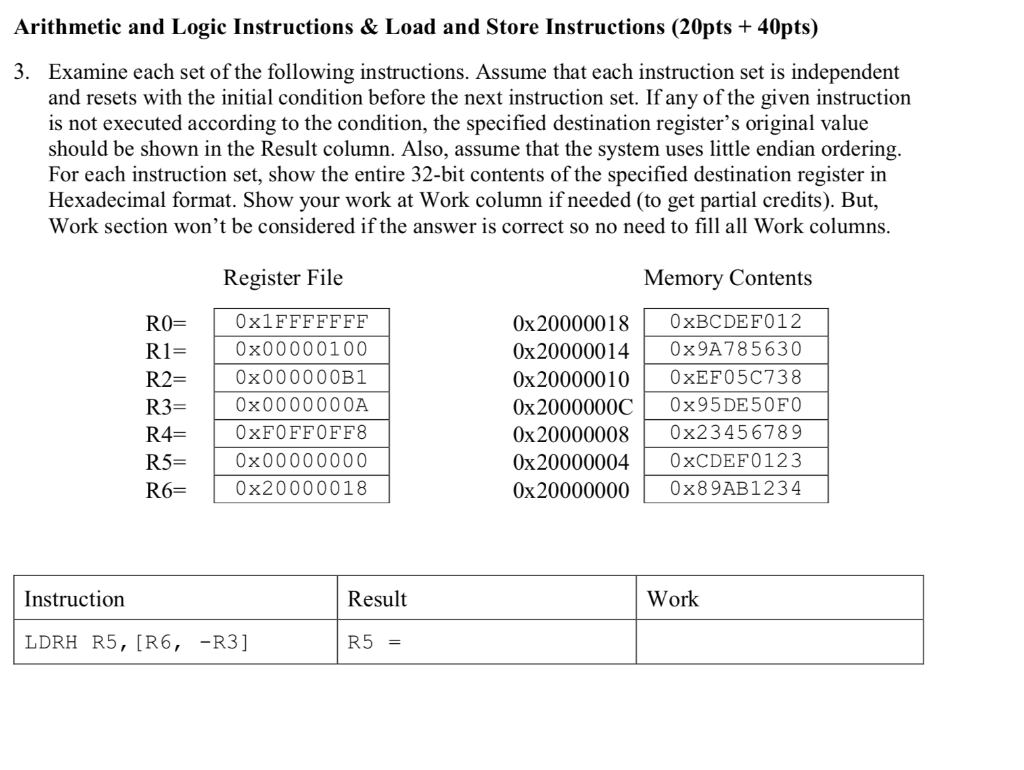


Arithmetic and Logic Instructions & Load and Store Instructions (20pts + 40pts) 3. Examine each set of the following instructions. Assume that each instruction set is independent and resets with the initial condition before the next instruction set. If any of the given instruction is not executed according to the condition, the specified destination register's original value should be shown in the Result column. Also, assume that the system uses little endian ordering For each instruction set, show the entire 32-bit contents of the specified destination register in Hexadecimal format. Show your work at Work column if needed (to get partial credits). But, Work section won't be considered if the answer is correct so no need to fill all Work columns Register File Memory Contents R0 0xlFFFFFFF RI R20x000000B1 R3 0x0000000A R4-1 OxFOFFOFF8 R5 R60x20000018 0x20000018 0xBCDEF012 0x200000140x9A785630 0x20000010 0xEF05C738 0x2000000C 0x95DE50FO 0x20000008 0x23456789 0x200000040xCDEF0123 0x20000000 x89AB1234 0x00000100 0x00000000 Instruction Result Work LDRH R5, [R6, -R3] R5- LDRSBR5, [R0 , #0x3] LDR R5, [R6], #-8 MOV R5, R4, LSL #OxC ADD R5, R4, R6, ASR #8 | R5- BFC R0, #12, #12 EOR R5, R4, RO MLS R5, R3, R3, R1 R5 R5 = 4. Implement a Vector-Vector Multiplication in ARM assembly. The Vector-Vector Multiplication normally is implemented in a for loop that explores all elements in the input vectors but as we will learn the instructions that are required to implement loop iterations later, we will implement a small Vector-Vector Multiplication without a loop iteration as can be seen in the following pseudo code int Inputl [5]-15, 4, 3, 2,1); int Input2 [5]-, 2, 3, 4, 5); int Output0; C Input1 [0] x Input2 [0] ; C C C +-input 1 [2] +-Input1 [3] +-Input1 [4] x x x Input2 [2] ; Input2 [3] ; Input2 [4];
Follow the instructions below Create a new projcct and add a new assembly filc "vector mul.s" to the project. Define two 5-clement integer arrays Input1 and Input2 and an integer variablc Output in DATA area. Usc vecData as DATA area's name. Initialize the variables with the values shown in the above code Define a function main in CODE area. Use vecCode as CODE area's name In main function, implement the lines 4 to 8 in the above code Use R1 for storing the values of Inputl array, R2 for the values of Input2 array, R3 for Output a. b. Use any register between R4 to R7 for the addresses of Inputl, Input2, or Output variables or for any other purposes if needed Store the value of R3 to the variable Output after finishing the execution of line 8 c. Arithmetic and Logic Instructions & Load and Store Instructions (20pts + 40pts) 3. Examine each set of the following instructions. Assume that each instruction set is independent and resets with the initial condition before the next instruction set. If any of the given instruction is not executed according to the condition, the specified destination register's original value should be shown in the Result column. Also, assume that the system uses little endian ordering For each instruction set, show the entire 32-bit contents of the specified destination register in Hexadecimal format. Show your work at Work column if needed (to get partial credits). But, Work section won't be considered if the answer is correct so no need to fill all Work columns Register File Memory Contents R0 0xlFFFFFFF RI R20x000000B1 R3 0x0000000A R4-1 OxFOFFOFF8 R5 R60x20000018 0x20000018 0xBCDEF012 0x200000140x9A785630 0x20000010 0xEF05C738 0x2000000C 0x95DE50FO 0x20000008 0x23456789 0x200000040xCDEF0123 0x20000000 x89AB1234 0x00000100 0x00000000 Instruction Result Work LDRH R5, [R6, -R3] R5- LDRSBR5, [R0 , #0x3] LDR R5, [R6], #-8 MOV R5, R4, LSL #OxC ADD R5, R4, R6, ASR #8 | R5- BFC R0, #12, #12 EOR R5, R4, RO MLS R5, R3, R3, R1 R5 R5 = 4. Implement a Vector-Vector Multiplication in ARM assembly. The Vector-Vector Multiplication normally is implemented in a for loop that explores all elements in the input vectors but as we will learn the instructions that are required to implement loop iterations later, we will implement a small Vector-Vector Multiplication without a loop iteration as can be seen in the following pseudo code int Inputl [5]-15, 4, 3, 2,1); int Input2 [5]-, 2, 3, 4, 5); int Output0; C Input1 [0] x Input2 [0] ; C C C +-input 1 [2] +-Input1 [3] +-Input1 [4] x x x Input2 [2] ; Input2 [3] ; Input2 [4]; Follow the instructions below Create a new projcct and add a new assembly filc "vector mul.s" to the project. Define two 5-clement integer arrays Input1 and Input2 and an integer variablc Output in DATA area. Usc vecData as DATA area's name. Initialize the variables with the values shown in the above code Define a function main in CODE area. Use vecCode as CODE area's name In main function, implement the lines 4 to 8 in the above code Use R1 for storing the values of Inputl array, R2 for the values of Input2 array, R3 for Output a. b. Use any register between R4 to R7 for the addresses of Inputl, Input2, or Output variables or for any other purposes if needed Store the value of R3 to the variable Output after finishing the execution of line 8 c









