Question
**ATTENTION** This is the third time posting this question. The first solution not right and second is partial. Please read the question carefully before giving
**ATTENTION** This is the third time posting this question. The first solution not right and second is partial.
Please read the question carefully before giving me an answer.
answer wrong again and i will call chegg.
Problem Description
The goal of this assignment is to make a basic directory maintenance simulator that processes basic UNIX/Linux commands. Suppose we wanted a directory tree that would allow us to represent the following directory structure: 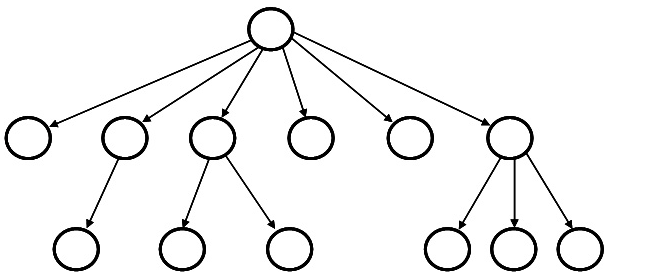 We could have an array or linked list of pointers in each node for child nodes, but the array might fill up and the linked list maintenance adds complexity for traversals, add and delete, etc. As an alternative, we could use a binary tree structure where one branch is essentially a linked list of sibling nodes at a given level, and the other branch is a pointer to the contents of the given directory. Pictorially, the data structure would look like this:
We could have an array or linked list of pointers in each node for child nodes, but the array might fill up and the linked list maintenance adds complexity for traversals, add and delete, etc. As an alternative, we could use a binary tree structure where one branch is essentially a linked list of sibling nodes at a given level, and the other branch is a pointer to the contents of the given directory. Pictorially, the data structure would look like this: 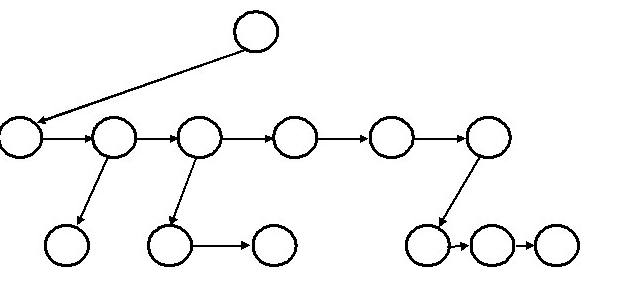 For simplicity, we will use the same type of node for a file or a directory. Requirements for this assignment: We will simulate several of the UNIX command-line operating system commands for a directory system in order to add directories, add files, list directory contents, etc. We will implement the following commands: ls // lists all files and directories in the current directory, indicating which (file or directory) it is mkdir
For simplicity, we will use the same type of node for a file or a directory. Requirements for this assignment: We will simulate several of the UNIX command-line operating system commands for a directory system in order to add directories, add files, list directory contents, etc. We will implement the following commands: ls // lists all files and directories in the current directory, indicating which (file or directory) it is mkdir
mv
cp
rm
whereis
It will illustrate that you can test interactive programs without having to do all the typing (most important)
It will simplify life for the person grading the assignment (me in this case)
Error Checking:
This assignment will require quite a bit of error checking. For instance, you should not be able to make a file or directory in a directory that already has a file or directory by that name. You obviously cannot switch into a directory that is not there, and you cannot switch to the parent directory of your root directory (although UNIX might permit you to do this if the System Administrator is not too picky). The data structure will be available in the background and will grow as we add subdirectories and files, or shrink as we remove them. Note the use of the $ as the command prompt - just like a typical command-line system!! Here is a typical output of a program run: $ pwd coffey/root/ $ mkdir abc abc $ cd abc coffey/root/abc/ $ addf f3 $ addf f2 $ addf f1 $ ls F f1 F f2 F f3 $ mkdir def def $ ls D def F f1 F f2 F f3 $ cd cdf cdf is not located in abc $ cd def coffey/root/abc/def/ $ pwd coffey/root/abc/def/
$ whereis f3
coffey/root/abc/
$ whereis qwerty
qwerty not found
$ cd .. coffey/root/abc/ $ ls D def F f1 F f2 F f3 $ cd .. coffey/root/ $ pwd coffey/root/ $ ls D abc $ cd abc coffey/root/abc/ $ pwd coffey/root/abc/ $ ls D def F f1 F f2 F f3
$ rm f5
f5 is not in coffey/root/abc/
$ rm f2
$ ls
D def F f1 F f3
$ mv f3 file3
$ ls
D def F f1 F file3 $ bye
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


