Question
//ArrayStack Class public class ArrayStack implements Stack { public static final int CAPACITY = 1000; private E[ ] data; private int t = -1; public

//ArrayStack Class
public class ArrayStack
public static final int CAPACITY = 1000;
private E[ ] data;
private int t = -1;
public ArrayStack( ) { this(CAPACITY); }
public ArrayStack(int capacity) {
data = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
}
@Override
public int size() {return (t + 1); }
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {return (t == -1);}
@Override
public void push(E e ) throws IllegalStateException {
if (size() == data.length) throw new IllegalStateException("Stack is full");
data[++t] =e;
}
@Override
public E top() {
if (isEmpty()) return null;
return data[t];
}
@Override
public E pop() {
if (isEmpty()) return null;
E answer = data[t];
data[t] = null;
t--;
return answer;
}
//LinkedStack Class
public class LinkedStack
private SinglyLinkedList
public LinkedStack( ) { }
@Override
public int size( ) { return list.size(); }
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {return list.isEmpty(); }
@Override
public void push(E element) { list.addFirst(element); }
@Override
public E top( ) { return list.first(); }
@Override
public E pop( ) { return list.removeFirst();
//SinglyLinkedList
public class SinglyLinkedList
private static class Node
private E element;
private Node
public Node(E e, Node
element = e;
next = n;
}
public E getElement() { return element;}
public Node
public void setNext(Node
}
private Node
private Node
private int size = 0;
public SinglyLinkedList( ) { }
public int size( ) { return size; }
public boolean isEmpty( ) { return size == 0; }
public E first( ) {
if (isEmpty( )) return null;
return head.getElement( );
}
public E last( ) {
if (isEmpty( )) return null;
return tail.getElement( );
}
public void addFirst(E e) {
head = new Node(e, head);
if (size == 0)
tail = head;
size++;
}
public void addLast(E e) {
Node
if (isEmpty( ))
head = newest;
else
tail.setNext(newest);
tail = newest;
size++;
}
public E removeFirst( ) {
if (isEmpty( )) return null;
E answer = head.getElement( );
head = head.getNext( );
size--;
if (size == 0)
tail = null;
return answer;
}
}
//ArrayQueue
public class ArrayQueue
private static final int CAPACITY = 100;
private E[] data;
private int f = 0;
private int sz = 0;
//Constructors
public ArrayQueue() {this(CAPACITY);}
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
data = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
}
//Methods
@Override
public int size() { return sz;}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() { return (sz == 0) ;}
@Override
public void enqueue(E e) throws IllegalStateException {
if (sz == data.length) throw new IllegalStateException("Queue is full");
int avail = (f + sz) % data.length;
data[avail] = e;
sz++;
}
@Override
public E first() {
if (isEmpty()) return null;
return data[f];
}
@Override
public E dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) return null;
E answer = data[f];
data[f] = null;
f = (f + 1) % data.length;
sz--;
return answer;
}
}
//LinkedQueue
public class LinkedQueue
private SinglyLinkedList
public LinkedQueue() {}
@Override
public int size() { return list.size();}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() { return list.isEmpty();}
@Override
public void enqueue(E element) { list.addLast(element); }
@Override
public E first() { return list.first(); }
@Override
public E dequeue() { return list.removeFirst(); }
}
//ArrayList
public class ArrayList
public static final int CAPACITY = 16;
private E[] data;
private int size = 0;
public ArrayList() {
this(CAPACITY); //Constructs list with default capacity
}
public ArrayList(int capacity) { //Constructs list with given capactity
data = (E[]) new Object[capacity]; //Safe Cast; compiler may give warning
}
@Override
public int size() {
return size;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public E get(int i) {
checkIndex(i, size);
return data[i];
}
@Override
public E set(int i, E e) {
checkIndex(i, size);
E temp = data[i];
data[i] = e;
return temp;
}
@Override
public void add(int i, E e) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException, IllegalStateException{
checkIndex(i, size + 1);
if (size == data.length)
resize(2 * data.length);
for (int k = size = 1; k >= i; k--)
data[k+1] = data[k];
data[i] = e;
size++;
}
@Override
public E remove(int i) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {
checkIndex(i, size);
E temp = data[i];
for (int k = i; k
data[k] = data[k+1];
data[size-1] = null;
size--;
return temp;
}
protected void checkIndex(int i, int n) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {
if (i = n)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Illegal Index: " + i);
}
protected void resize(int capacity) {
E[ ] temp = (E[ ]) new Object[capacity];
for (int k=0; k
temp[k] = data[k];
data = temp;
}
}
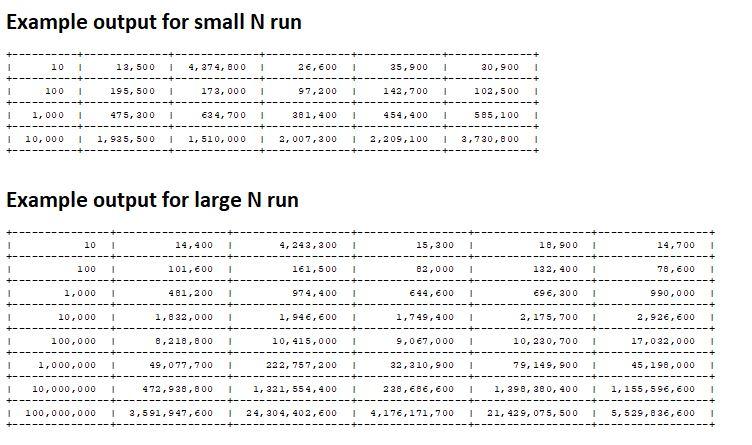
Write a client class with a main method that tests the data structures as follows: For the ArrayStack, LinkedStack, ArrayQueue, LinkedQueue, and ArrayList: Perform a timing test for each of these data structures. Each timing test should measure in nanoseconds how long it takes to add and remove N Integers from the structure. N should vary from 10 to 1,000,000,000 increasing N by a factor of 10 for each test. Depending on your system you may run out of memory before you reach the maximum value of N. If you run out of memory, and your program crashes just decrease the maximum value of N by a factor of 10 and try a new run. You should see that your program throws an OutOfMemoryError Generally, you should not try to catch an OutOfMemoryError because your memory space might be corrupted and there is no guarantee that you can recover from the error. Test results must be displayed in a nicely formatted ASCII table similar to the examples provided. In the ASCII table: Values in each cell are padded by 2 blank spaces Each column is just wide enough to display the widest entry in that column including the cell padding. Your program must dynamically adjust the width of each column based on the values that it needs to print. Numeric values must be printed using the comma thousand separator, i.e. you must print a large number like 12,345 and not 12345 It is strongly suggested that you create a method that generates and prints the ASCII table. You could pass this method a 2-dimensional array of values that are to be printed. Future assignments may require that you print out results in a similar ASCII table. Example output for small N run 10 1 13,500 1 4,374, 800 1 26,600 1 35,900 1 30,900 1 100 1 195,500 1 173,000 1 97,200 1 142,700 1 102,500 1 1,000 1 475, 300 1 634, 700 1 301,400 1 454,400 1 585,100 1 1 10,000 1 1,935, 500 1,510,000 1 2,007,200 2,209,100 1 3,730,800 ! Example output for large N run 10 14,400 1 4, 243,300 15,200 18,900 1 14,700 100 101,600 1 161,500 82,000 132, 400 1 78,600 1,000 481,200 1 974,400 644,600 696, 200 1 990,000 1 10,000 1,8 32,000 1 1,946, 600 1,749,400 2, 175, 700 1 2,926,600 1 100,000 8,218,800 1 10,415,000 9,067,000 10, 230, 700 1 17,0 32,000 1 1,000,000 49,077,700 1 222, 757,200 32,310,900 79, 149, 900 1 45,198,000 1 10,000,000 472,938,800 1, 321,554,400 238,686,600 1, 398, 380, 400 1 1,155, 596, 600 1 100,000,000 1 3, 591,947, 600 1 24, 304, 402,600 4,176, 171,700 1 21,429,075,500 1 5,529,8 36, 600Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


