Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Applied Overhead and Unit Overhead Cost: Plantwide Rates Seco, Inc., produces two types of clothes dryers: deluxe and regular. Seco uses a plantwide rate

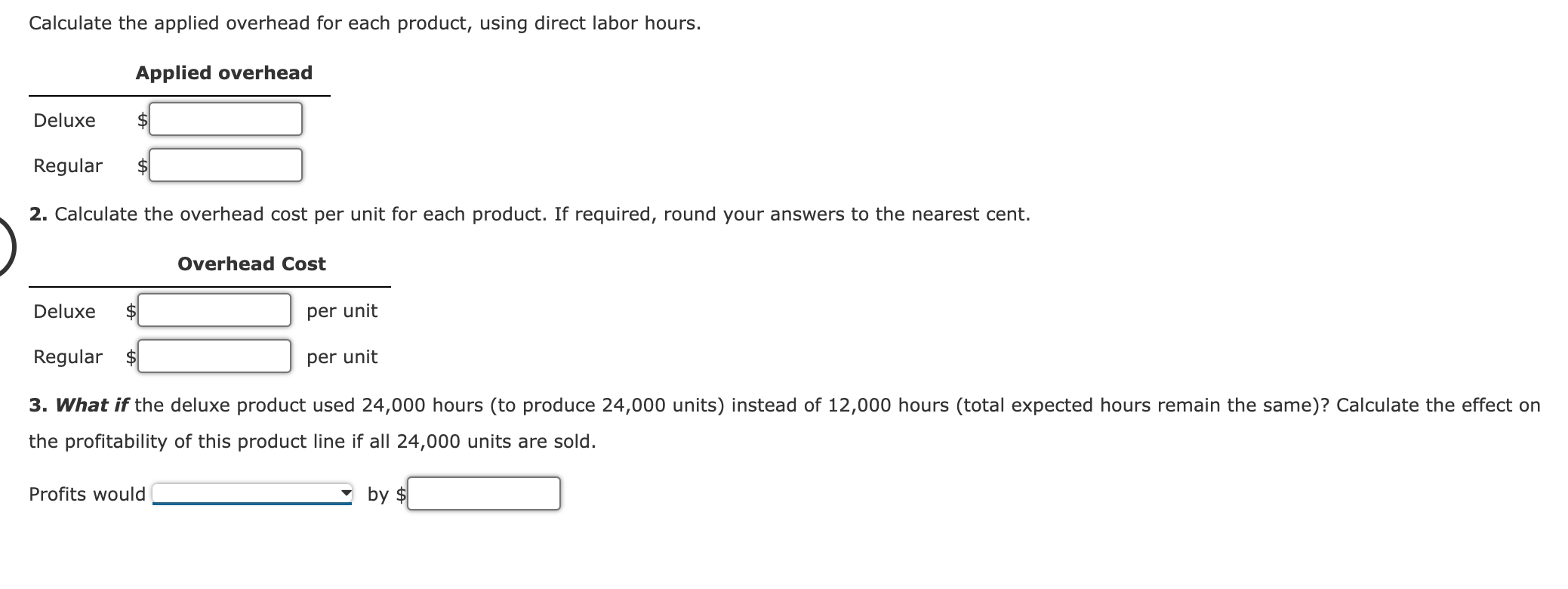


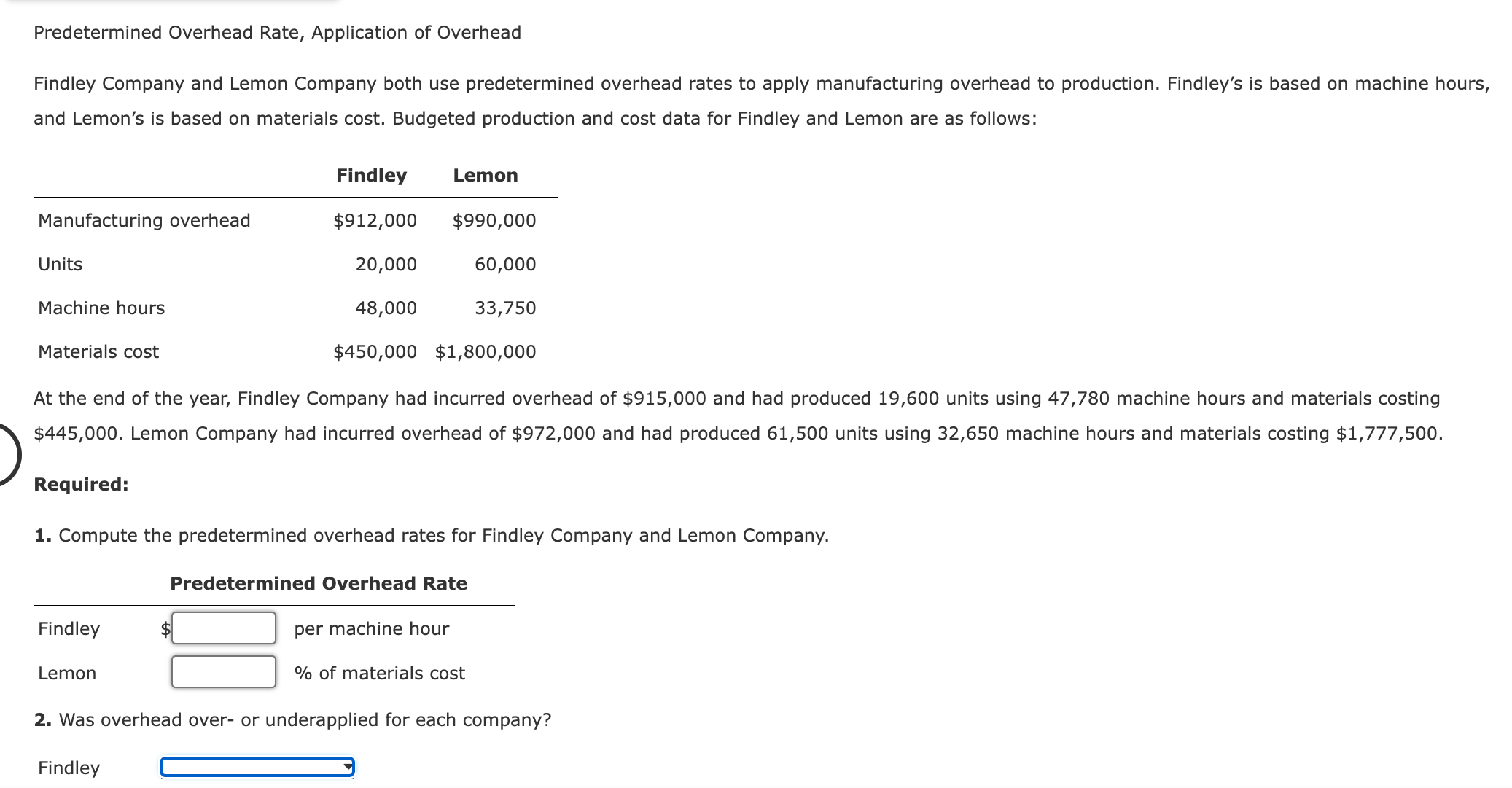

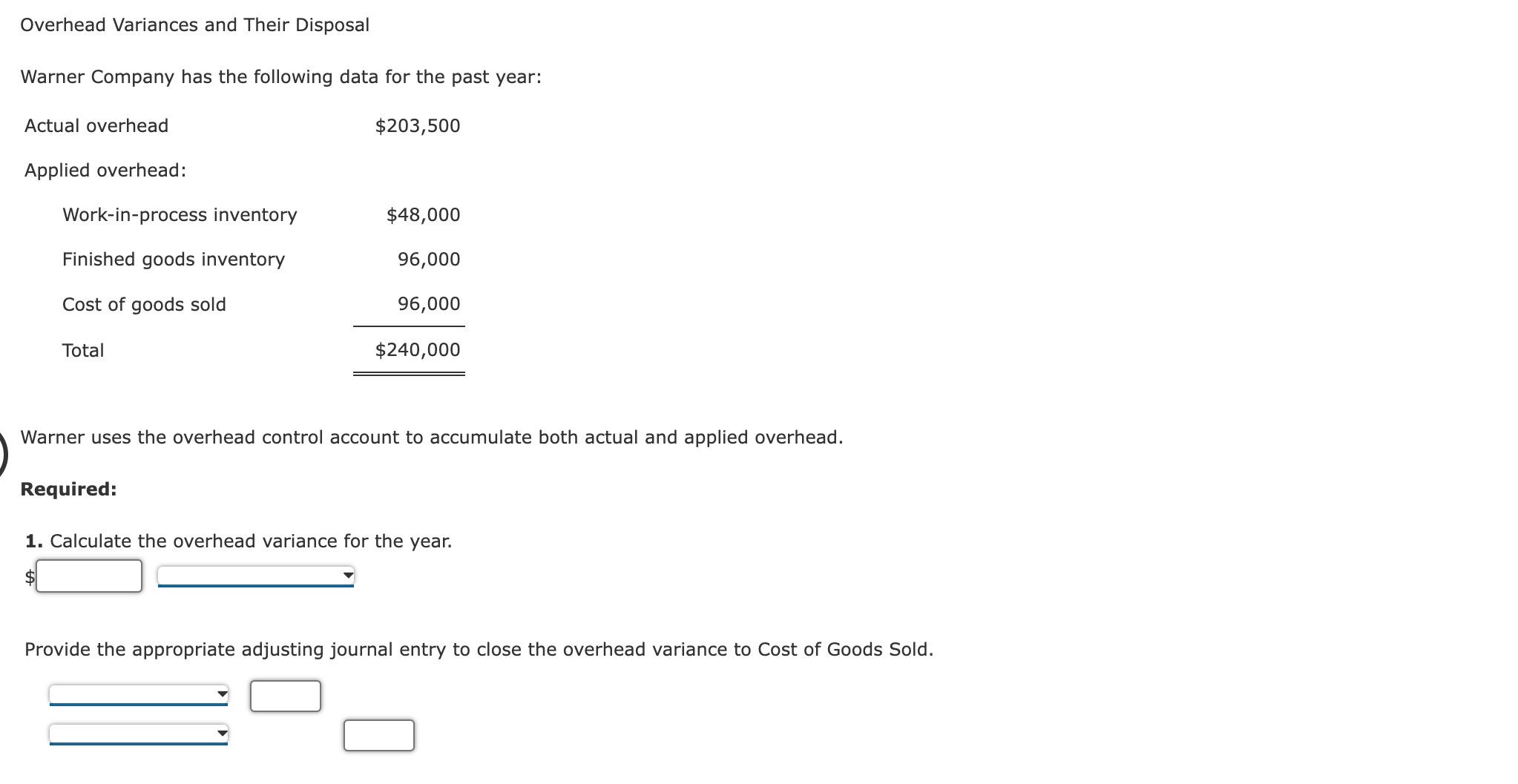
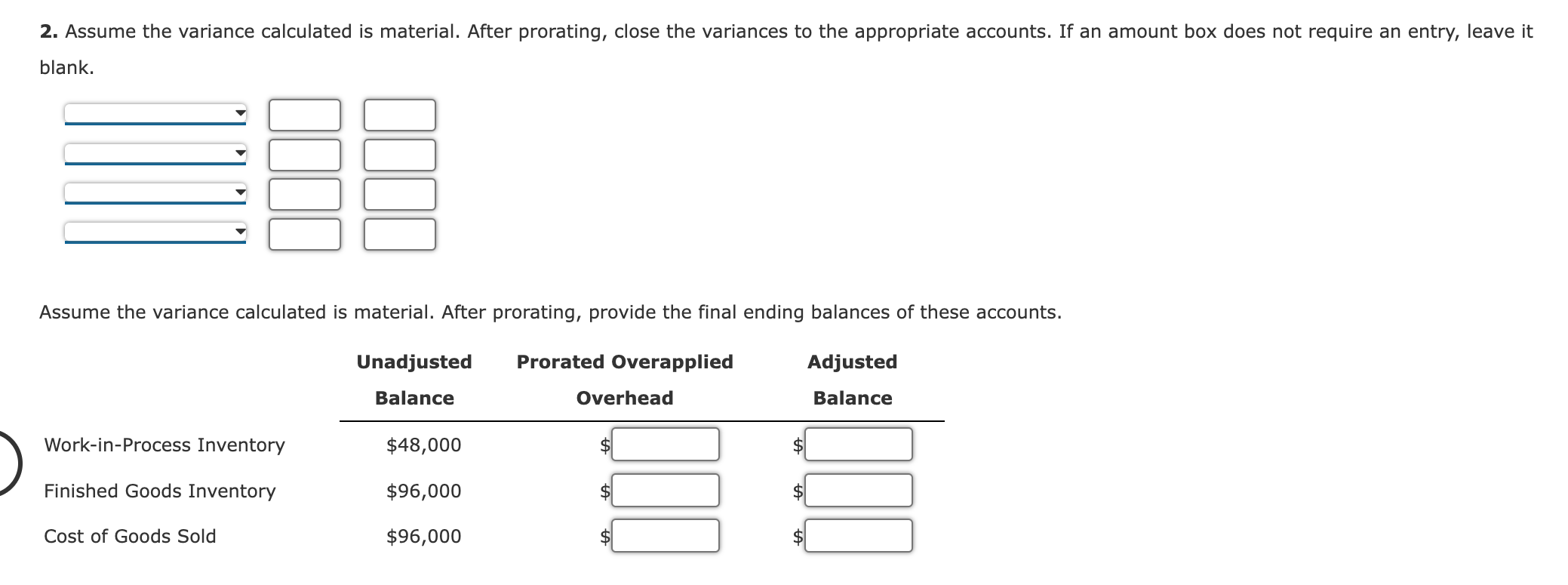


Applied Overhead and Unit Overhead Cost: Plantwide Rates Seco, Inc., produces two types of clothes dryers: deluxe and regular. Seco uses a plantwide rate based on direct labor hours to assign its overhead costs. The company has the following estimated and actual data for the coming year: Estimated overhead $2,162,000 Expected activity 47,000 Actual activity (direct labor hours): Deluxe dryer 12,000 Regular dryer 35,000 Units produced: Deluxe dryer 24,000 Regular dryer 175,000 Required: 1. Calculate the predetermined plantwide overhead rate, using direct labor hours. per hour Calculate the applied overhead for each product, using direct labor hours. Applied overhead Deluxe $ Regular $ 2. Calculate the overhead cost per unit for each product. If required, round your answers to the nearest cent. Deluxe Regular $ Overhead Cost per unit per unit 3. What if the deluxe product used 24,000 hours (to produce 24,000 units) instead of 12,000 hours (total expected hours remain the same)? Calculate the effect on the profitability of this product line if all 24,000 units are sold. Profits would by $ Predetermined Overhead Rate, Applied Overhead, Unit Cost Ripley, Inc., costs products using a normal costing system. The following data are available for last year: Budgeted: Overhead Machine hours Direct labor hours $309,400 81,000 9,100 Actual: Overhead $308,900 Machine hours 78,900 Direct labor hours 8,760 Prime cost $822,160 Number of units 140,000 Overhead is applied on the basis of direct labor hours. Required: 1. What was the predetermined overhead rate? $ per direct labor hour 2. What was the applied overhead for last year? $ 3. Was overhead over- or underapplied, and by how much? = 4. What was the total cost per unit produced? (Carry your answer to four significant digits.) $ per unit Predetermined Overhead Rate, Application of Overhead Findley Company and Lemon Company both use predetermined overhead rates to apply manufacturing overhead to production. Findley's is based on machine hours, and Lemon's is based on materials cost. Budgeted production and cost data for Findley and Lemon are as follows: Findley Lemon Manufacturing overhead $912,000 $990,000 20,000 60,000 33,750 Units Machine hours Materials cost 48,000 $450,000 $1,800,000 At the end of the year, Findley Company had incurred overhead of $915,000 and had produced 19,600 units using 47,780 machine hours and materials costing $445,000. Lemon Company had incurred overhead of $972,000 and had produced 61,500 units using 32,650 machine hours and materials costing $1,777,500. Required: 1. Compute the predetermined overhead rates for Findley Company and Lemon Company. Predetermined Overhead Rate Findley $ per machine hour Lemon % of materials cost 2. Was overhead over- or underapplied for each company? Findley Lemon By how much? Findley: $ Lemon: $ Overhead Variances and Their Disposal Warner Company has the following data for the past year: Actual overhead $203,500 Applied overhead: Work-in-process inventory $48,000 Finished goods inventory 96,000 Cost of goods sold 96,000 Total $240,000 Warner uses the overhead control account to accumulate both actual and applied overhead. Required: 1. Calculate the overhead variance for the year. Provide the appropriate adjusting journal entry to close the overhead variance to Cost of Goods Sold. 2. Assume the variance calculated is material. After prorating, close the variances to the appropriate accounts. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. Assume the variance calculated is material. After prorating, provide the final ending balances of these accounts. Unadjusted Balance Work-in-Process Inventory $48,000 Finished Goods Inventory $96,000 Cost of Goods Sold $96,000 Prorated Overapplied Overhead Adjusted Balance 3. What if the variance is of the opposite sign calculated in Requirement 1? Provide the appropriate adjusting journal entries for Requirements 1 and 2. For a compound transaction, if an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. Variance immaterial Variance material Predetermined Overhead Rate, Overhead Variances, Journal Entries Craig Company uses a predetermined overhead rate to assign overhead to jobs. Because Craig's production is machine intensive, overhead is applied on the basis of machine hours. The expected overhead for the year was $4,368,000, and the practical level of activity is 364,000 machine hours. During the year, Craig used 370,000 machine hours and incurred actual overhead costs of $4,360,000. Craig also had the following balances of applied overhead in its accounts: Work-in-process inventory Finished goods inventory Cost of goods sold Required: $ 554,680 585,810 1,689,510 1. Compute a predetermined overhead rate for Craig. Round your answer to the nearest cent. per machine hour 2. Compute the overhead variance, and label it as under- or overapplied. 3. Assuming the overhead variance is immaterial, prepare the journal entry to dispose of the variance at the end of the year. 4. Assuming the overhead variance is material, prepare the journal entry that appropriately disposes of the overhead variance at the end of the year. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


