Question
*Armed with this information, Mr. Tar constructed a spreadsheet to calculate the NPV of the duffel canvas project, assuming that Sheetbends bid would be accepted
*Armed with this information, Mr. Tar constructed a spreadsheet to calculate the NPV of the duffel canvas project, assuming that Sheetbends bid would be accepted by the navy.
*He had just finished debugging the spreadsheet when another confidential envelope arrived from Sheetbends CEO. It contained a firm offer from a Maine real estate developer to purchase Sheetbends Pleasantboro land and plant for $1.5 million in cash.
*Should Mr. Tar recommend submitting the bid to the navy at the proposed price of $30 per yard? The discount rate for this project is 12%.
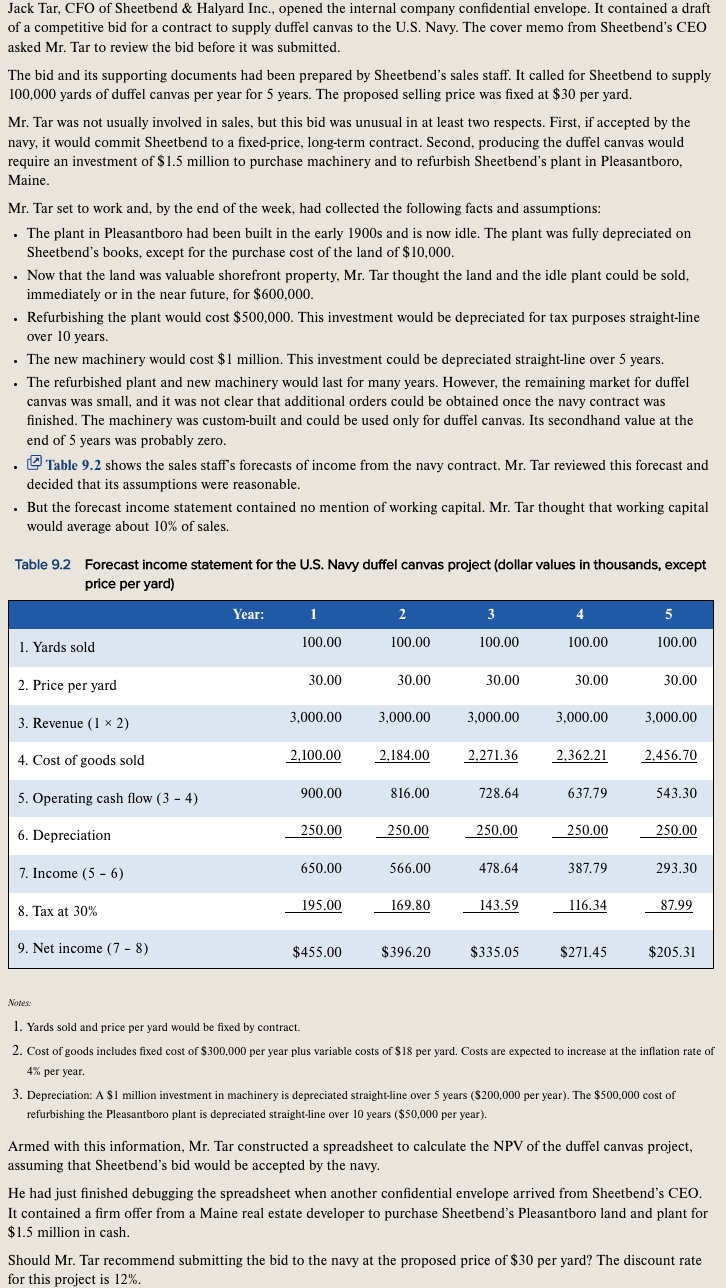
Jack Tar, CFO of Sheetbend & Halyard Inc., opened the internal company confidential envelope. It contained a draft of a competitive bid for a contract to supply duffel canvas to the U.S. Navy. The cover memo from Sheetbend's CEO asked Mr. Tar to review the bid before it was submitted. The bid and its supporting documents had been prepared by Sheetbend's sales staff. It called for Sheetbend to supply 100,000 yards of duffel canvas per year for 5 years. The proposed selling price was fixed at $30 per yard. Mr. Tar was not usually involved in sales, but this bid was unusual in at least two respects. First, if accepted by the navy, it would commit Sheetbend to a fixed-price, long-term contract. Second, producing the duffel canvas would require an investment of $1.5 million to purchase machinery and to refurbish Sheetbend's plant in Pleasantboro, Maine. Mr. Tar set to work and, by the end of the week, had collected the following facts and assumptions: . The plant in Pleasantboro had been built in the early 1900s and is now idle. The plant was fully depreciated on Sheetbend's books, except for the purchase cost of the land of $10,000. . Now that the land was valuable shorefront property, Mr. Tar thought the land and the idle plant could be sold, immediately or in the near future, for $600,000. Refurbishing the plant would cost $500,000. This investment would be depreciated for tax purposes straight-line over 10 years. The new machinery would cost $ 1 million. This investment could be depreciated straight-line over 5 years. The refurbished plant and new machinery would last for many years. However, the remaining market for duffel canvas was small, and it was not clear that additional orders could be obtained once the navy contract was finished. The machinery was custom-built and could be used only for duffel canvas. Its secondhand value at the end of 5 years was probably zero. . Table 9.2 shows the sales staff's forecasts of income from the navy contract. Mr. Tar reviewed this forecast and decided that its assumptions were reasonable. . But the forecast income statement contained no mention of working capital. Mr. Tar thought that working capital would average about 10% of sales. Table 9.2 Forecast income statement for the U.S. Navy duffel canvas project (dollar values in thousands, except price per yard) Year: 1 2 3 4 5 1. Yards sold 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 2. Price per yard 30.00 30.00 30.00 30.00 30.00 3.000.00 3. Revenue (1 x 2) 3,000.00 3,000.00 3,000.00 3,000.00 4. Cost of goods sold 2,100.00 2,184.00 2.271.36 2,362.21 2.456.70 900.00 816.00 728.64 637.79 543.30 5. Operating cash flow (3 - 4) 250.00 250.00 6. Depreciation 250.00 250.00 250.00 7. Income (5 - 6) 650.00 566.00 478.64 387.79 293.30 8. Tax at 30% 195.00 169.80 143.59 116.34 87.99 9. Net income (7-8) $455.00 $396.20 $335.05 $271.45 $205.31 Notes: 1. Yards sold and price per yard would be fixed by contract. 2. Cost of goods includes fixed cost of $300,000 per year plus variable costs of $18 per yard. Costs are expected to increase at the inflation rate of 4% per year. 3. Depreciation: A $1 million investment in machinery is depreciated straight-line over 5 years ($200,000 per year). The $500,000 cost of refurbishing the Pleasantboro plant is depreciated straight-line over 10 years ($50,000 per year). ($ Armed with this information, Mr. Tar constructed a spreadsheet to calculate the NPV of the duffel canvas project, assuming that Sheetbend's bid would be accepted by the navy. He had just finished debugging the spreadsheet when another confidential envelope arrived from Sheetbend's CEO. It contained a firm offer from a Maine real estate developer to purchase Sheetbend's Pleasantboro land and plant for $1.5 million in cash. Should Mr. Tar recommend submitting the bid to the navy at the proposed price of $30 per yard? The discount rate for this project is 12%. Jack Tar, CFO of Sheetbend & Halyard Inc., opened the internal company confidential envelope. It contained a draft of a competitive bid for a contract to supply duffel canvas to the U.S. Navy. The cover memo from Sheetbend's CEO asked Mr. Tar to review the bid before it was submitted. The bid and its supporting documents had been prepared by Sheetbend's sales staff. It called for Sheetbend to supply 100,000 yards of duffel canvas per year for 5 years. The proposed selling price was fixed at $30 per yard. Mr. Tar was not usually involved in sales, but this bid was unusual in at least two respects. First, if accepted by the navy, it would commit Sheetbend to a fixed-price, long-term contract. Second, producing the duffel canvas would require an investment of $1.5 million to purchase machinery and to refurbish Sheetbend's plant in Pleasantboro, Maine. Mr. Tar set to work and, by the end of the week, had collected the following facts and assumptions: . The plant in Pleasantboro had been built in the early 1900s and is now idle. The plant was fully depreciated on Sheetbend's books, except for the purchase cost of the land of $10,000. . Now that the land was valuable shorefront property, Mr. Tar thought the land and the idle plant could be sold, immediately or in the near future, for $600,000. Refurbishing the plant would cost $500,000. This investment would be depreciated for tax purposes straight-line over 10 years. The new machinery would cost $ 1 million. This investment could be depreciated straight-line over 5 years. The refurbished plant and new machinery would last for many years. However, the remaining market for duffel canvas was small, and it was not clear that additional orders could be obtained once the navy contract was finished. The machinery was custom-built and could be used only for duffel canvas. Its secondhand value at the end of 5 years was probably zero. . Table 9.2 shows the sales staff's forecasts of income from the navy contract. Mr. Tar reviewed this forecast and decided that its assumptions were reasonable. . But the forecast income statement contained no mention of working capital. Mr. Tar thought that working capital would average about 10% of sales. Table 9.2 Forecast income statement for the U.S. Navy duffel canvas project (dollar values in thousands, except price per yard) Year: 1 2 3 4 5 1. Yards sold 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 2. Price per yard 30.00 30.00 30.00 30.00 30.00 3.000.00 3. Revenue (1 x 2) 3,000.00 3,000.00 3,000.00 3,000.00 4. Cost of goods sold 2,100.00 2,184.00 2.271.36 2,362.21 2.456.70 900.00 816.00 728.64 637.79 543.30 5. Operating cash flow (3 - 4) 250.00 250.00 6. Depreciation 250.00 250.00 250.00 7. Income (5 - 6) 650.00 566.00 478.64 387.79 293.30 8. Tax at 30% 195.00 169.80 143.59 116.34 87.99 9. Net income (7-8) $455.00 $396.20 $335.05 $271.45 $205.31 Notes: 1. Yards sold and price per yard would be fixed by contract. 2. Cost of goods includes fixed cost of $300,000 per year plus variable costs of $18 per yard. Costs are expected to increase at the inflation rate of 4% per year. 3. Depreciation: A $1 million investment in machinery is depreciated straight-line over 5 years ($200,000 per year). The $500,000 cost of refurbishing the Pleasantboro plant is depreciated straight-line over 10 years ($50,000 per year). ($ Armed with this information, Mr. Tar constructed a spreadsheet to calculate the NPV of the duffel canvas project, assuming that Sheetbend's bid would be accepted by the navy. He had just finished debugging the spreadsheet when another confidential envelope arrived from Sheetbend's CEO. It contained a firm offer from a Maine real estate developer to purchase Sheetbend's Pleasantboro land and plant for $1.5 million in cash. Should Mr. Tar recommend submitting the bid to the navy at the proposed price of $30 per yard? The discount rate for this project is 12%Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


