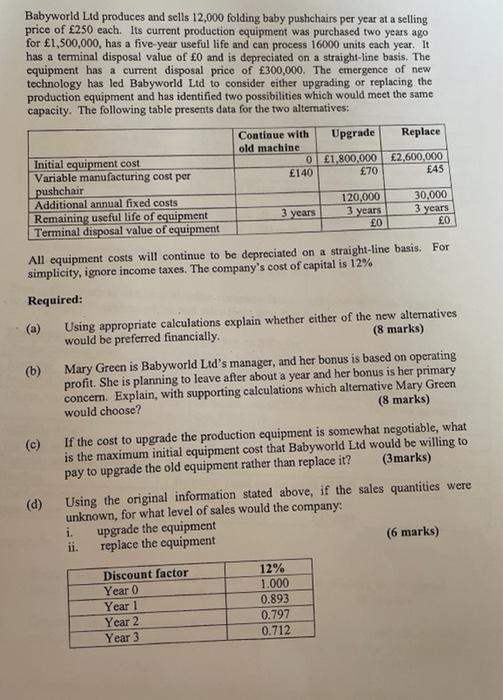
Babyworld Ltd produces and sells 12,000 folding baby pushchairs per year at a selling price of 250 each. Its current production equipment was purchased two years ago for 1,500,000, has a five-year useful life and can process 16000 units each year. It has a terminal disposal value of 0 and is depreciated on a straight-line basis. The equipment has a current disposal price of 300,000. The emergence of new technology has led Babyworld Ltd to consider either upgrading or replacing the production equipment and has identified two possibilities which would meet the same capacity. The following table presents data for the two alternatives: Continue with Upgrade Replace old machine Initial equipment cost 0 1,800,000 2,600,000 Variable manufacturing cost per 140 70 45 pushchair Additional annual fixed costs 120,000 30.000 3 years Remaining useful life of equipment 3 years 3 years 0 0 Terminal disposal value of equipment All equipment costs will continue to be depreciated on a straight-line basis. For simplicity, ignore income taxes. The company's cost of capital is 12% Required: Using appropriate calculations explain whether either of the new alternatives would be preferred financially. (8 marks) (b) Mary Green is Babyworld Ltd's manager, and her bonus is based on operating profit. She is planning to leave after about a year and her bonus is her primary concern. Explain, with supporting calculations which alternative Mary Green would choose? (8 marks) (c) If the cost to upgrade the production equipment is somewhat negotiable, what is the maximum initial equipment cost that Babyworld Ltd would be willing to pay to upgrade the old equipment rather than replace it? (3marks) Using the original information stated above, if the sales quantities were unknown, for what level of sales would the company: upgrade the equipment ii. replace the equipment (6 marks) (d) Discount factor Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 12% 1.000 0.893 0.797 0.712 Babyworld Ltd produces and sells 12,000 folding baby pushchairs per year at a selling price of 250 each. Its current production equipment was purchased two years ago for 1,500,000, has a five-year useful life and can process 16000 units each year. It has a terminal disposal value of 0 and is depreciated on a straight-line basis. The equipment has a current disposal price of 300,000. The emergence of new technology has led Babyworld Ltd to consider either upgrading or replacing the production equipment and has identified two possibilities which would meet the same capacity. The following table presents data for the two alternatives: Continue with Upgrade Replace old machine Initial equipment cost 0 1,800,000 2,600,000 Variable manufacturing cost per 140 70 45 pushchair Additional annual fixed costs 120,000 30.000 3 years Remaining useful life of equipment 3 years 3 years 0 0 Terminal disposal value of equipment All equipment costs will continue to be depreciated on a straight-line basis. For simplicity, ignore income taxes. The company's cost of capital is 12% Required: Using appropriate calculations explain whether either of the new alternatives would be preferred financially. (8 marks) (b) Mary Green is Babyworld Ltd's manager, and her bonus is based on operating profit. She is planning to leave after about a year and her bonus is her primary concern. Explain, with supporting calculations which alternative Mary Green would choose? (8 marks) (c) If the cost to upgrade the production equipment is somewhat negotiable, what is the maximum initial equipment cost that Babyworld Ltd would be willing to pay to upgrade the old equipment rather than replace it? (3marks) Using the original information stated above, if the sales quantities were unknown, for what level of sales would the company: upgrade the equipment ii. replace the equipment (6 marks) (d) Discount factor Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 12% 1.000 0.893 0.797 0.712