Question
As you can see the check_sum function, receives an array of integers as its input and returns an integer value. The return value is the
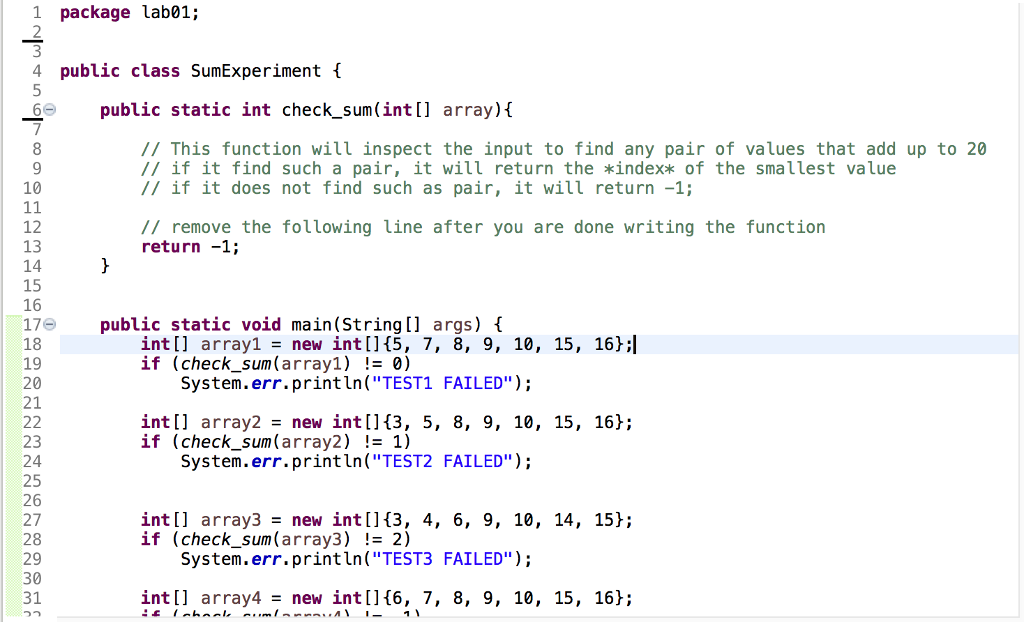
As you can see the check_sum function, receives an array of integers as its input and returns an integer value. The return value is the index for the smaller value in the pair. If such a pair does not exist in the array, the function is supposed to return -1. For instance, if we give the following array to check_sum function: {5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15, 16}, check_sum should return 0. Why?
IMPORTANT NOTE: DO NOT CHANGE THE SIGNATURE OF THE FUNCTION OR THE JAVA FILE. IF YOU CHANGE THE SIGNATURE OF THE FUNCTION (ITS NAME, INPUT OR OUTPUT OR THE FILE NAME) YOU WILL LOSE POINTS (rational: we use automated scripts for grading so if you change things, the grading will become tedious for the TA who is a student just like yourself!)
Now start thinking about how would you accomplish this task. Take a moment to come up with a solution on your own before you go to the next step!
The naive way to accomplish this task is to check all the pairs in the array. However, remember that the array is sorted, can we somehow deploy this property do this task more quickly? Again, try to think about it before you look at the next step. Hint: think about how you can use two pointers (or iterators) to accomplish this task more
efficiently than looking at all pairs.
Okay, hopefully you already got the idea. If not, I strongly encourage you to stop reading and think about it I will NOT provide the idea every time ;)
Here is how you can do it more efficiently: Imagine you have two pointers (they can simply be two integer values that keep the index of the array), one pointing to the beginning of the array and advances forward and the other one points to the last element of the array and advances backward. All you need to do is to sum the values these two pointers point to and see if they are equal to 20, if so, great! you can prepare the output of the function.
If not, you inspect the sum, if the sum is greater than 20, you will decrement the second pointer and if the sum is less than 20, you increment the first pointer.
Before start coding, try the idea on a piece of paper with some example (you can use the ones provided in the main function) and convince yourself that this would work.
Now, start writing the body of the function. Again, do not change the signature!
After you are finished writing the function, you can use the main function provided to test your code. You see that we have four arrays in there. Try to workout each case in your mind (or with pen and paper) and understand what those if statements are going to do.
If you see any TEST FAIL when you run your program, something is wrong with your function. Go back and debug your function. If your function is working properly, you show only see Done!!!!. If you see anything else, something is wrong!
I know these instructions are super straightforward but I'm really lost on writing the code itself. If you can write the code for check_sum, I would greatly appreciate it!
In Java
1 package lab01; 4 public class SumExperiment t 6 public static int check_sum(int[l array)1 // This function will inspect the input to find any pair of values that add up to 20 // if it find such a pair, it will return the index* of the smallest value // if it does not find such as pair, it will return -1; 10 // remove the following line after you are done writing the function return -1; 12 13 14 15 16 17e 18 19 20 21 public static void main(String[] args) int[] array1 -new int[l(5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15, 16] if (check_sum(arrayl) !- 0) System.err.println("TEST1 FAILED"); 15, 16); int[] array2 = new int [ ]{3, 5, if (check-sum(array2) != 1) 8, 9, 10, 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 System.err.println("TEST2 FAILED"); int[] array3 new int[113, 4, 6, 9, 10, 14, 151; if (check_sum(array3) 2) System.err.println("TEST3 FAILED"); int[] array4 = new int[] {6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15, 16)Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


