Question
ASSIGNMENT: 1. Accompanying this assignment is a compressed file named CardGame.zip which contains the following files: o Card.java o CardGame.java Save the ZIP file on
ASSIGNMENT: 1. Accompanying this assignment is a compressed file named CardGame.zip which contains the following files: o Card.java o CardGame.java Save the ZIP file on your computer, unzip it, and open the two Java files it contains using the IDE/editor that you typically use to compile and run Java. 2. Print Card.java. Complete the following actions using your printed copy of Card.java:
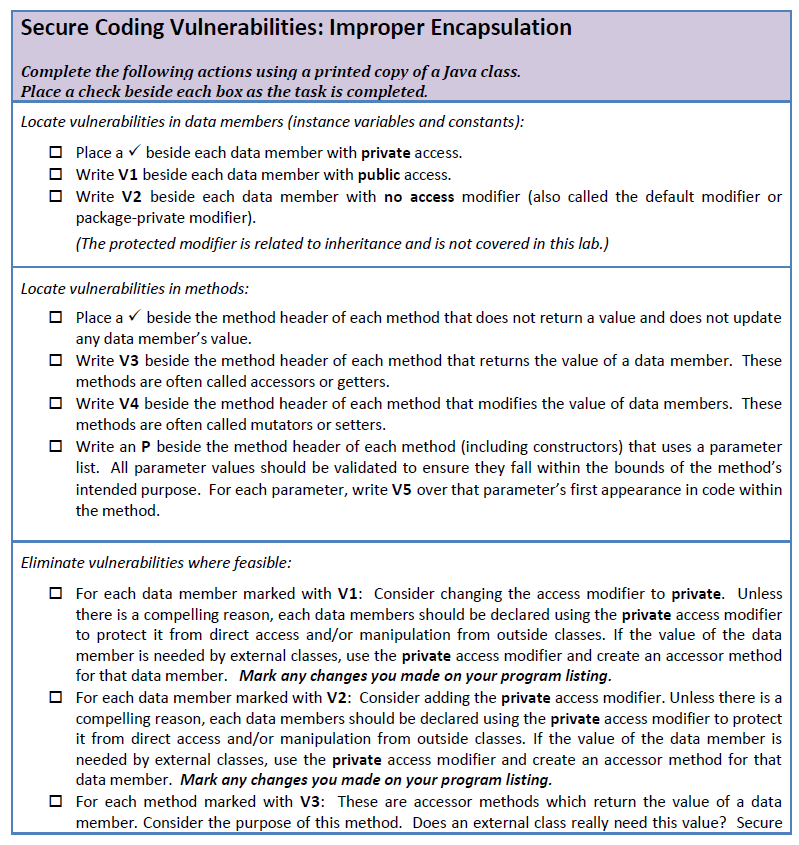
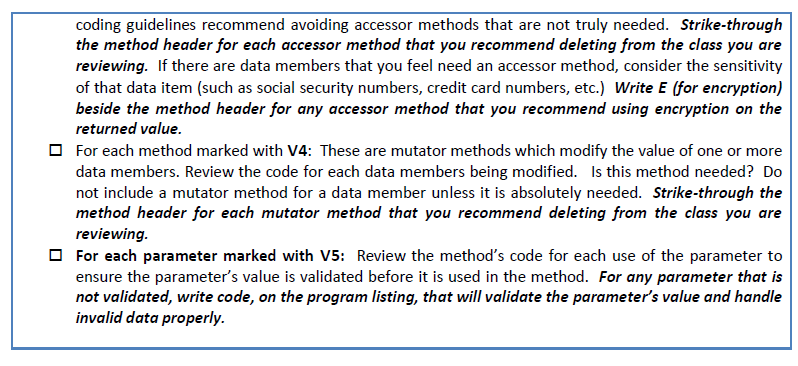
3. Using your marked-up Card.java listing, update the class to improve class encapsulation. 4. Compile your modified version of the Card class. Debug the program to ensure it is working properly with CardGame.java. Modify CardGame.java, if needed (i.e. remove references to methods you may have removed from Card.java). Scan your marked up class for submitting your work. DISCUSSION QUESTIONS: 1. Define encapsulation. 2. What are four different access modifiers in Java? Explain each. 3. Explain why method parameters should be validated before they are used in a method. 4. Why are private data members in a class more secure than public data members? 5. Why are private data members in a class more secure than package-private data members (fields without an access modifier)? 6. From a security viewpoint, why should you not routinely create an accessor for each instance variable? 7. From a security viewpoint, why should you not routinely create a mutator for each instance variable? 8. Describe the changes you made to Card.java and CardGame.java and why you made each change.
Secure Coding Vulnerabilities: Improper Encapsulation Complete the following actions using a printed copy of a Java class. Place a check beside each box as the task is completed. Locate vulnerabilities in data members (instance variables and constants) Place a beside each data member with private access. write V1 beside each data member with public access. write V2 beside each data member with no access modifier (also called the default modifier or package-private modifier) (The protected modifier is related to inheritance and is not covered in this lab.) Locate vulnerabilities in methods Place a V beside the method header of each method that does not return a value and does not update any data member's value write V3 beside the method header of each method that returns the value of a data member. These methods are often called accessors or getters write V4 beside the method header of each method that modifies the value of data members. These methods are often called mutators or setters write an P beside the method header of each method (including constructors) that uses a parameter list. All parameter values should be validated to ensure they fall within the bounds of the method's intended purpose. For each parameter, write V5 over that parameter's first appearance in code within the metho Eliminate vulnerabilities where feasible For each data member marked with V1: Consider changing the access modifier to private. Unless there is a compelling reason, each data members should be declared using the private access modifier to protect it from direct access and/or manipulation from outside classes. If the value of the data member is needed by external classes, use the private access modifier and create an accessor method for that data member. Mark any changes you made on your program listing For each data member marked with V2: Consider adding the private access modifier. Unless there is a compelling reason, each data members should be declared using the private access modifier to protect it from direct access and/or manipulation from outside classes. If the value of the data member is needed by external classes, use the private access modifier and create an accessor method for that data member. Mark any changes you made on your program listing For each method marked with V3: These are accessor methods which return the value of a data member. Consider the purpose of this method. Does an external class really need this value? Secure Secure Coding Vulnerabilities: Improper Encapsulation Complete the following actions using a printed copy of a Java class. Place a check beside each box as the task is completed. Locate vulnerabilities in data members (instance variables and constants) Place a beside each data member with private access. write V1 beside each data member with public access. write V2 beside each data member with no access modifier (also called the default modifier or package-private modifier) (The protected modifier is related to inheritance and is not covered in this lab.) Locate vulnerabilities in methods Place a V beside the method header of each method that does not return a value and does not update any data member's value write V3 beside the method header of each method that returns the value of a data member. These methods are often called accessors or getters write V4 beside the method header of each method that modifies the value of data members. These methods are often called mutators or setters write an P beside the method header of each method (including constructors) that uses a parameter list. All parameter values should be validated to ensure they fall within the bounds of the method's intended purpose. For each parameter, write V5 over that parameter's first appearance in code within the metho Eliminate vulnerabilities where feasible For each data member marked with V1: Consider changing the access modifier to private. Unless there is a compelling reason, each data members should be declared using the private access modifier to protect it from direct access and/or manipulation from outside classes. If the value of the data member is needed by external classes, use the private access modifier and create an accessor method for that data member. Mark any changes you made on your program listing For each data member marked with V2: Consider adding the private access modifier. Unless there is a compelling reason, each data members should be declared using the private access modifier to protect it from direct access and/or manipulation from outside classes. If the value of the data member is needed by external classes, use the private access modifier and create an accessor method for that data member. Mark any changes you made on your program listing For each method marked with V3: These are accessor methods which return the value of a data member. Consider the purpose of this method. Does an external class really need this value? SecureStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


