Question
Array with Iterator. Java style Implement an array data structure as a class JstyArray to support the Iterable interface such that the following code works:
Array with Iterator. Java style
Implement an array data structure as a class JstyArray
JstyArraydata; data = new JstyArray (10); for (int i = 0; i The iterator provided by this class follows the behaviour of typical Java style (Jsty). If the underlying collection is modified, the iterator becomes invalid and an exception is raised.
An example of code that may generate an exception is below:
try { int sum = 0; for ( int v : data ) { if (v == null) continue; if (vThere are 4 necessary methods for the Array. get(), set(), remove() and iterator().
There are 2 necessary methods for Iterator. hasNext() and next().
Other than these, you need to create more methods for communicating between Array and the Iterator. Object references are very useful in this scenario.
Once you have an iterator going. There is the next step of handling multiple iterators for the same data structure. More than one iterator can exist, at different times. There are iterators which are
are invalid and have raised an exception, or
are invalid and have not yet raised an exception, or
are valid, they were created after modification to the data structure.
Multiple iterators are one of the harder tests
THERE ARE TWO CLASSES USED as shown below:
....................................................................................................................
JstyIterator.java:
/* * An iterator for the class JstyArray. Performs all standard tasks of an iterator. * Specifically, when calling next() on an invalid iterator, a NoSuchElementException is raised by this class. * */ import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; public class JstyIterator implements Iterator{ private JstyArray array; private int index; public JstyIterator(JstyArray array) { this.array = array; index = 0; } // YOUR CODE ANYWHERE IN THIS CLASS public boolean hasNext() { // YOUR CODE ANYWHERE IN THIS CLASS if (array.size == index) return false; else return true; } public E next() throws NoSuchElementException { // YOUR CODE ANYWHERE IN THIS CLASS if (array.list.size() != array.size) throw new NoSuchElementException("Array elements have been modified !"); else if (hasNext()) { return array.get(index++); } else { throw new NoSuchElementException("There are no elements in the array. Size = " + array.size); } } public void remove() { // we need this method for the nagging Java compiler // you may leave empty } }
..........................................................................................................................................................
JstyArray.java:
/* * An array that implements the Iterable interface. * Returns an iterator that would raise an exception if the array was modified (set or remove) * */ import java.util.LinkedList; public class JstyArray implements Iterable{ // YOUR CODE ANYWHERE IN THIS CLASS private E[] array; public static final int CAPACITY = 100; public int size; public int capacity; public LinkedList list; // there could be more instance variables! /* * initialise array with capacity. If capacity is less than 1, use CAPACITY. * */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public JstyArray(int capacity) { // YOUR CODE ANYWHERE IN THIS CLASS if (capacity { array = (E[]) new Object[CAPACITY]; this.capacity = CAPACITY; list = new LinkedList(); size = 0; } else { array = (E[]) new Object[capacity]; this.capacity = capacity; list = new LinkedList(); size = 0; } } /* * if index is outside range of array. simply return * */ public void set(int i, E val) { // YOUR CODE ANYWHERE IN THIS CLASS if (i >= capacity) return; else { array[i] = val; list.add(i, val); size++; } } /* * if index is outside range of array. return null * */ public E get(int i) { // YOUR CODE ANYWHERE IN THIS CLASS if (i >= capacity) return null; else return array[i]; } /* * if index is outside range of array. return null * */ public E remove(int i) { // YOUR CODE ANYWHERE IN THIS CLASS if (i >= capacity) return null; else { list.remove(i); E e = array[i]; array[i] = null; return e; } } public JstyIterator iterator() { // YOUR CODE ANYWHERE IN THIS CLASS return new JstyIterator(this); } }
.........................................................................................................................................................................
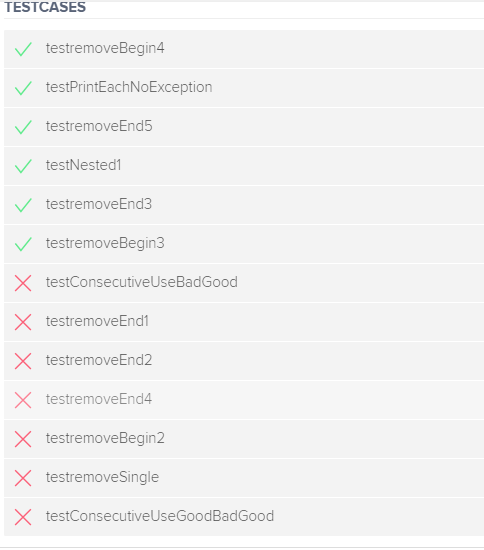
It passes some testcase but not all.
Can you fix my code for it to pass all testcases
TESTCASES testremove Begin4 V testPrintEachNoException testremoveEnd5 V testNested1 testremoveEnd3 V testremove Begin3 X testConsecutiveUseBadGood X testremoveEnd1 X testremoveEnd2 X testremoveEnd4 X testremoveBegin2 X testremove Single X testConsecutiveUseGoodBadGood
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started