Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Apply the EOQ model to the following quantity discount situation in which D = 450 units per year, Co = $42, and the annual
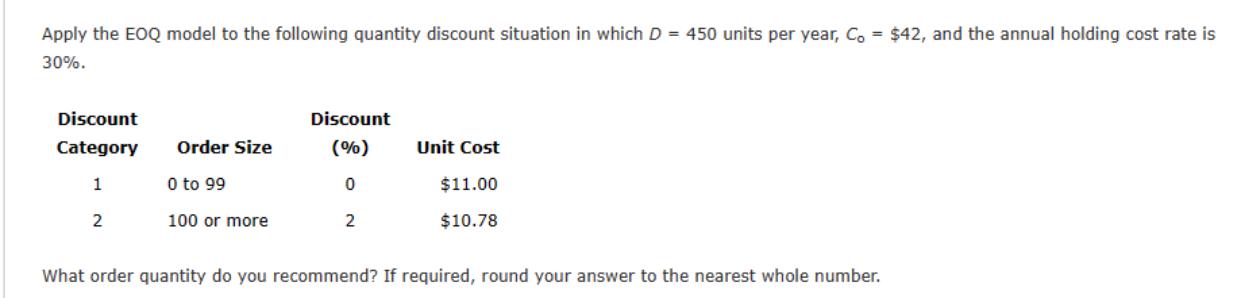

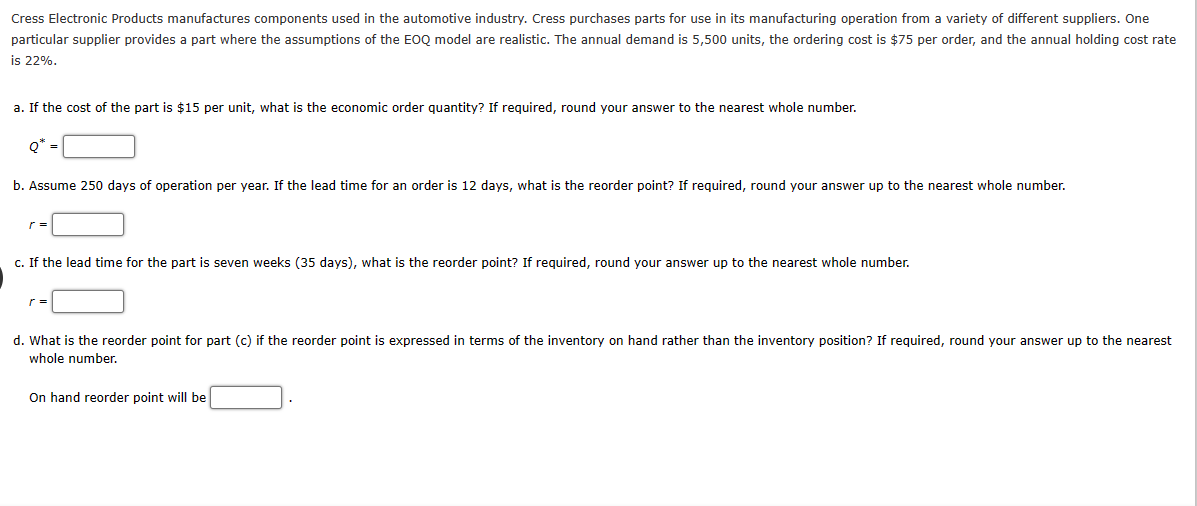

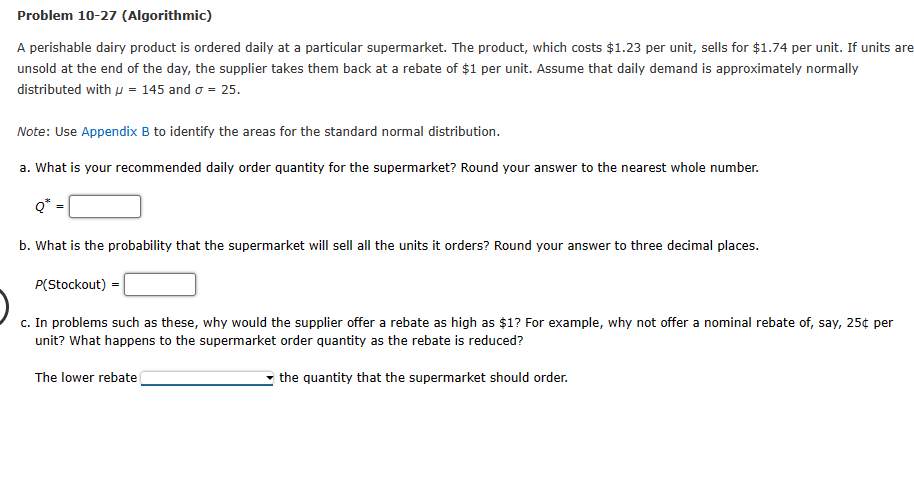
Apply the EOQ model to the following quantity discount situation in which D = 450 units per year, Co = $42, and the annual holding cost rate is 30%. Discount Discount Category Order Size (%) Unit Cost 1 0 to 99 0 2 100 or more 2 $11.00 $10.78 What order quantity do you recommend? If required, round your answer to the nearest whole number. Problem 10-05 (Algorithmic) The Metropolitan Bus Company (MBC) purchases diesel fuel from American Petroleum Supply. In addition to the fuel cost, American Petroleum Supply charges MBC $150 per order to cover the expenses of delivering and transferring the fuel to MBC's storage tanks. The lead time for a new shipment from American Petroleum is 10 days; the cost of holding a gallon of fuel in the storage tanks is $0.05 per month, or $0.6 per year; and annual fuel usage is 50,000 gallons. MBC buses operate 250 days a year. a. What is the optimal order quantity for MBC? b. How frequently should MBC order to replenish the gasoline supply? orders per year c. The MBC storage tanks have a capacity of 15,000 gallons. Should MBC consider expending the capacity of its storage tanks? Metropolitan Bus Company ( d. What is the reorder point? the capacity of its storage tanks. r = gallons Cress Electronic Products manufactures components used in the automotive industry. Cress purchases parts for use in its manufacturing operation from a variety of different suppliers. One particular supplier provides a part where the assumptions of the EOQ model are realistic. The annual demand is 5,500 units, the ordering cost is $75 per order, and the annual holding cost rate is 22%. a. If the cost of the part is $15 per unit, what is the economic order quantity? If required, round your answer to the nearest whole number. Q* = b. Assume 250 days of operation per year. If the lead time for an order is 12 days, what is the reorder point? If required, round your answer up to the nearest whole number. c. If the lead time for the part is seven weeks (35 days), what is the reorder point? If required, round your answer up to the nearest whole number. r = d. What is the reorder point for part (c) if the reorder point is expressed in terms of the inventory on hand rather than the inventory position? If required, round your answer up to the nearest whole number. On hand reorder point will be The Gilbert Air-Conditioning Company is considering the purchase of a special shipment of portable air conditioners manufactured in Japan. Each unit will cost Gilbert $75, and it will be sold for $130. Gilbert does not want to carry surplus air conditioners over until the following year. Thus, all surplus air conditioners will be sold to a wholesaler for $40 per unit. Assume that the air conditioner demand follows a normal probability distribution with = 21 and = 9. Note: Use Appendix B to identify the areas for the standard normal distribution. Round "cumulative standard normal probability" to two decimal places. a. What is the recommended order quantity? Round your answer to the nearest whole number. Q* b. What is the probability that Gilbert will sell all units it orders? Round your answer to two decimal places. P(Sell All) = Problem 10-27 (Algorithmic) A perishable dairy product is ordered daily at a particular supermarket. The product, which costs $1.23 per unit, sells for $1.74 per unit. If units are unsold at the end of the day, the supplier takes them back at a rebate of $1 per unit. Assume that daily demand is approximately normally distributed with = 145 and = 25. Note: Use Appendix B to identify the areas for the standard normal distribution. a. What is your recommended daily order quantity for the supermarket? Round your answer to the nearest whole number. Q* = b. What is the probability that the supermarket will sell all the units it orders? Round your answer to three decimal places. P(Stockout) c. In problems such as these, why would the supplier offer a rebate as high as $1? For example, why not offer a nominal rebate of, say, 25 per unit? What happens to the supermarket order quantity as the rebate is reduced? The lower rebate the quantity that the supermarket should order.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


