Assume that iron rubber tire store completed the following perpetual inventory transactions for a line of tires
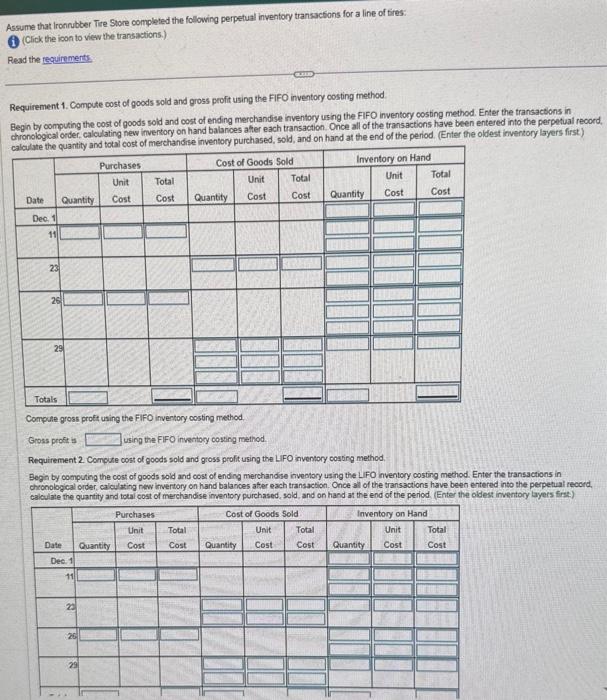
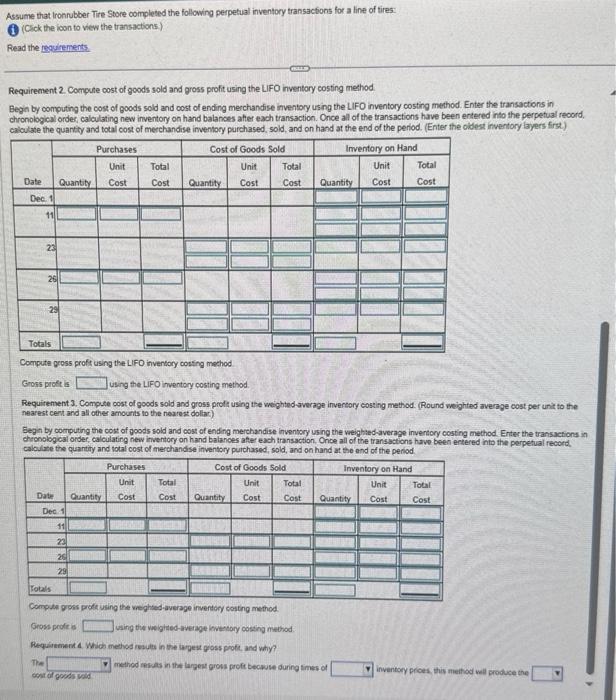
Requirements 1. Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit using the FIFO inventory costing method. 2. Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit using the LIFO inventory costing method. 3. Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit using the weighted-average inventory costing method. (Round weighted-average cost per unit to the nearest cent and all other amounts to the nearest dollar.) 4. Which method results in the largest gross profit, and why? to the nearest cent and all other amounts to the nearest dollar.) actions in chronobgical order, calculating new inventory on hand balances aiter each transt the end of the period. More info Assume that Ironnbber Tre Store completed the following perpetual inventory transactions for a line of tires: (i) (Click the icon to view the transactions.) Read the reguirements Requirement 1. Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit using the FIFO inventory costing method. Begin by computing the cost of goods sold and cost of ending merchandise inventory using the FIFO inventory costing method. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new invertory on hand balanoes aher each transaction. Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetival reoord. ciluduta the nuiantitv and total cost of merchandise inventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (Enter the oldest inventory layers first) Compute gross proft using the fiFO inventory costing method. Grons profit is using the FIFO inventory costing method. Requirement 2 Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit using the LiFO inventory costing method. Begin by compuing the cost of goods sold and cost of ending merchandise inventory using the LIFO nventory costing mechod. Enter the transactions in chronological order, caloulating new invertory on hand balances ater each transaction. Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetuat record. calculate the quantity and tocai cost of merchandise imventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (Enter the oldest inventory layers first.) Assume that Ironrubber Tire Store completed the following perpetual inventory transactions for a line of tires: (1) (Crick the ioon to view the transactions) Read the requirments. Requirement 2 Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit using the LIFO inventory costing method. Begin by computing the cost of goods sold and cost of ending merchandise inventory using the LIFO inventory costing method. Enter the transactions in chronological ordes, caloulating new inventory on hand balances after each transaction. Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetual record, caloulate the quantity and total cost of merchandise imventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (Enter the oldest inventory layers first.) Compute gross profis using the LIFO inventory cosing mechod Gross prode is Ueing the LIFO inventory costing method Requirtment 3. Compute cost of goods sold and gross proft using the weighted wverage invertory costing method. (Round weighted average cost per unit to the nearest cent and all other amounts to the nearest doliac) Eegin by computing the cost of goods sold and cost of ending merchandise inventory using the weighthed-average invertory costing method Erter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balances afte each transaction, Once all of the transactions have been entered into the perpetual record. caloulate the quantity and total cost of merchandse inventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the and of the period. Comple goss prole using the weghted average inventory costing method. Gross profic is using the veigitied average inversory costing method: Requitement a Which metiod result in the iapest poss polic, and why? The method aikes in the largeu grous proft beckise during times of osiror goces vad inventory proes, this method well produce the









