Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
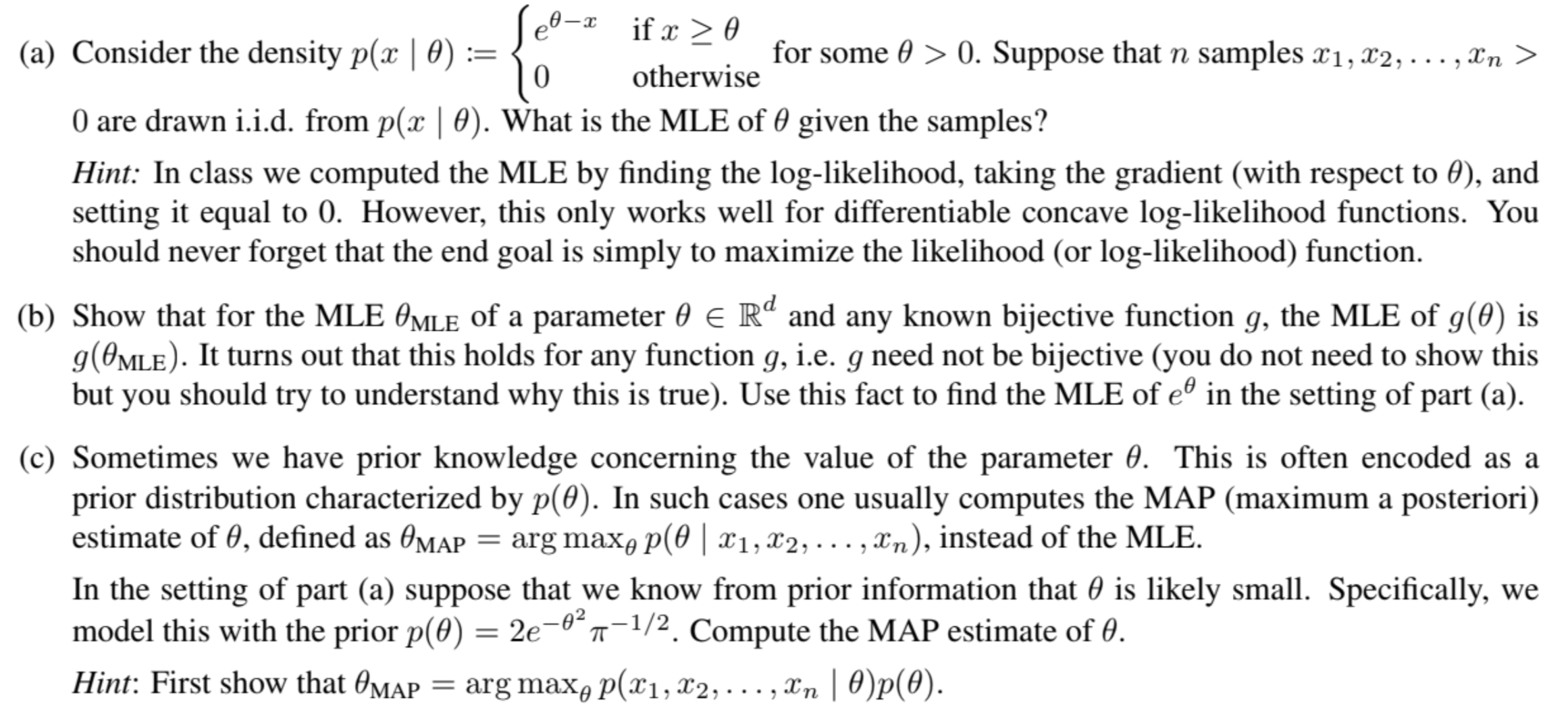
Question
1 Approved Answer
( b ) Show that for the MLE M L E of a parameter i n R d and any known bijective function g ,
b Show that for the MLE of a parameter and any known bijective function the MLE of is
It turns out that this holds for any function ie need not be bijective you do not need to show this
but you should try to understand why this is true Use this fact to find the MLE of in the setting of part a
c Sometimes we have prior knowledge concerning the value of the parameter This is often encoded as a
prior distribution characterized by In such cases one usually computes the MAP maximum a posteriori
estimate of defined as dots, instead of the MLE.
In the setting of part a suppose that we know from prior information that is likely small. Specifically, we
model this with the prior Compute the MAP estimate of
Hint: First show that dots,
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


