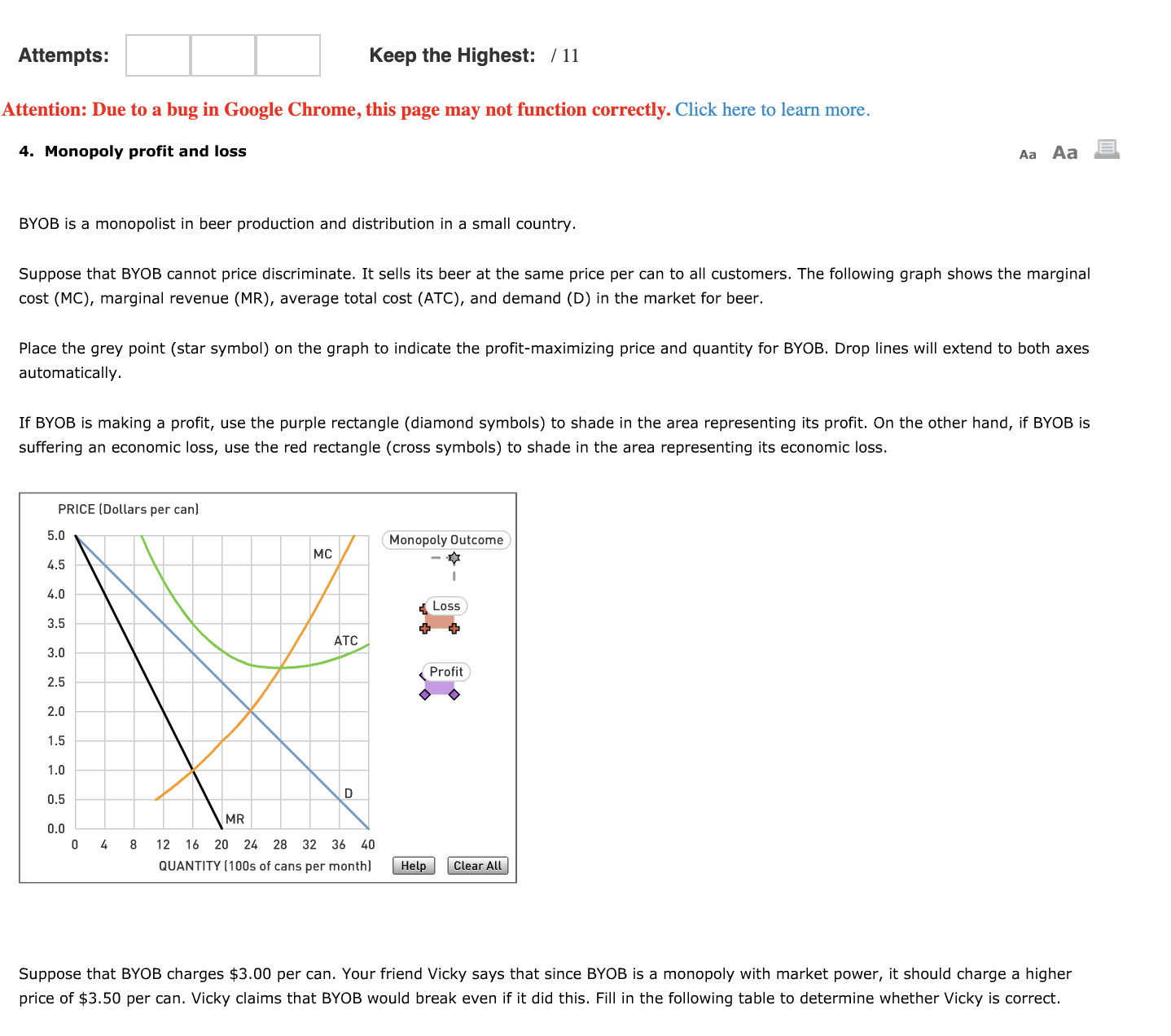
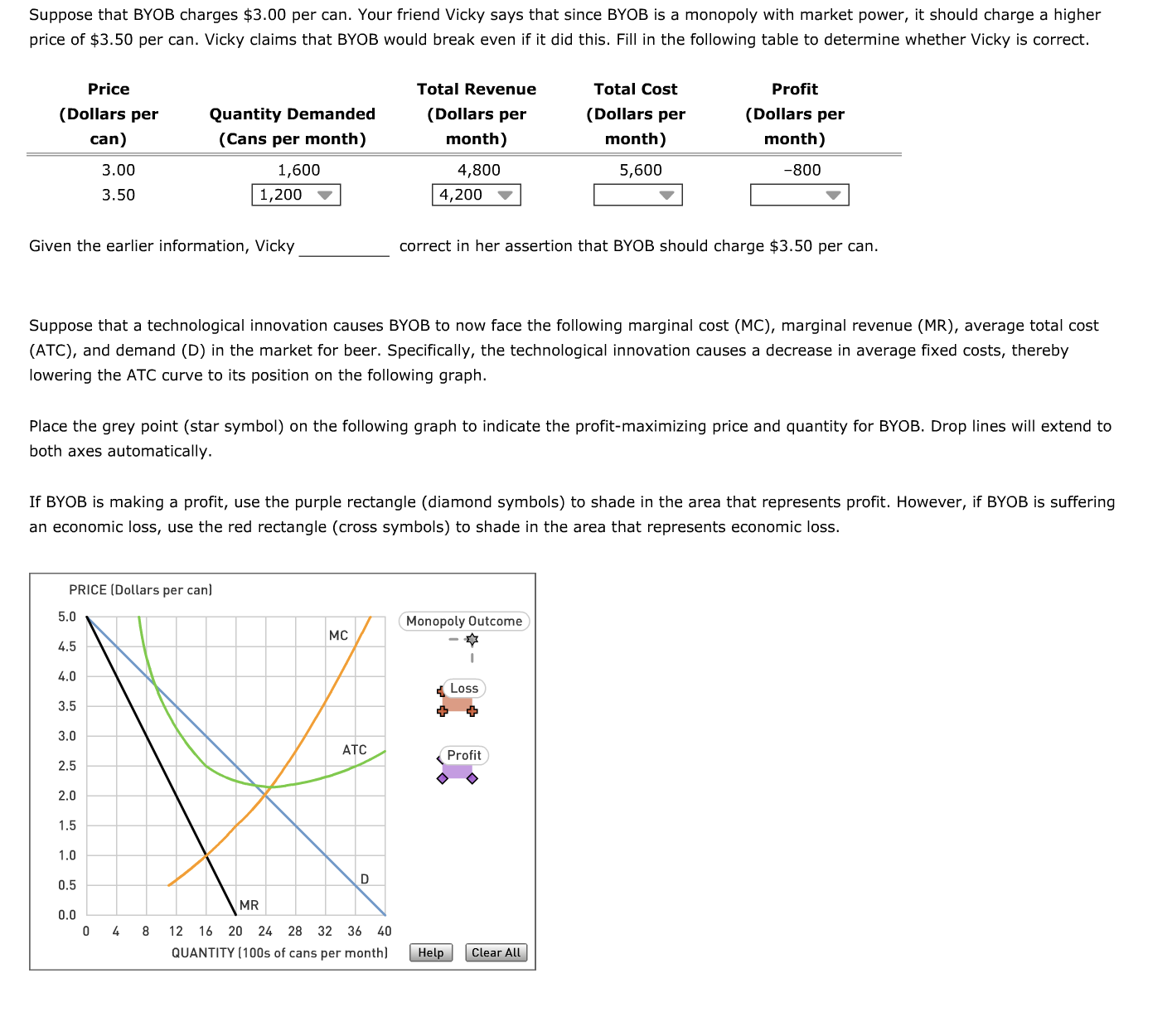
Attempts: |:|:|:| Keep the Highest: I11 Attention: Due to a bug in Google Chrome, this page may not function correctly. Click here to learn more. 4. Monopoly prot and loss A: Aa EL BYOB is a monopolist in beer production and distribution in a small country. Suppose that BYOB cannot price discriminate. It sells its beer at the same price per can to all customers. The following graph shows the marginal cost (MC), marginal revenue (MR), average total cost (ATC), and demand (D) in the market for beer. Place the grey point (star symbol) on the graph to indicate the prot-maximizing price and quantity for BYOB. Drop lines will extend to both axes automatically. If BYOB is making a prot, use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to shade in the area representing its prot. 0n the other hand, if BYOB is suffering an economic loss, use the red rectangle (cross symbols) to shade in the area representing its economic loss. PRICE [Dollars per can] 5.. 4.5 ' T 5.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 MR 0.0 04312162021523.3236\"! QUANTITYHDOS ofcans permonlh] @ Suppose that BYOB charges $3.00 per can. Your friend Vicky says that since BYOB is a monopoly with market power, it should charge a higher price of $3.50 per can. Vicky claims that BYOB would break even if it did this. Fill in the following table to determine whether Vicky is correct. Suppose that BYOB charges $3.00 per can. Your friend Vicky says that since BYOB is a monopoly with market power, it should charge a higher price of $3.50 per can. Vicky claims that BYOB would break even if it did this. Fill in the following table to determine whether Vicky is correct. Price Total Revenue Total Cost Prot (Dollars per Quantity Demanded (Dollars per (Dollars per (Dollars per can) (Cans per month) month) month) month) 3.00 1,600 4,800 5,600 800 3.50 moo v 4.200 v |:| I:I Given the earlier information, Vicky correct in her assertion that BYOB should charge $3.50 per can. Suppose that a technological innovation causes BYOB to now face the following marginal cost (MC), marginal revenue (MR), average total cost (ATC), and demand (D) in the market for beer. Specically, the technological innovation causes a decrease in average xed costs, thereby lowering the ATC curve to its position on the following graph. Place the grey point (star symbol) on the following graph to indicate the prot-maximizing price and quantity for BYOB. Drop lines will extend to both axes automatically. If BYOB is making a prot, use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to shade in the area that represents prot. However, if BYOB is suffering an economic loss, use the red rectangle (cross symbols) to shade in the area that represents economic loss. PRICE [Dollars per canl 5.0 Monopoty Outcome 5.5 5.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 MR 0.0 0 t. 812 1.512024233236130 QUANTITY [1005 of cans per month] @