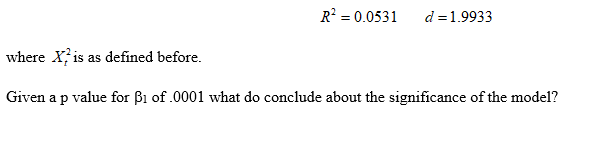Assignment 4 Business Analytics Question All of the models that have been discussed in the lessons and text have been linear in nature that is, the model is linear in the parameters, so that there is one parameter multiplied by each variable in the model- For example, a structural model could be something like 1- J' =Jl 4751151 +3xs +34% +1\" ormore compactly y = X+ Hi ;__It was additionally assumed that Hr ~ Armani). One particular nonlinear model in widespread usage in nance is known as an 'ARCH' model {ARCH stands for 'autoregressive conditionally heteroscedastic'}. To see why this class of models is useful, recall that a typical structural model could be expressed by an equation of the form given above with Hr ~ N{D,Jl);__The assumption of multiple regression that the variance of the errors is constant is known as homoscedasticity 'Li it is assumed that vartfur) = {II}. If the variance of the errors is not constant, this would be known as heteroscedasticity. If the errors are heteroscedastic, but assumed homoscedastic, an implication would be that standard error estimates could be wrong. It is unlikely in the context of nancial time series that the variance of the errors will be constant over time, and hence it makes sense to consider a model that does not assume that the variance is constant, and which describes how the variance of the errors evolves. Under the ARCH model, the 'autocorrelation in volatihty' is modeled by allowing the conditional variance of the error term {If , to depend on the immediately previous value of the squared error 1 _ 1 2- J: as + \"our1 The above model is lcnown as an ARCH-Kl ), since the conditional variance depends on only one lagged squared error. Notice that (2} is only a partial model, since nothing has been said vet about the conditional mean. Under ARCH, the conditional mean equation (which describes how the dependent variable. 3;], varies over time) could take almost any form that the researcher wishes- One example of a rll model would be 3- s; = .51 + 161171: + 53x3: + 334174: + #1. #1. ~ mo. of) 4- 5:1 = as + \"ME1 The ARCH model is an important tool x the analyst as it provides a method of measuring time varying volatility. [11 risk management, volatilityr is often used as a measure of risk. Let us illustrate this with an exchange rate example. (See Basic Econometrics (Fifth Edition) by M N. Gujarati and Dawn C- Porter= Chapter 22 for a more complete discussion)- Let it: U_S_:"U_K exchange rate ET: log :1ng QT; =F; Fr:1 = relative change in the exchange rate 1- as. =meanofdf; 1- Xeniad1: Thus, Xt is the mean-adjusted relative change in the exchange rate. Now we can use X, as a measure of volatility.. Being a squared quantity, its value will be high in periods when there are big changes in the prices of financial assets and its value will be comparatively small when there are modest changes in the prices of financial assets. Accepting X, as a measure of volatility, how do we know if it changes over time? Suppose we consider the following model: This model postulates that volatility in the current period is related to its value in the previous period plus a white noise error term. If Bi is positive, it suggests that if volatility was high in the previous period, it will continue to be high in the current period, indicating volatility clustering. If Bi is zero, then there is no volatility clustering . The statistical significance of the estimated By can be judged by the usual t test. a. The estimation of the model provided the following: X, = 0.00043 + 0.23036X7-] t = (7.71) (4.97)R' = 0.0531 d = 1.9933 where X, is as defined before. Given a p value for Bi of .0001 what do conclude about the significance of the model