Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
asap please Q2 Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The following information is available for ADT Company, which produces special-order
asap please Q2
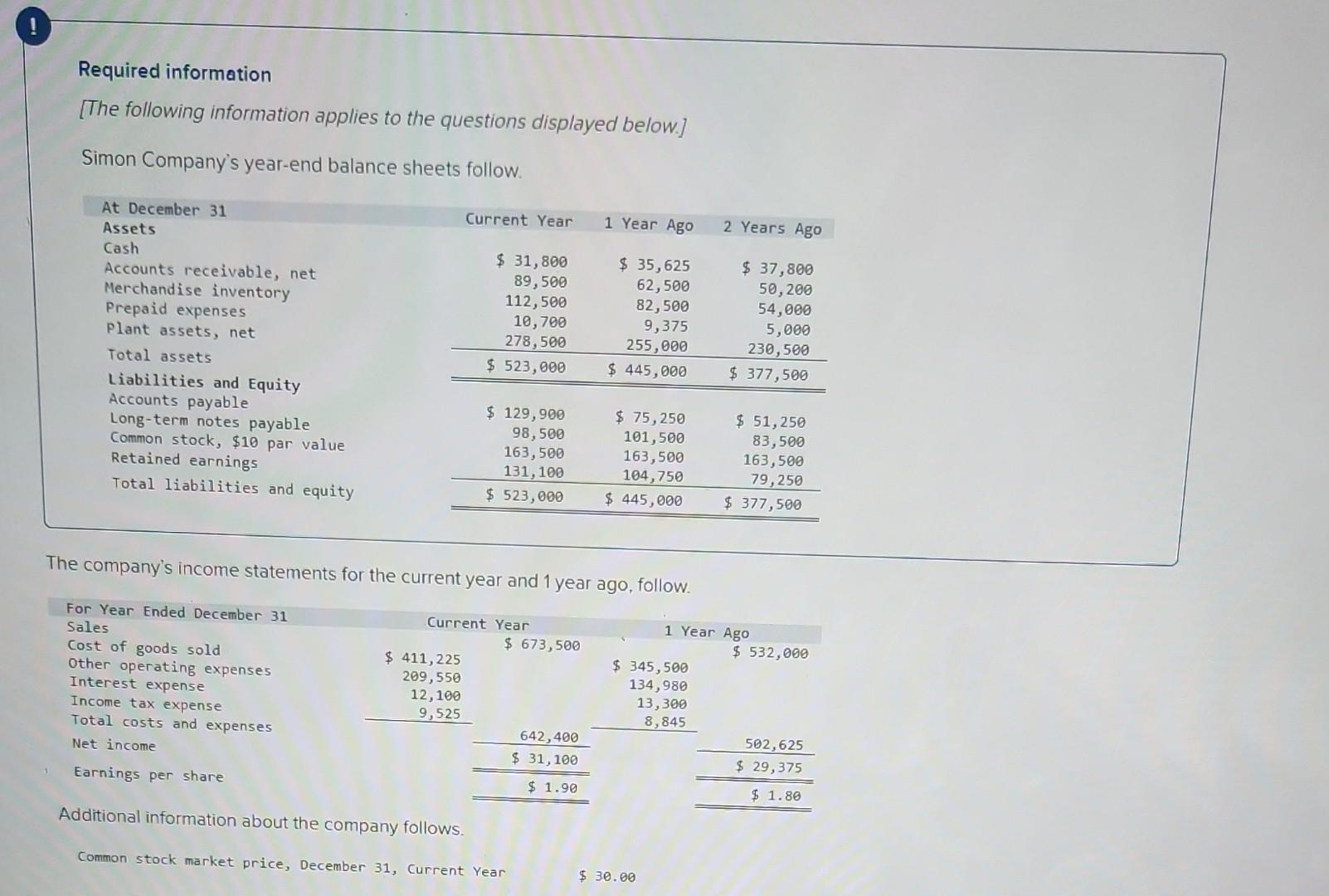
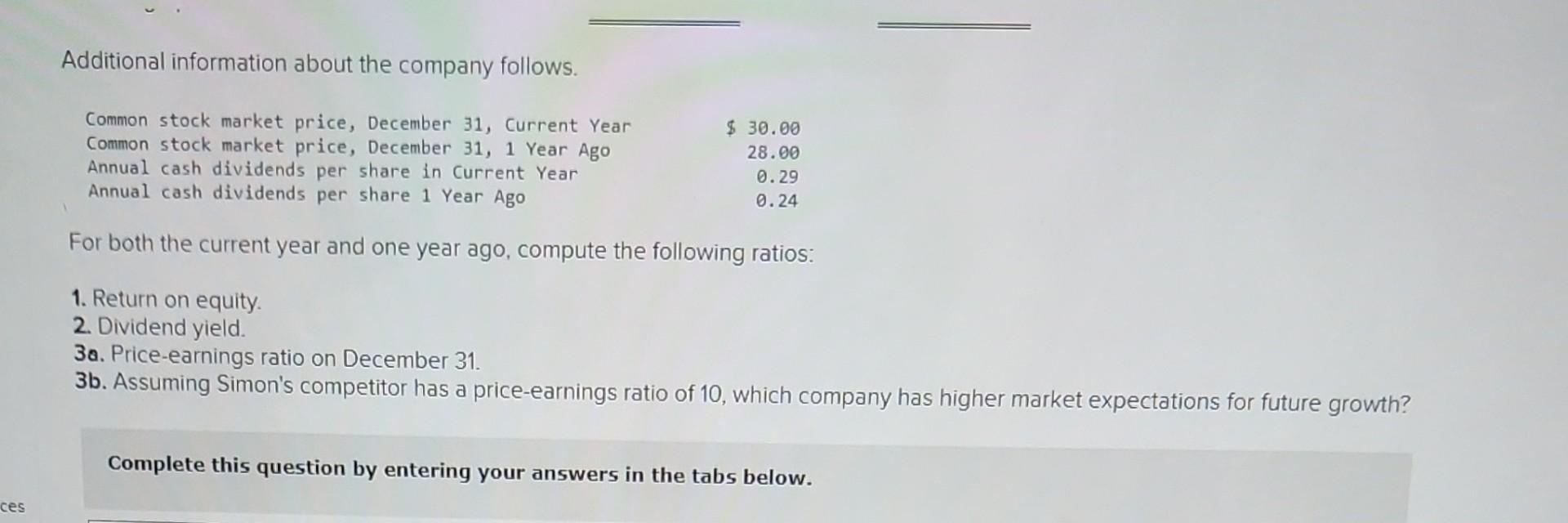
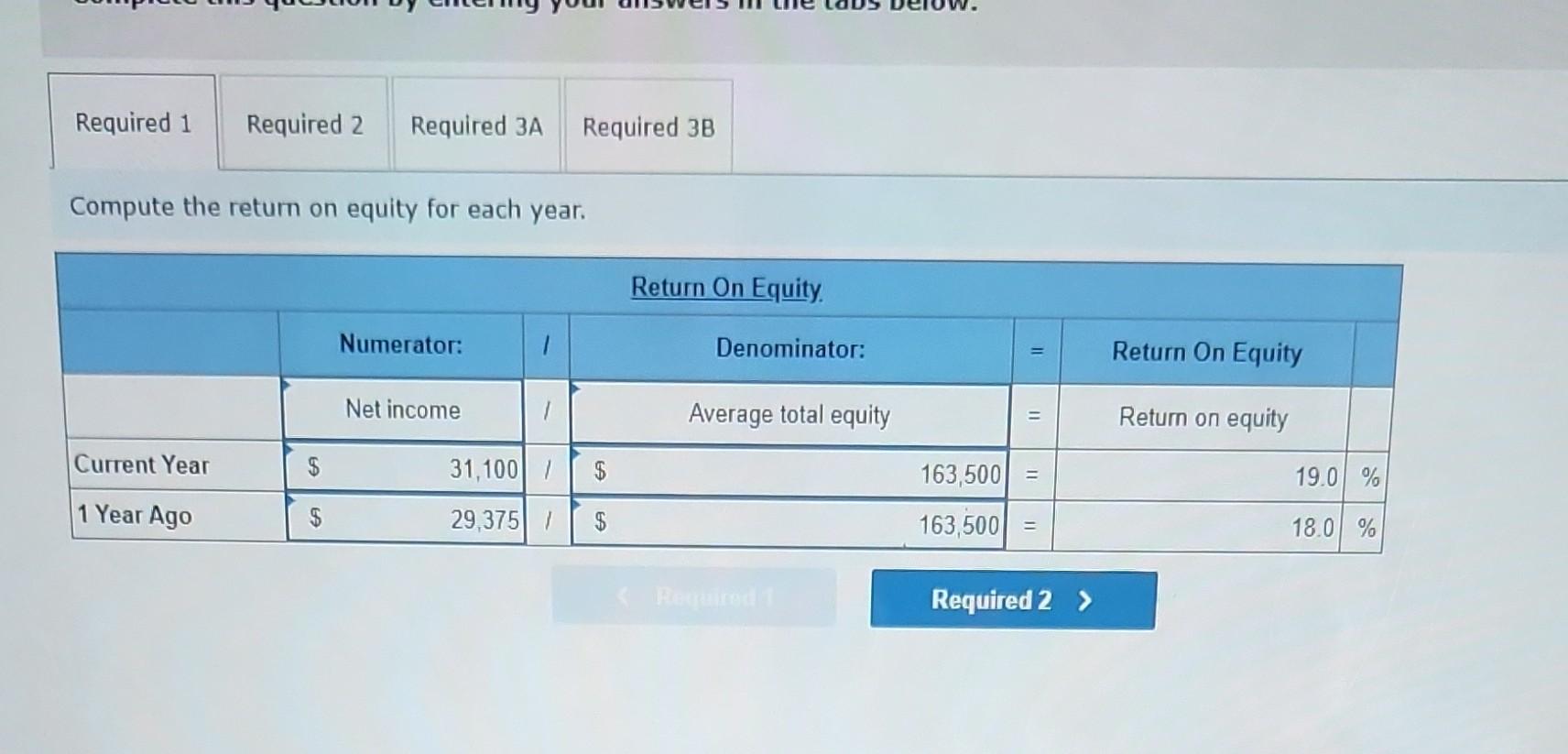
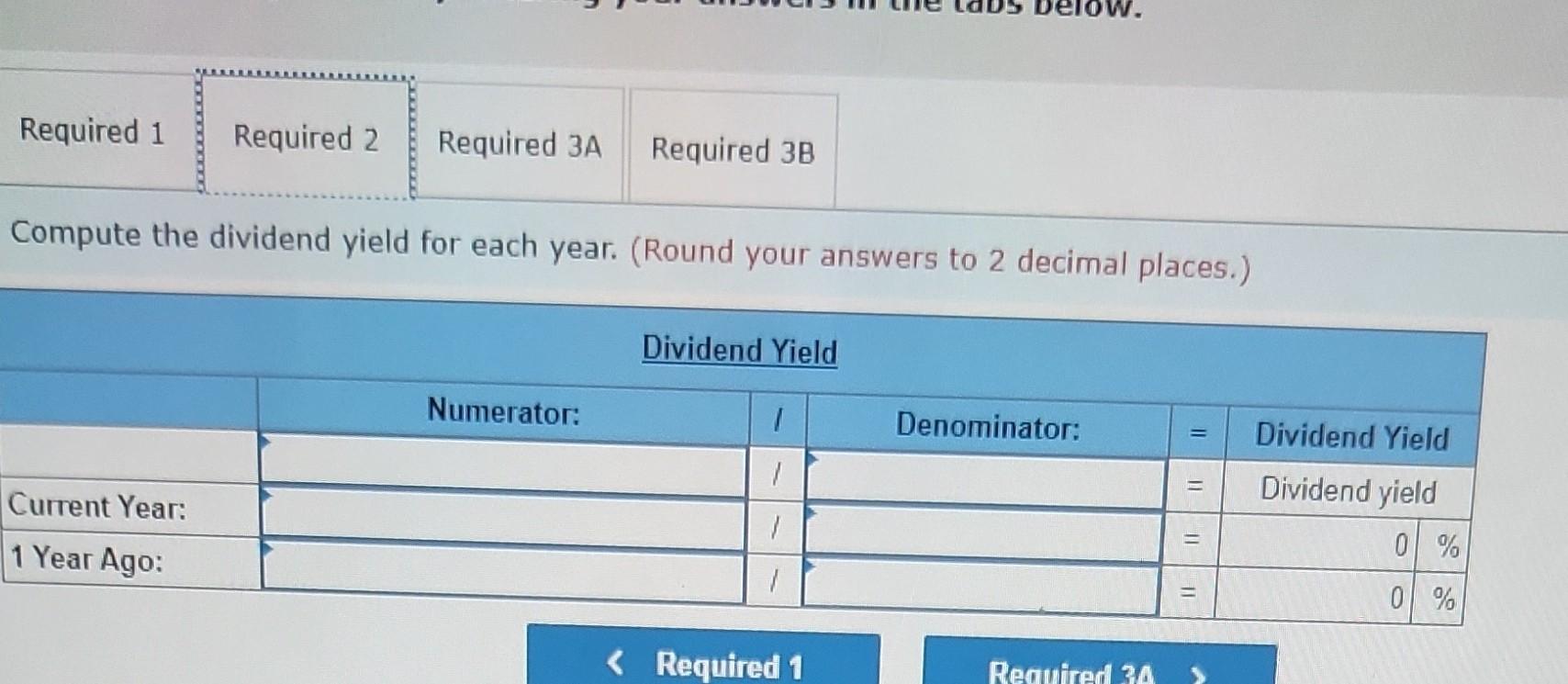
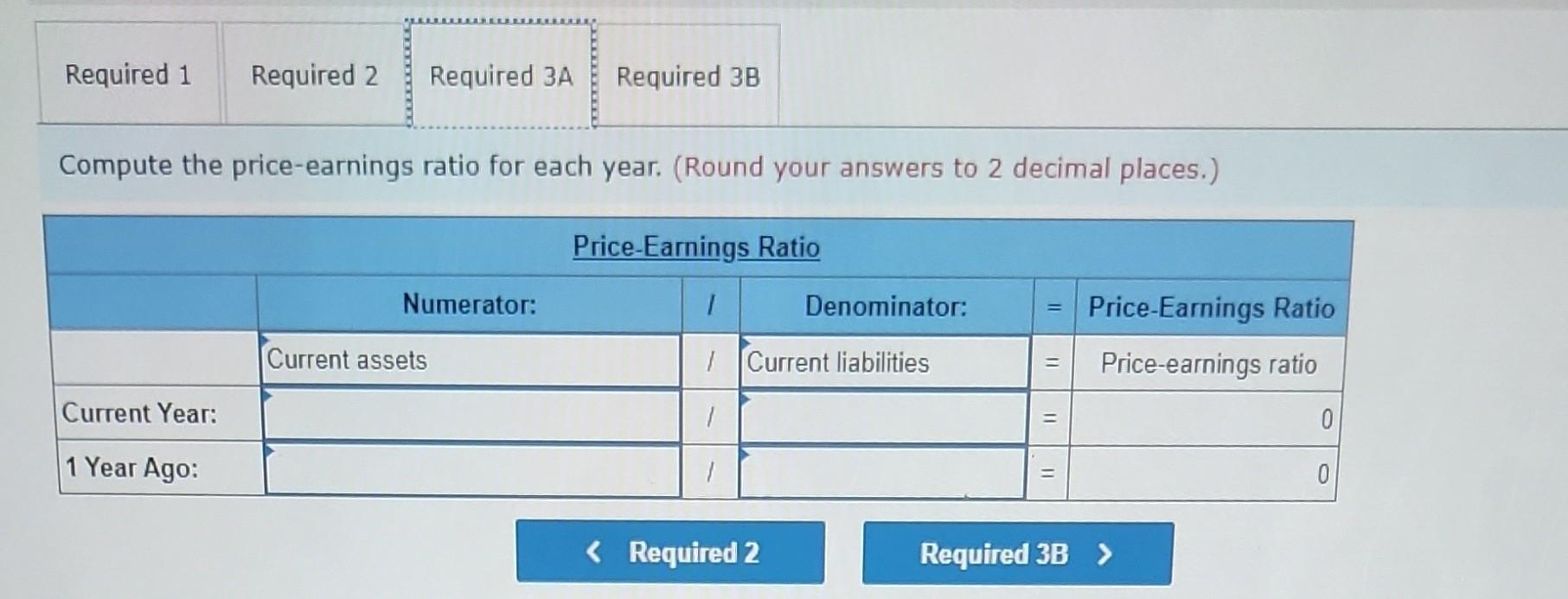
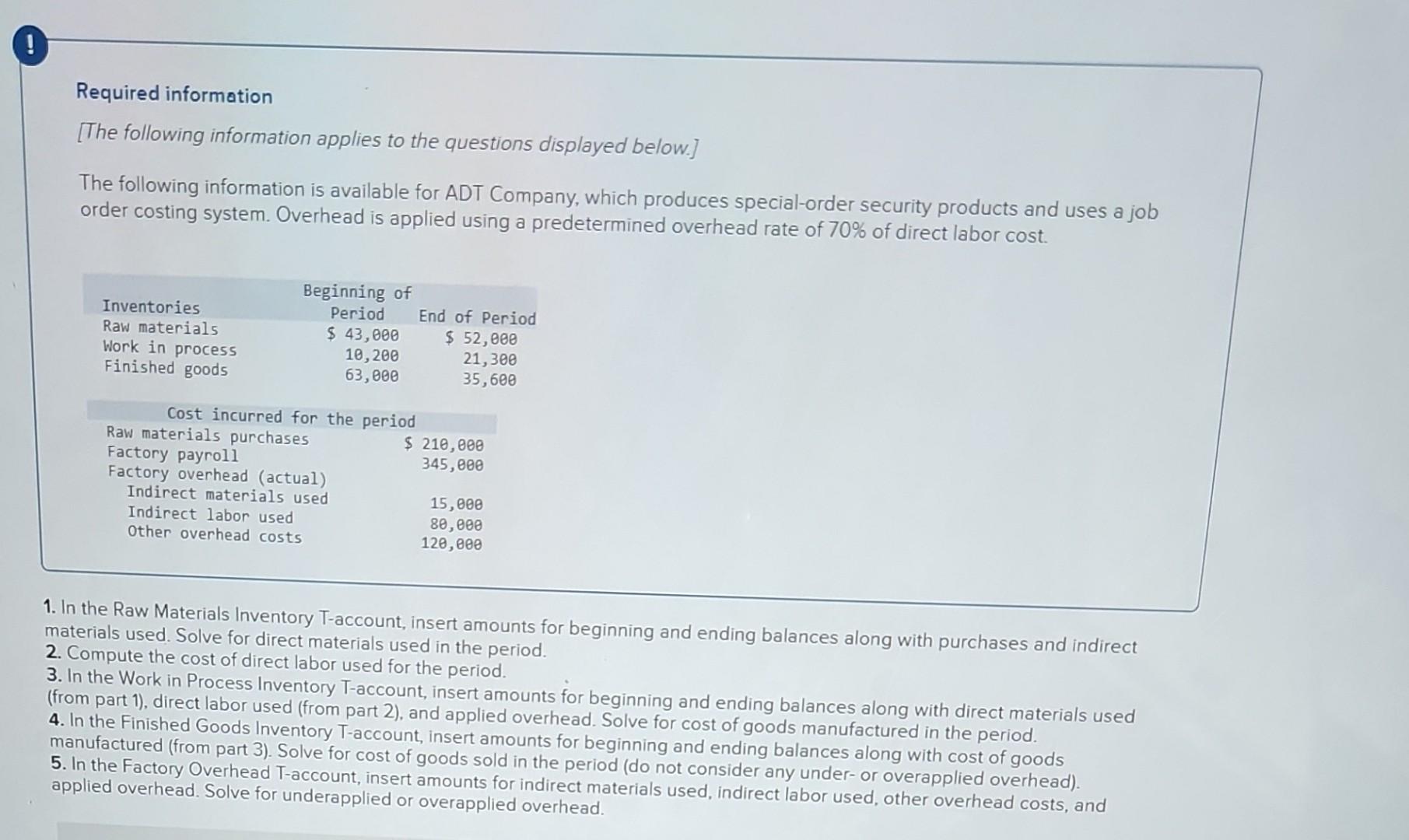
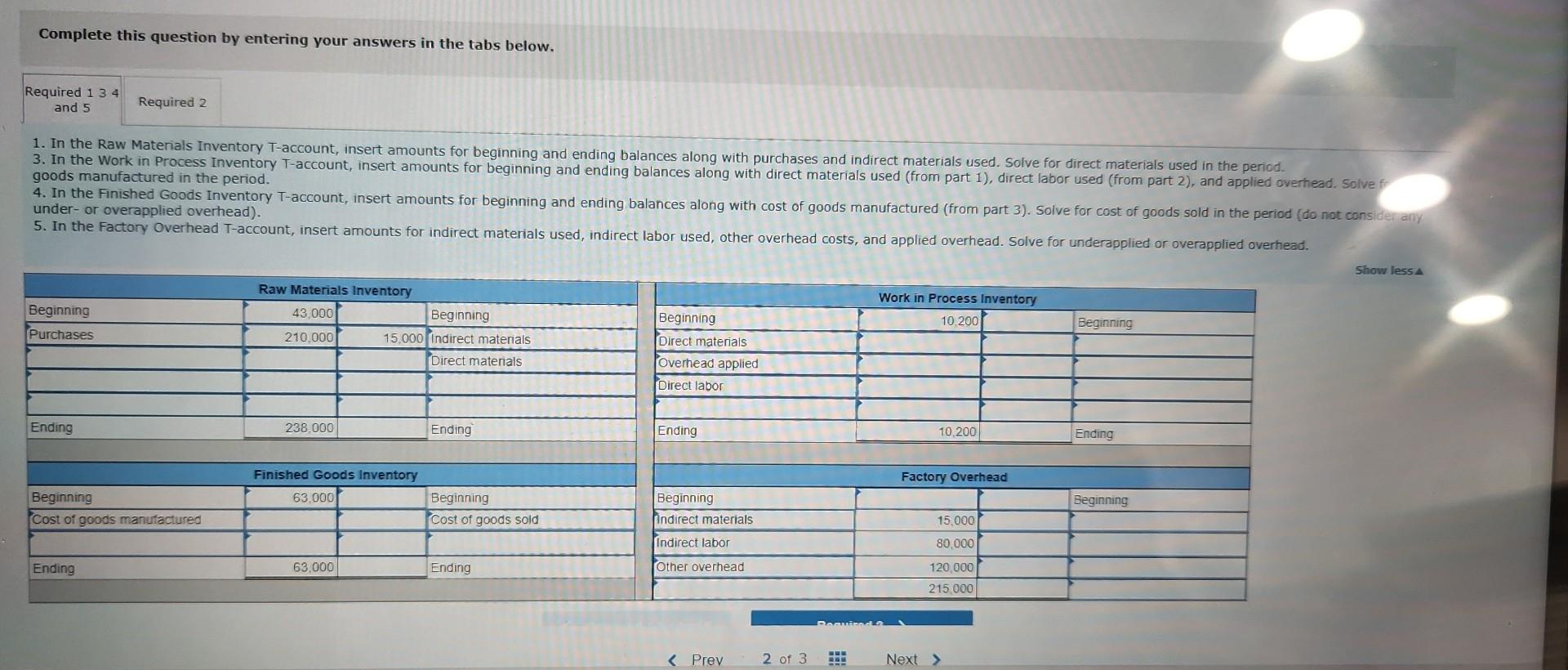
Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The following information is available for ADT Company, which produces special-order security products and uses a job order costing system. Overhead is applied using a predetermined overhead rate of 70% of direct labor cost. Inventories Raw materials Work in process Finished goods Beginning of Period $ 43,000 10,200 63,000 Cost incurred for the period Raw materials purchases Factory payroll Factory overhead (actual) Indirect materials used Indirect labor used Other overhead costs End of Period $ 52,000 21,300 35,600 $ 210,000 345,000 15,000 80,000 120,000 1. In the Raw Materials Inventory T-account, insert amounts for beginning and ending balances along with purchases and indirect materials used. Solve for direct materials used in the period. 2. Compute the cost of direct labor used for the period. 3. In the Work in Process Inventory T-account, insert amounts for beginning and ending balances along with direct materials used (from part 1), direct labor used (from part 2), and applied overhead. Solve for cost of goods manufactured in the period. 4. In the Finished Goods Inventory T-account, insert amounts for beginning and ending balances along with cost of goods manufactured (from part 3). Solve for cost of goods sold in the period (do not consider any under- or overapplied overhead). 5. In the Factory Overhead T-account, insert amounts for indirect materials used, indirect labor used, other overhead costs, and applied overhead. Solve for underapplied or overapplied overhead. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 3 4 and 5 1. In the Raw Materials Inventory T-account, insert amounts for beginning and ending balances along with purchases and indirect materials used. Solve for direct materials used in the period. 3. In the Work in Process Inventory T-account, insert amounts for beginning and ending balances along with direct materials used (from part 1), direct labor used (from part 2), and applied overhead. Solve fr goods manufactured in the period. 4. In the Finished Goods Inventory T-account, insert amounts for beginning and ending balances along with cost of goods manufactured (from part 3). Solve for cost of goods sold in the period (do not consider any under- or overapplied overhead). 5. In the Factory Overhead T-account, insert amounts for indirect materials used, indirect labor used, other overhead costs, and applied overhead. Solve for underapplied or overapplied overhead. Beginning Purchases Required 2 Ending Beginning Cost of goods manufactured Ending Raw Materials Inventory 43,000 210,000 238,000 Beginning 15,000 Indirect materials Direct materials Finished Goods Inventory 63,000 63,000 Ending Beginning Cost of goods sold Ending Beginning Direct materials Overhead applied Direct labor Ending Beginning Indirect materials Indirect labor Other overhead Beginning Ending Beginning Show less A Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Simon Company's year-end balance sheets follow. At December 31 Assets Cash Accounts receivable, net Merchandise inventory Prepaid expenses Plant assets, net Total assets Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable Long-term notes payable Common stock, $10 par value Retained earnings Total liabilities and equity Current Year $ 411,225 209,550 12,100 9,525 $ 31,800 89,500 112,500 10,700 278,500 $ 523,000 $ 129,900 98,500 163,500 131, 100 $ 523,000 Current Year Interest expense Income tax expense Total costs and expenses Net income Earnings per share Additional information about the company follows. The company's income statements for the current year and 1 year ago, follow. For Year Ended December 31 Sales Cost of goods sold Other operating expenses $ 673,500 Common stock market price, December 31, Current Year 1 Year Ago 642,400 $ 31,100 $ 1.90 $ 35,625 62,500 82,500 9,375 255,000 $ 445,000 $ 75,250 101,500 163,500 104,750 $ 445,000 $ 345,500 134,980 13,300 8,845 $ 30.00 2 Years Ago $ 37,800 50,200 54,000 5,000 230,500 $ 377,500 $ 51,250 83,500 163,500 79,250 $ 377,500 1 Year Ago $ 532,000 502,625 $ 29,375 $ 1.80 ces Additional information about the company follows. Common stock market price, December 31, Current Year Common stock market price, December 31, 1 Year Ago Annual cash dividends per share in Current Year Annual cash dividends per share 1 Year Ago For both the current year and one year ago, compute the following ratios: 1. Return on equity. 2. Dividend yield. $ 30.00 28.00 0.29 0.24 3a. Price-earnings ratio on December 31. 3b. Assuming Simon's competitor has a price-earnings ratio of 10, which company has higher market expectations for future growth? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3A Required 3B Compute the return on equity for each year. Current Year 1 Year Ago Numerator: Net income 31,100/ $ 29,375 / $ Return On Equity. Denominator: Average total equity Return On Equity Return on equity 19.0 % 18.0 % Required 1 Required 2 Required 3A Required 3B Compute the dividend yield for each year. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Current Year: 1 Year Ago: Numerator: Dividend Yield 1 1 1 1 0 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


