
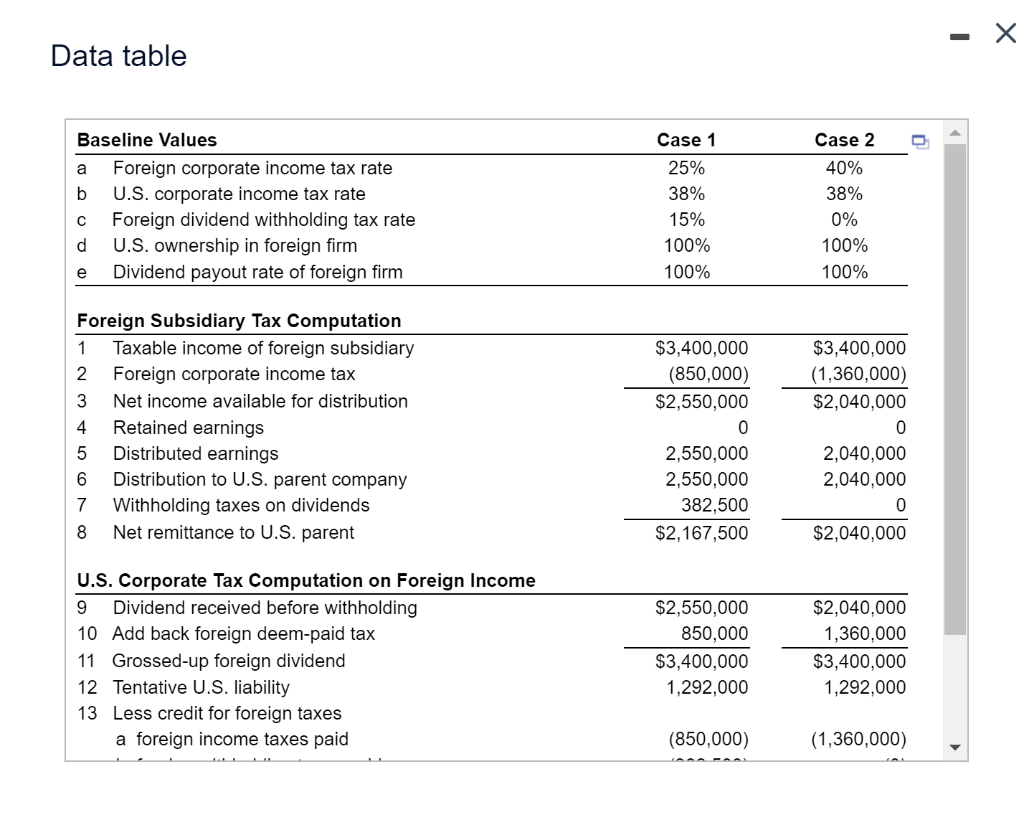
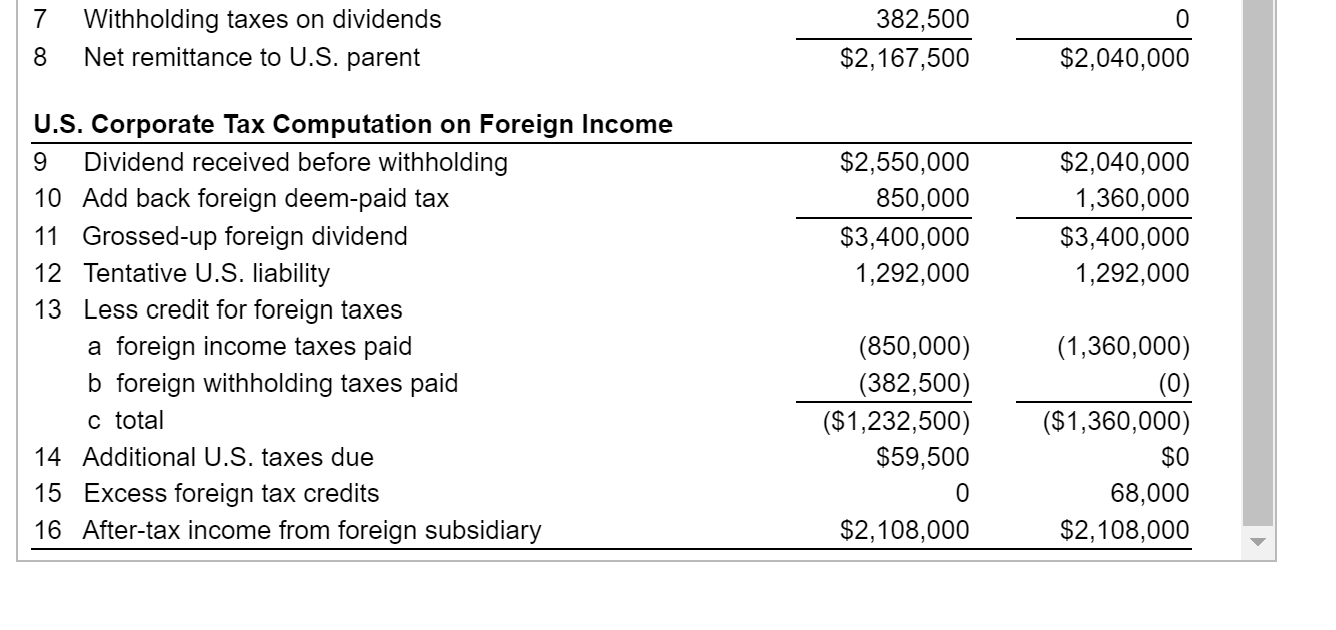
Avon's Foreign-Source Income. Avon is a U.S.-based direct seller of a wide array of products. Avon markets leading beauty, fashion, and home products in more than 100 countries. As part of the training in its corporate treasury offices, it has its interns build a spreadsheet analysis of the following hypothetical subsidiary earnings/distribution analysis. Use the tax analysis presented in the popup window for your basic structure, a. What is the total tax payment, foreign and domestic combined, for this income? b. What is the effective tax rate paid on this income by the U.S.-based parent company? c. What would be the total tax payment and effective tax rate if the foreign corporate tax rate was 40% and there were no withholding taxes on dividends? d. What would be the total tax payment and effective tax rate if the income was earned by a branch of the U.S. corporation? - Data table a Baseline Values Foreign corporate income tax rate b U.S. corporate income tax rate Foreign dividend withholding tax rate d U.S. ownership in foreign firm e Dividend payout rate of foreign firm Case 1 25% 38% 15% 100% 100% Case 2 40% 38% 0% 100% 100% Foreign Subsidiary Tax Computation 1 Taxable income of foreign subsidiary 2 Foreign corporate income tax 3 Net income available for distribution 4 Retained earnings 5 Distributed earnings 6 Distribution to U.S. parent company 7 Withholding taxes on dividends 8 Net remittance to U.S. parent $3,400,000 (850,000) $2,550,000 0 2,550,000 2,550,000 382,500 $2,167,500 $3,400,000 (1,360,000) $2,040,000 0 2,040,000 2,040,000 0 $2,040,000 U.S. Corporate Tax Computation on Foreign Income 9 Dividend received before withholding 10 Add back foreign deem-paid tax 11 Grossed-up foreign dividend 12 Tentative U.S. liability 13 Less credit for foreign taxes a foreign income taxes paid $2,550,000 850,000 $3,400,000 1,292,000 $2,040,000 1,360,000 $3,400,000 1,292,000 (850,000) (1,360,000) 7 Withholding taxes on dividends Net remittance to U.S. parent 382,500 $2,167,500 8 $2,040,000 $2,550,000 850,000 $3,400,000 1,292,000 $2,040,000 1,360,000 $3,400,000 1,292,000 U.S. Corporate Tax Computation on Foreign Income 9 Dividend received before withholding 10 Add back foreign deem-paid tax 11 Grossed-up foreign dividend 12 Tentative U.S. liability 13 Less credit for foreign taxes a foreign income taxes paid b foreign withholding taxes paid C total 14 Additional U.S. taxes due 15 Excess foreign tax credits 16 After-tax income from foreign subsidiary (850,000) (382,500) ($1,232,500) $59,500 (1,360,000) (0) ($1,360,000) $0 68,000 $2,108,000 $2,108,000 Avon's Foreign-Source Income. Avon is a U.S.-based direct seller of a wide array of products. Avon markets leading beauty, fashion, and home products in more than 100 countries. As part of the training in its corporate treasury offices, it has its interns build a spreadsheet analysis of the following hypothetical subsidiary earnings/distribution analysis. Use the tax analysis presented in the popup window for your basic structure, a. What is the total tax payment, foreign and domestic combined, for this income? b. What is the effective tax rate paid on this income by the U.S.-based parent company? c. What would be the total tax payment and effective tax rate if the foreign corporate tax rate was 40% and there were no withholding taxes on dividends? d. What would be the total tax payment and effective tax rate if the income was earned by a branch of the U.S. corporation? - Data table a Baseline Values Foreign corporate income tax rate b U.S. corporate income tax rate Foreign dividend withholding tax rate d U.S. ownership in foreign firm e Dividend payout rate of foreign firm Case 1 25% 38% 15% 100% 100% Case 2 40% 38% 0% 100% 100% Foreign Subsidiary Tax Computation 1 Taxable income of foreign subsidiary 2 Foreign corporate income tax 3 Net income available for distribution 4 Retained earnings 5 Distributed earnings 6 Distribution to U.S. parent company 7 Withholding taxes on dividends 8 Net remittance to U.S. parent $3,400,000 (850,000) $2,550,000 0 2,550,000 2,550,000 382,500 $2,167,500 $3,400,000 (1,360,000) $2,040,000 0 2,040,000 2,040,000 0 $2,040,000 U.S. Corporate Tax Computation on Foreign Income 9 Dividend received before withholding 10 Add back foreign deem-paid tax 11 Grossed-up foreign dividend 12 Tentative U.S. liability 13 Less credit for foreign taxes a foreign income taxes paid $2,550,000 850,000 $3,400,000 1,292,000 $2,040,000 1,360,000 $3,400,000 1,292,000 (850,000) (1,360,000) 7 Withholding taxes on dividends Net remittance to U.S. parent 382,500 $2,167,500 8 $2,040,000 $2,550,000 850,000 $3,400,000 1,292,000 $2,040,000 1,360,000 $3,400,000 1,292,000 U.S. Corporate Tax Computation on Foreign Income 9 Dividend received before withholding 10 Add back foreign deem-paid tax 11 Grossed-up foreign dividend 12 Tentative U.S. liability 13 Less credit for foreign taxes a foreign income taxes paid b foreign withholding taxes paid C total 14 Additional U.S. taxes due 15 Excess foreign tax credits 16 After-tax income from foreign subsidiary (850,000) (382,500) ($1,232,500) $59,500 (1,360,000) (0) ($1,360,000) $0 68,000 $2,108,000 $2,108,000









