market Risk Price follower with average market share (Position within industry and level of competition) Leader with large share in stable industry Pricing leader and low-cost producer Performance ratios rank high Reasonable market share nationally or strong regional presence May dominate local market Competitive pricing with good margins . Above average performance ratios Stable demand Established and loyal customers Smaller firm with strong local position Performance ratios generally better than peers Management Risk Highly experienced management with continuity and depth Excellent internal controls and reporting (Management and controls) Broad industry experience with good continuity Depth in key positions High level of internal controls with quality reporting Position within industry weak or deteriorating Maintenance of market share difficult and expensive Customer/supplier relations price- driven Smaller firm with average local presence Limited industry experience with little depth Actual or potential friction between owners or potential successors Internal controls marginal with some manual processes Acceptable character Higher litigation risk High owner compensation relative to revenues and earnings Reasonable industry experience with modest depth at key positions Good internal controls Proven character and ability to deal with adversity Principals' ability and willingness to inject capital Good labor relations Low litigation potential APPENDIX B: INITIAL RESEARCH FINDINGS FOR DRY SUPPLY, INC. The following are Schippels initial research findings on wholesalers of cleaning equip- ment and supplies: . . As a wholesaler, Dry Supply's operating cycle involves purchasing finished products for sale to retailers such as laundries and dry cleaners For this industry, the largest asset is inventory, closely followed by accounts receivable. The largest liability is accounts payable, which tends to follow or mirror inventory As a wholesaler, the following are risks that may disrupt the operating cycle: Quality of product Inability to market products Credit approval policies Collection of accounts receivable Relationship with vendors (accounts payable) - As Schippel obtained more detailed financial information, she conducted a thorough financial analysis of Dry Supply. The chart below shows the most recent three years of summary financial ratios compared with the wholesale dry cleaning equipment industry, plus excerpts from Schippels comparative analysis. Comparative analysis involves evalu- ating the performance of a business against other companies in the industry. Dry Supply Comparative Analysis Ratio Dry Supply, Inc. Trend Analysis 20xy Wholesale Dry Cleaning Equipment Industry Quartiles 20xz igher Median Lower 2.4x 1.5x 1.2x 20xx Oxz Current 1.3x 1.5x 1.8x Quick 0.8x 1.Ox 1.2x 1.2x 0.8x 0.5x 3.3x 2.7x 1.9x 0.9x 2.5x 5. 1x 4.3x 4.7x 4.6x 5.5x 2.1x 1.0x Tangible leverage Interest coverage Pretax profit margin Return on assets 2.2x 2.8x 4.3x n/a 2. 1x n/a 8.2x 10.0x 14.8x 10.7x 3.2x (0.3x) Dry Supply's 20xz current ratio is in the second quartile and above the median for the industry. Firms in the industry with a current ratio above 2.4x are in the highest or first quartile. Firms with a current ratio between 2.4x and 1.5x are in the second quartile, with 1.5x also being the median. Firms with a current ratio between 1.5x and 1.2.x are below the median and in the third quartile. Finally, firms with a current ratio below 1.2x are in the lowest or fourth quartile. The three numbers shown in the chart on the next page are the breakpoints between the quartiles. Interpreting Industry Data Using the Current Ratio From Dry Supply Comparative Analysis Breakpoint Second Quartile Breakpoint First or Highest Quartile Third Quartile Breakpoint Fourth or Lowest Quartile 2.4x 1.5x 1.2x The current ratio of 1.8x suggests that, in liquidation, Dry Supply's current assets, even after discounts of almost 45 percent, would be sufficient to current liabilities. Moreover, its 20xz quick ratio is in the top quartile for its industry. An experienced business banker would recognize that Dry Supply's liquidity compares favorably to the industry. However, because the primary purpose of a ratio is to reflect trends, it is dif- ficult to be conclusive about any single ratio in isolation. This is why a business banker needs to understand the business and its industry. Dry Supply's tangible leverage ratio of 1.9x at 12/31/20xz indicates that creditors continue to have more risk than its owners. While this ratio has improved over the three years, it is still fairly high and may limit the company's ability to borrow addi- tional funds. At 12/31/20xz, this ratio is better than (lower than) the median, since it is below 2.5x, which means that, in general, Dry Supply has a lower (more favorable) tangible leverage ratio than most of its competitors. The coverage ratio available for the industry is interest coverage, which shows Dry Supply to be higher than the median for the industry. This is the result of having a lower leverage position than its peers, which likely includes having fewer borrowed funds to generate interest expense, together with favorable levels of profits as compared to the industry. Dry Supply's pretax profit margin for 20xz is well above the median for the in- dustry, with full quartiles not available from the industry data. A business banker should look further at the common-size income statement data for the industry to see which components cause the favorable position relative to the industry. Dry Supply could have a higher gross profit margin, lower operating expense levels, or a combination of both. The relatively high levels of profits contribute to Dry Supply being in the highest or first quartile for the return on assets (ROA) ratio for 20xz. This is because Dry Supply's ROA of 14.8 percent exceeds the 10.7 percent breakpoint between the first and second quartile. It is possible that Dry Supply uses its assets more efficiently than others in the industry to produce profits, but perhaps Dry Supply does not have as much new equipment as its competitors. If industry data for the sales to assets ratio is available, as well as the other efficiency ratios, a business banker can make better conclusions about this ratio. Instructions Review the Risk Rating Grid for Qualitative Factors and Schippel's financial review findings for Dry Supply in Appendix A and Appendix B in this chapter. Then answer these questions. 1. What are some initial risk rating conclusions you can make for the following: Industry risk? Market risk? Management risk










