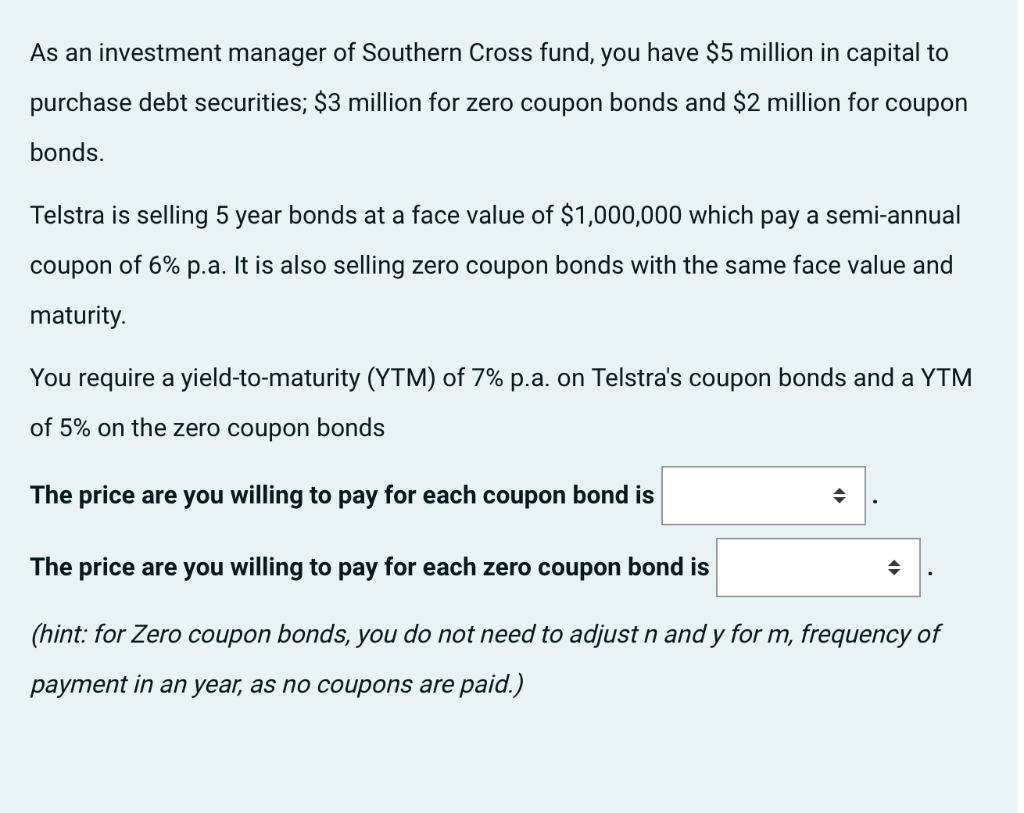

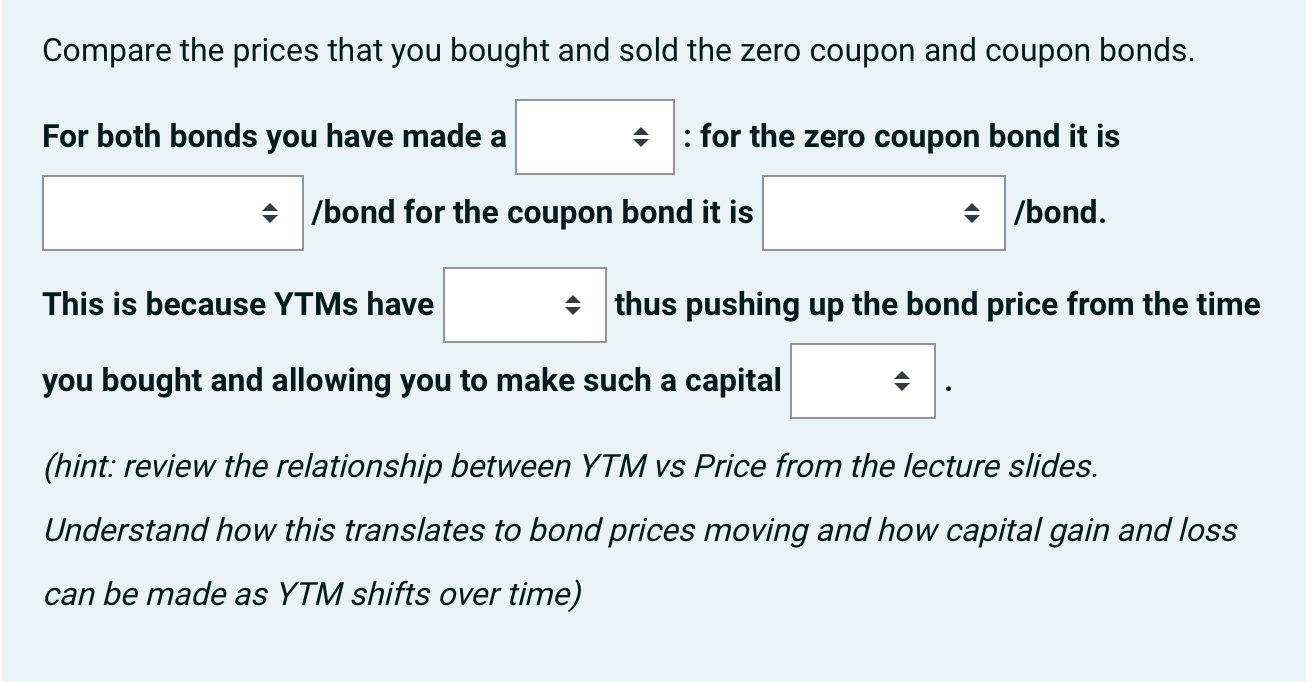



As an investment manager of Southern Cross fund, you have $5 million in capital to purchase debt securities; $3 million for zero coupon bonds and $2 million for coupon bonds. Telstra is selling 5 year bonds at a face value of $1,000,000 which pay a semi-annual coupon of 6% p.a. It is also selling zero coupon bonds with the same face value and maturity. You require a yield-to-maturity (YTM) of 7% p.a. on Telstra's coupon bonds and a YTM of 5% on the zero coupon bonds The price are you willing to pay for each coupon bond is The price are you willing to pay for each zero coupon bond is (hint: for Zero coupon bonds, you do not need to adjust n and y for m, frequency of payment in an year, as no coupons are paid.) Given the capital that you have available to buy each type of bond and the prices of each bond just calculated, you are able to buy coupon bonds and zero coupon bonds. (hint: You can only buy bonds in whole units, so the question is whether you round up or round down. The principal to apply is the same as when you go cash shopping. You cannot buy more than the money that you have in your pocket. So, when buying bonds, do you round up or round down? You will also need the correct bond prices to get the correct answers here.) 2 years have passed and you decide to sell the bonds on the secondary market. Another investment fund, Eastern Cross Securities, wishes to buy your bonds and they have a YTM of 5% p.a. for the coupon bond and 3% for the zero coupon bond. Eastern Cross will pay for your coupon bonds and for zero coupon bonds. (hint: 2 years have passed on a 5 year maturity for the bonds, how many years remain and how does this affect n in the valuation?) Compare the prices that you bought and sold the zero coupon and coupon bonds. For both bonds you have made a : for the zero coupon bond it is /bond for the coupon bond it is /bond. This is because YTMs have thus pushing up the bond price from the time you bought and allowing you to make such a capital (hint: review the relationship between YTM vs Price from the lecture slides. Understand how this translates to bond prices moving and how capital gain and loss can be made as YTM shifts over time) Monash Co. pays dividends annually and has a current dividend of $7 per share. It is expected to grow at a rate of 25% per annum for the next 5 years, after which dividends stop growing. Dividends are still paid into perpetuity after the growth period. The company has a required rate of return of 12%, calculate the current implied price of the share. (hint: construct the timeline of cashflows carefully and see staff in consultation if unclear. Do this question with classmates, compare your timelines and follow the guideline solutions of similar questions in Tutorial 3) a. $150.26 b. $105.26 c. $125.06 d. $120.62 e. $160.25 Monash Co. pays dividends annualy and has a current dividend of $7 per share. It is expected to grow at a rate of 25% per annum for the next 2 years, 20% for the following 3 years, after which dividends stop growing. Dividends are still paid into perpetuity after the growth period. The company has a required rate of return of 12%, calculate the current implied price of the share. (hint: construct the timeline of cashflows carefully and see staff in consultation if unclear. Do this question with classmates, compare your timelines and follow the guideline solutions of similar questions in Tutorial 3) a. $189.53 b. $135.98 c. $153.98 d. $123.89 e. $198.35 Monash Co. pays dividends annualy and has a current dividend of $7 per share. Dividends start growing at the third year. The third year dividend grows by 20% from the second and this growth lasts till the fifth year after which dividends stop growing. Dividends are still paid into perpetuity after the growth period. The company has a required rate of return of 12%, calculate the current implied price of the share. (hint: construct the timeline of cashflows carefully and see staff in consultation if unclear. Do this question with classmates, compare your timelines and follow the guideline solutions of similar questions in Tutorial 3) a. $99.28 b. $66.28 c. $77.28 d. $100.28 e. $88.28












