Question
Assume Universal Accountancy services provide bookkeeping, tax, and audit services to its clients. Management believes the company has several unprofitable customers and would like to
Assume Universal Accountancy services provide bookkeeping, tax, and audit services to its clients. Management believes the company has several unprofitable customers and would like to perform differential analysis to find out how profits would change if they dropped these customers. Alternative 1 includes the annual revenues, costs, and resulting profit if the company keeps all existing customers. Alternative 2 includes the annual revenues, costs, and resulting profit if the company drops what it believes are unprofitable customers. How should management decide whether to keep all existing customers or drop certain customers?
Figure 7.1 Differential Analysis for Universal Accountancy
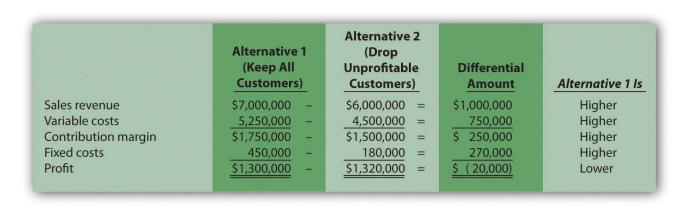
This figure confirms that Universal Accountancy would be better off dropping the unprofitable customers (Alternative 2) because company profits would increase by $20,000. The general rule is to select the alternative with the highest differential profit.
Page 2 of 2 Now it's your turn: Kabul Express is a small coffee shop in Kurdistan and looking for expansion. The company is evaluating two alternatives—sandwiches and cookies. Annual projections for sales of sandwiches are sales, $180,000; variable costs, $130,000; and fixed costs, $500. Annual projections for sales of cookies are sales, $100,000; variable costs, $30,000; and no additional fixed costs.
Using the format in Figure 7.1 "Differential Analysis for Universal Accountancy", perform differential analysis to determine which alternative is more profitable, and by how much. Assume adding sandwiches is Alternative 1 and adding cookies is Alternative 2.
Present your data on an excel sheet. You can also add graphs for impactful data presentation.
Alternative 2 Alternative 1 (Keep All Customers) (Drop Unprofitable Customers) Differential Amount Alternative 1 Is Sales revenue $7,000,000 $6,000,000 = $1,000,000 Higher Higher Higher Higher Lower 5,250,000 $1,750,000 750,000 $ 250,000 270,000 $ (20,000) Variable costs 4,500,000 $1,500,000 Contribution margin Fixed costs 450,000 180,000 Profit $1,300,000 $1,320,000 = I III I IIIII
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (161 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
ANSWER Universal accounting analysis for comparison two alternatives in marginal costing which gives ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


