Background information is listed first then the questions listed after. Will upvote

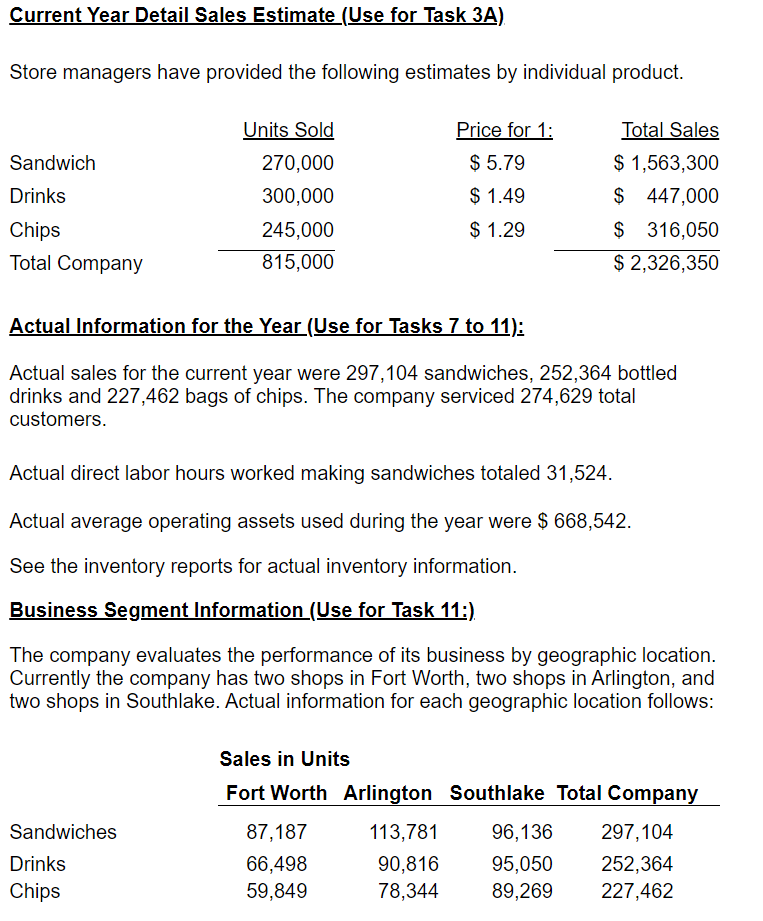
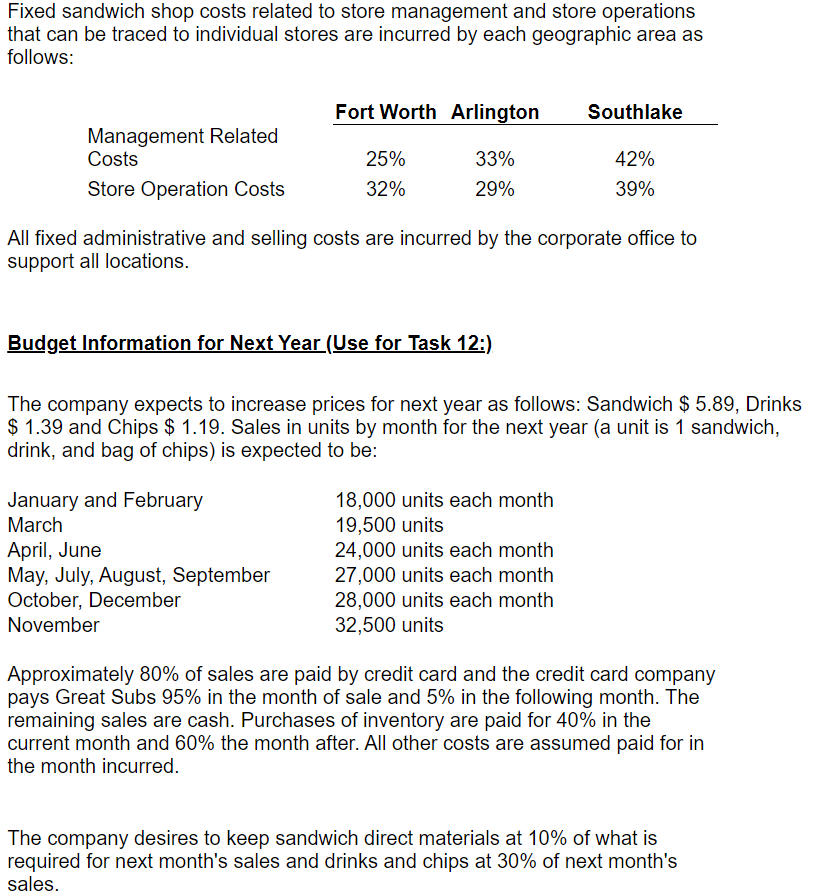

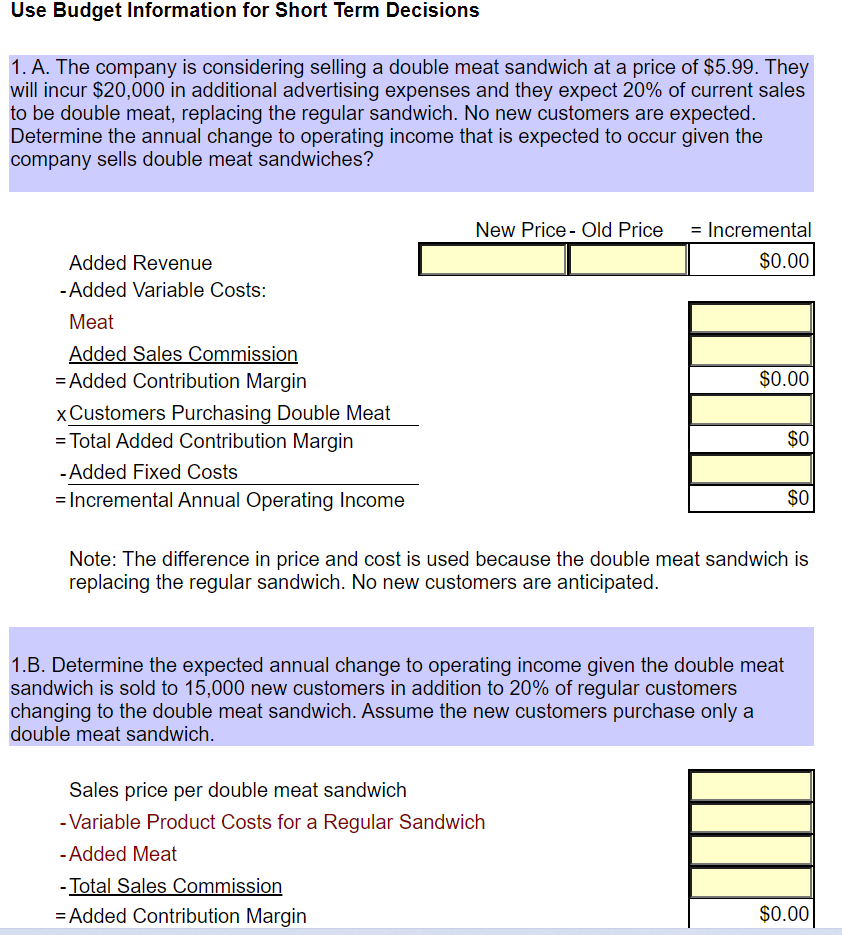


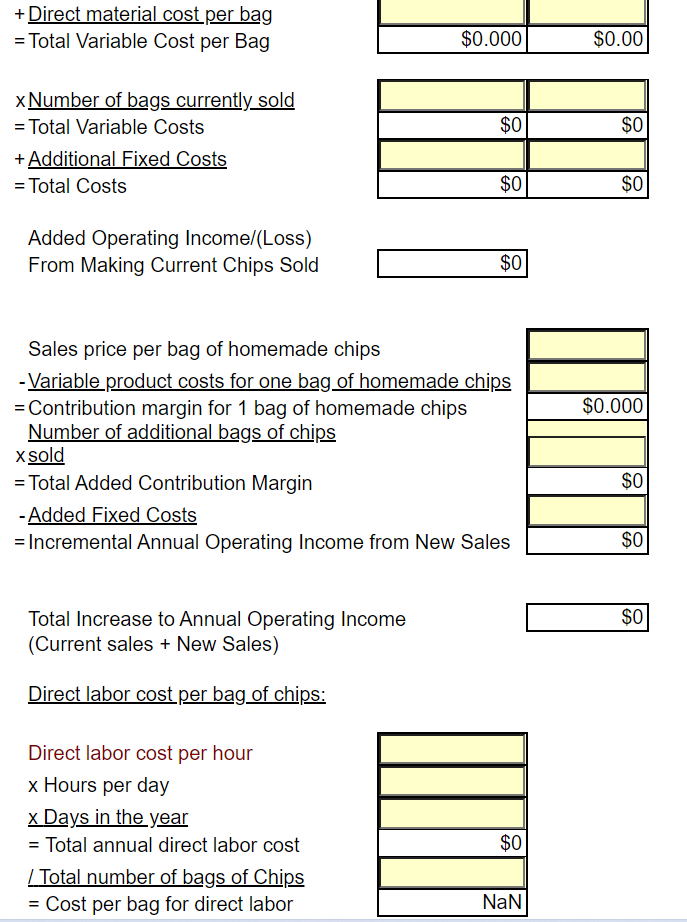
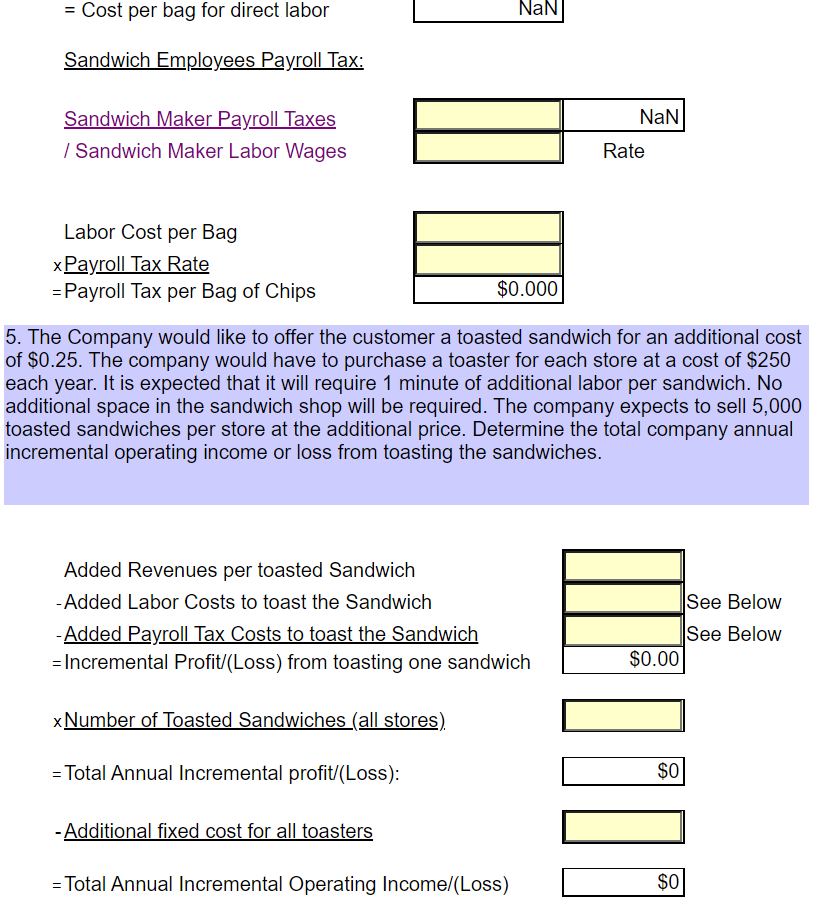
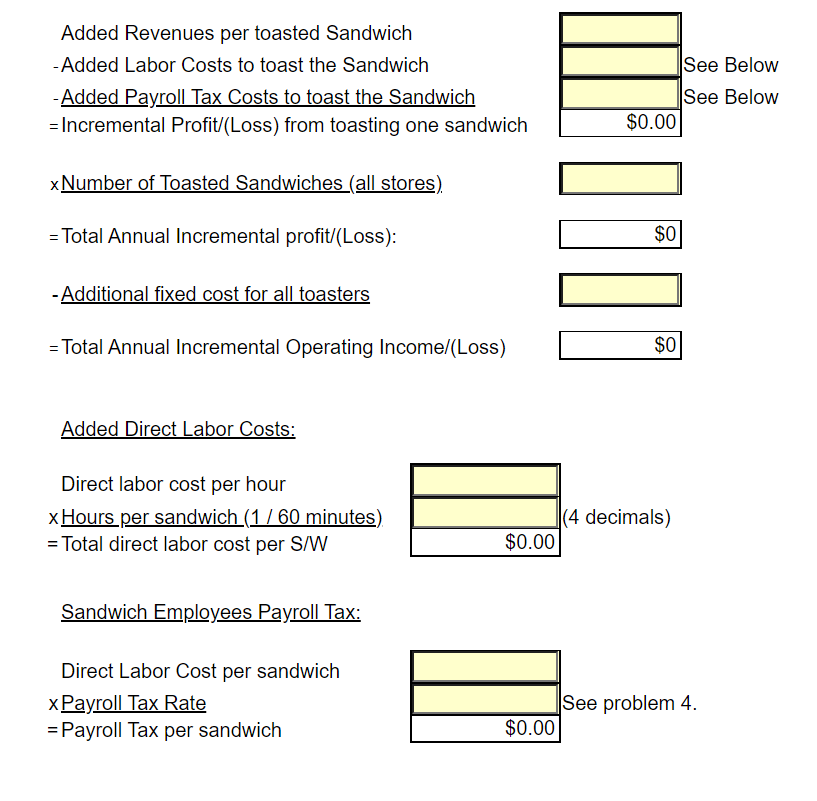
Great Subs, Inc. sells 8 inch sub sandwiches. All sandwiches are sold for the same price of $ 5.79 each. Bottled drinks are sold for $ 1.49 each and bags of potato chips are sold for $1.29 each. All sandwiches are made to order. It is estimated that each store can sell a maximum of 75,000 sandwiches each year. The company owns 6 sandwich shops. The company estimates that making a sandwich requires the following: Bread: 8 inches at $ 0.06 per inch Meat: 5 ounces at $ 0.18 per ounce Cheese: 2 slices at $ 0.22 per slice Condiments (lettuce, pickles, etc.) are not tracked per sandwich. It is expected to take an average of 0.10 hours to make a sandwich and sandwich makers are expected to be paid $8.45 per hour. Manufacturing overhead consists of the costs to operate the store and is allocated to sandwiches only based on direct labor hours. The company purchases bottled drinks and bags of potato chips for an estimated average cost of $0.71 for one bottle and $0.61 for one bag of potato chips. Bottled drinks and packages of chips are considered to be finished goods and are sold as purchased. Store managers are paid a sales commission of 1% of sales dollars. Average operating assets for the year are expected to be $725,000. Current Year Sales Estimate (Use for Tasks 1 through 6, except Task 3A): Total sales for the current year are estimated to be 269,000 units. A unit is a sandwich, bottled drink and a bags of chips. Each customer will not order all three products; however, sales are expected to average 269,000 of each product for all customers. Use budget information for cost volume profit analysis. Current Year Detail Sales Estimate (Use for Task 3A) Store managers have provided the following estimates by individual product. Units Sold Sandwich Price for 1: $ 5.79 $ 1.49 Drinks 270,000 300,000 245,000 815,000 Total Sales $ 1,563,300 $ 447,000 $ $ 316,050 $ 2,326,350 $ 1.29 Chips Total Company Actual Information for the Year (Use for Tasks 7 to 11); Actual sales for the current year were 297,104 sandwiches, 252,364 bottled drinks and 227,462 bags of chips. The company serviced 274,629 total customers. Actual direct labor hours worked making sandwiches totaled 31,524. Actual average operating assets used during the year were $ 668,542. See the inventory reports for actual inventory information. Business Segment Information (Use for Task 11:) The company evaluates the performance of its business by geographic location. Currently the company has two shops in Fort Worth, two shops in Arlington, and two shops in Southlake. Actual information for each geographic location follows: Sales in Units Fort Worth Arlington Southlake Total Company Sandwiches Drinks Chips 87,187 66,498 59,849 113,781 90,816 78,344 96,136 95,050 89,269 297,104 252,364 227,462 Fixed sandwich shop costs related to store management and store operations that can be traced to individual stores are incurred by each geographic area as follows: Fort Worth Arlington Southlake Management Related Costs Store Operation Costs 25% 32% 33% 29% 42% 39% All fixed administrative and selling costs are incurred by the corporate office to support all locations. Budget Information for Next Year (Use for Task 12:) The company expects to increase prices for next year as follows: Sandwich $ 5.89, Drinks $ 1.39 and Chips $ 1.19. Sales in units by month for the next year (a unit is 1 sandwich, drink, and bag of chips) is expected to be: January and February March April, June May, July, August, September October, December November 18,000 units each month 19,500 units 24,000 units each month 27,000 units each month 28,000 units each month 32,500 units Approximately 80% of sales are paid by credit card and the credit card company pays Great Subs 95% in the month of sale and 5% in the following month. The remaining sales are cash. Purchases of inventory are paid for 40% in the current month and 60% the month after. All other costs are assumed paid for in the month incurred. The company desires to keep sandwich direct materials at 10% of what is required for next month's sales and drinks and chips at 30% of next month's sales. The company desires to keep sandwich direct materials at 10% of what is required for next month's sales and drinks and chips at 30% of next month's sales. The company expects the following costs to be incurred next year: (includes depreciation) Total Variable Manufacturing Overhead Total Fixed Manufacturing Overhead Total Fixed Administrative Expense Total Fixed Selling Expense Sales Commission $ 200,000 $ 525,000 $ 320,000 $ 60,000 1% of sales dollars Depreciation expense is expected to remain the same as the current year actual cost. The company has a line of credit in place. Borrowings can be made in increments of $ 1,000 and interest is paid at the end of March, June, September and December at an annual interest rate of 10%. The company desires to keep a minimum amount of cash on hand of $ 20,000. Use Budget Information for Short Term Decisions 1. A. The company is considering selling a double meat sandwich at a price of $5.99. They will incur $20,000 in additional advertising expenses and they expect 20% of current sales to be double meat, replacing the regular sandwich. No new customers are expected. Determine the annual change to operating income that is expected to occur given the company sells double meat sandwiches? New Price - Old Price = Incremental $0.00 Added Revenue -Added Variable Costs: Meat Added Sales Commission = Added Contribution Margin x Customers Purchasing Double Meat = Total Added Contribution Margin - Added Fixed Costs = Incremental Annual Operating Income $0.00 $0 $0 Note: The difference in price and cost is used because the double meat sandwich is replacing the regular sandwich. No new customers are anticipated. 1.B. Determine the expected annual change to operating income given the double meat sandwich is sold to 15,000 new customers in addition to 20% of regular customers changing to the double meat sandwich. Assume the new customers purchase only a double meat sandwich. Sales price per double meat sandwich - Variable Product Costs for a Regular Sandwich - Added Meat - Total Sales Commission = Added Contribution Margin $0.00 $0.00 - Total Sales Commission = Added Contribution Margin xCustomers Added = Total Contribution Margin from New Customers - Added Fixed Costs = Incremental Operating Income from Additional Customers $0 $0 + Incremental Operating Income from Customers that Switch (1.A.) = Total change to annual operating income: $0 2. The company is considering selling a wrap made out of an 8 inch wheat tortilla. The company intends to sell the wrap for $3.29 and expects 10,000 new customers to purchase the wrap. The wrap takes the same amount of labor to make as the sandwich and requires the same amount of meat, cheese, and condiments. Each wheat tortilla costs $0.15. Determine the additional annual operating income that is expected to be earned from the wheat tortilla wrap? Sales price for a wheat tortilla - Variable Product Costs (same as a regular sandwich) + Cost of Bread that is saved -Cost of the tortilla -Sales Commission = Contribution Margin from 1 Wheat Tortilla Sandwich xCustomers Added = Total Contribution Margin from Wheat Tortilla Sandwiches - Added Fixed Costs = Incremental Operating Income from Wheat Tortilla Sandwiches $0.00 $0 $0 3. The Company has been given an order from a nonprofit organization for 500 sandwiches. The organization is offering to pay $2.75 per sandwich. No sales commission will be paid on the order. It will cost an additional $35 to deliver the order. Determine the incremental operating income from the special order. $0.00 Sales Price per Sandwich - Variable Product Costs for 1 Sandwich = Contribution Margin for 1 Sandwich xNumber of Sandwiches in the Special Order = Total Added Contribution Margin - Added Fixed Costs = Incremental Operating Income $0 $0 4. The Company believes that home-made chips will increase chip sales. The company has determined that if it purchases a fryer for $5,000 and hires additional labor 5 hours per day for 350 days a year that it can make all chips sold at all stores. The cost of potatoes is expected to be $0.22 for each bag of chips. The bags will cost $0.05 each. Fryer grease and salt for the entire year is expected to be $1,200 (treat as a fixed cost because the grease must be changed each week.) The fryer will be replaced each year. No additional space in the sandwich shop will be required. The company expects to sell 250,000 bags of homemade chips for $0.99 per bag. Use the detail sales projection for expected purchased chips sales. Determine the incremental annual operating income or loss from making their own chips. Make Buy Cost to Buy per Unit Direct labor cost per bag (see below) +Payroll tax per bag (see below) + Direct material cost per bag = Total Variable Cost per Bag = $0.000 $0.00 +Direct material cost per bag = Total Variable Cost per Bag $0.000 $0.00 $0 $0 x Number of bags currently sold = Total Variable Costs + Additional Fixed Costs = Total Costs $0 $0 Added Operating Income/(Loss) From Making Current Chips Sold $0 $0.000 Sales price per bag of homemade chips -Variable product costs for one bag of homemade chips = Contribution margin for 1 bag of homemade chips Number of additional bags of chips x sold = Total Added Contribution Margin - Added Fixed Costs = Incremental Annual Operating Income from New Sales $0 $0 $0 Total Increase to Annual Operating Income (Current sales + New Sales) Direct labor cost per bag of chips: Direct labor cost per hour x Hours per day x Days in the year = Total annual direct labor cost / Total number of bags of Chips = Cost per bag for direct labor $0 NaN = Cost per bag for direct labor NaN Sandwich Employees Payroll Tax: NaN Sandwich Maker Payroll Taxes / Sandwich Maker Labor Wages Rate Labor Cost per Bag xPayroll Tax Rate =Payroll Tax per Bag of Chips $0.000 5. The Company would like to offer the customer a toasted sandwich for an additional cost of $0.25. The company would have to purchase a toaster for each store at a cost of $250 each year. It is expected that it will require 1 minute of additional labor per sandwich. No additional space in the sandwich shop will be required. The company expects to sell 5,000 toasted sandwiches per store at the additional price. Determine the total company annual incremental operating income or loss from toasting the sandwiches. Added Revenues per toasted Sandwich -Added Labor Costs to toast the Sandwich - Added Payroll Tax Costs to toast the Sandwich = Incremental Profit/(Loss) from toasting one sandwich See Below See Below $0.00 xNumber of Toasted Sandwiches (all stores) HONOI Total Annual Incremental profit/(Loss): - Additional fixed cost for all toasters = Total Annual Incremental Operating Income (Loss) Added Revenues per toasted Sandwich - Added Labor Costs to toast the Sandwich - Added Payroll Tax Costs to toast the Sandwich = Incremental Profit/(Loss) from toasting one sandwich See Below See Below $0.00 xNumber of Toasted Sandwiches (all stores) LOLOGII = Total Annual Incremental profit/(Loss): $0 - Additional fixed cost for all toasters = Total Annual Incremental Operating Income/(Loss) $0 Added Direct Labor Costs: Direct labor cost per hour x Hours per sandwich (1/60 minutes) = Total direct labor cost per S/W (4 decimals) $0.00 Sandwich Employees Payroll Tax: Direct Labor Cost per sandwich x Payroll Tax Rate = Payroll Tax per sandwich See problem 4. $0.00 Great Subs, Inc. sells 8 inch sub sandwiches. All sandwiches are sold for the same price of $ 5.79 each. Bottled drinks are sold for $ 1.49 each and bags of potato chips are sold for $1.29 each. All sandwiches are made to order. It is estimated that each store can sell a maximum of 75,000 sandwiches each year. The company owns 6 sandwich shops. The company estimates that making a sandwich requires the following: Bread: 8 inches at $ 0.06 per inch Meat: 5 ounces at $ 0.18 per ounce Cheese: 2 slices at $ 0.22 per slice Condiments (lettuce, pickles, etc.) are not tracked per sandwich. It is expected to take an average of 0.10 hours to make a sandwich and sandwich makers are expected to be paid $8.45 per hour. Manufacturing overhead consists of the costs to operate the store and is allocated to sandwiches only based on direct labor hours. The company purchases bottled drinks and bags of potato chips for an estimated average cost of $0.71 for one bottle and $0.61 for one bag of potato chips. Bottled drinks and packages of chips are considered to be finished goods and are sold as purchased. Store managers are paid a sales commission of 1% of sales dollars. Average operating assets for the year are expected to be $725,000. Current Year Sales Estimate (Use for Tasks 1 through 6, except Task 3A): Total sales for the current year are estimated to be 269,000 units. A unit is a sandwich, bottled drink and a bags of chips. Each customer will not order all three products; however, sales are expected to average 269,000 of each product for all customers. Use budget information for cost volume profit analysis. Current Year Detail Sales Estimate (Use for Task 3A) Store managers have provided the following estimates by individual product. Units Sold Sandwich Price for 1: $ 5.79 $ 1.49 Drinks 270,000 300,000 245,000 815,000 Total Sales $ 1,563,300 $ 447,000 $ $ 316,050 $ 2,326,350 $ 1.29 Chips Total Company Actual Information for the Year (Use for Tasks 7 to 11); Actual sales for the current year were 297,104 sandwiches, 252,364 bottled drinks and 227,462 bags of chips. The company serviced 274,629 total customers. Actual direct labor hours worked making sandwiches totaled 31,524. Actual average operating assets used during the year were $ 668,542. See the inventory reports for actual inventory information. Business Segment Information (Use for Task 11:) The company evaluates the performance of its business by geographic location. Currently the company has two shops in Fort Worth, two shops in Arlington, and two shops in Southlake. Actual information for each geographic location follows: Sales in Units Fort Worth Arlington Southlake Total Company Sandwiches Drinks Chips 87,187 66,498 59,849 113,781 90,816 78,344 96,136 95,050 89,269 297,104 252,364 227,462 Fixed sandwich shop costs related to store management and store operations that can be traced to individual stores are incurred by each geographic area as follows: Fort Worth Arlington Southlake Management Related Costs Store Operation Costs 25% 32% 33% 29% 42% 39% All fixed administrative and selling costs are incurred by the corporate office to support all locations. Budget Information for Next Year (Use for Task 12:) The company expects to increase prices for next year as follows: Sandwich $ 5.89, Drinks $ 1.39 and Chips $ 1.19. Sales in units by month for the next year (a unit is 1 sandwich, drink, and bag of chips) is expected to be: January and February March April, June May, July, August, September October, December November 18,000 units each month 19,500 units 24,000 units each month 27,000 units each month 28,000 units each month 32,500 units Approximately 80% of sales are paid by credit card and the credit card company pays Great Subs 95% in the month of sale and 5% in the following month. The remaining sales are cash. Purchases of inventory are paid for 40% in the current month and 60% the month after. All other costs are assumed paid for in the month incurred. The company desires to keep sandwich direct materials at 10% of what is required for next month's sales and drinks and chips at 30% of next month's sales. The company desires to keep sandwich direct materials at 10% of what is required for next month's sales and drinks and chips at 30% of next month's sales. The company expects the following costs to be incurred next year: (includes depreciation) Total Variable Manufacturing Overhead Total Fixed Manufacturing Overhead Total Fixed Administrative Expense Total Fixed Selling Expense Sales Commission $ 200,000 $ 525,000 $ 320,000 $ 60,000 1% of sales dollars Depreciation expense is expected to remain the same as the current year actual cost. The company has a line of credit in place. Borrowings can be made in increments of $ 1,000 and interest is paid at the end of March, June, September and December at an annual interest rate of 10%. The company desires to keep a minimum amount of cash on hand of $ 20,000. Use Budget Information for Short Term Decisions 1. A. The company is considering selling a double meat sandwich at a price of $5.99. They will incur $20,000 in additional advertising expenses and they expect 20% of current sales to be double meat, replacing the regular sandwich. No new customers are expected. Determine the annual change to operating income that is expected to occur given the company sells double meat sandwiches? New Price - Old Price = Incremental $0.00 Added Revenue -Added Variable Costs: Meat Added Sales Commission = Added Contribution Margin x Customers Purchasing Double Meat = Total Added Contribution Margin - Added Fixed Costs = Incremental Annual Operating Income $0.00 $0 $0 Note: The difference in price and cost is used because the double meat sandwich is replacing the regular sandwich. No new customers are anticipated. 1.B. Determine the expected annual change to operating income given the double meat sandwich is sold to 15,000 new customers in addition to 20% of regular customers changing to the double meat sandwich. Assume the new customers purchase only a double meat sandwich. Sales price per double meat sandwich - Variable Product Costs for a Regular Sandwich - Added Meat - Total Sales Commission = Added Contribution Margin $0.00 $0.00 - Total Sales Commission = Added Contribution Margin xCustomers Added = Total Contribution Margin from New Customers - Added Fixed Costs = Incremental Operating Income from Additional Customers $0 $0 + Incremental Operating Income from Customers that Switch (1.A.) = Total change to annual operating income: $0 2. The company is considering selling a wrap made out of an 8 inch wheat tortilla. The company intends to sell the wrap for $3.29 and expects 10,000 new customers to purchase the wrap. The wrap takes the same amount of labor to make as the sandwich and requires the same amount of meat, cheese, and condiments. Each wheat tortilla costs $0.15. Determine the additional annual operating income that is expected to be earned from the wheat tortilla wrap? Sales price for a wheat tortilla - Variable Product Costs (same as a regular sandwich) + Cost of Bread that is saved -Cost of the tortilla -Sales Commission = Contribution Margin from 1 Wheat Tortilla Sandwich xCustomers Added = Total Contribution Margin from Wheat Tortilla Sandwiches - Added Fixed Costs = Incremental Operating Income from Wheat Tortilla Sandwiches $0.00 $0 $0 3. The Company has been given an order from a nonprofit organization for 500 sandwiches. The organization is offering to pay $2.75 per sandwich. No sales commission will be paid on the order. It will cost an additional $35 to deliver the order. Determine the incremental operating income from the special order. $0.00 Sales Price per Sandwich - Variable Product Costs for 1 Sandwich = Contribution Margin for 1 Sandwich xNumber of Sandwiches in the Special Order = Total Added Contribution Margin - Added Fixed Costs = Incremental Operating Income $0 $0 4. The Company believes that home-made chips will increase chip sales. The company has determined that if it purchases a fryer for $5,000 and hires additional labor 5 hours per day for 350 days a year that it can make all chips sold at all stores. The cost of potatoes is expected to be $0.22 for each bag of chips. The bags will cost $0.05 each. Fryer grease and salt for the entire year is expected to be $1,200 (treat as a fixed cost because the grease must be changed each week.) The fryer will be replaced each year. No additional space in the sandwich shop will be required. The company expects to sell 250,000 bags of homemade chips for $0.99 per bag. Use the detail sales projection for expected purchased chips sales. Determine the incremental annual operating income or loss from making their own chips. Make Buy Cost to Buy per Unit Direct labor cost per bag (see below) +Payroll tax per bag (see below) + Direct material cost per bag = Total Variable Cost per Bag = $0.000 $0.00 +Direct material cost per bag = Total Variable Cost per Bag $0.000 $0.00 $0 $0 x Number of bags currently sold = Total Variable Costs + Additional Fixed Costs = Total Costs $0 $0 Added Operating Income/(Loss) From Making Current Chips Sold $0 $0.000 Sales price per bag of homemade chips -Variable product costs for one bag of homemade chips = Contribution margin for 1 bag of homemade chips Number of additional bags of chips x sold = Total Added Contribution Margin - Added Fixed Costs = Incremental Annual Operating Income from New Sales $0 $0 $0 Total Increase to Annual Operating Income (Current sales + New Sales) Direct labor cost per bag of chips: Direct labor cost per hour x Hours per day x Days in the year = Total annual direct labor cost / Total number of bags of Chips = Cost per bag for direct labor $0 NaN = Cost per bag for direct labor NaN Sandwich Employees Payroll Tax: NaN Sandwich Maker Payroll Taxes / Sandwich Maker Labor Wages Rate Labor Cost per Bag xPayroll Tax Rate =Payroll Tax per Bag of Chips $0.000 5. The Company would like to offer the customer a toasted sandwich for an additional cost of $0.25. The company would have to purchase a toaster for each store at a cost of $250 each year. It is expected that it will require 1 minute of additional labor per sandwich. No additional space in the sandwich shop will be required. The company expects to sell 5,000 toasted sandwiches per store at the additional price. Determine the total company annual incremental operating income or loss from toasting the sandwiches. Added Revenues per toasted Sandwich -Added Labor Costs to toast the Sandwich - Added Payroll Tax Costs to toast the Sandwich = Incremental Profit/(Loss) from toasting one sandwich See Below See Below $0.00 xNumber of Toasted Sandwiches (all stores) HONOI Total Annual Incremental profit/(Loss): - Additional fixed cost for all toasters = Total Annual Incremental Operating Income (Loss) Added Revenues per toasted Sandwich - Added Labor Costs to toast the Sandwich - Added Payroll Tax Costs to toast the Sandwich = Incremental Profit/(Loss) from toasting one sandwich See Below See Below $0.00 xNumber of Toasted Sandwiches (all stores) LOLOGII = Total Annual Incremental profit/(Loss): $0 - Additional fixed cost for all toasters = Total Annual Incremental Operating Income/(Loss) $0 Added Direct Labor Costs: Direct labor cost per hour x Hours per sandwich (1/60 minutes) = Total direct labor cost per S/W (4 decimals) $0.00 Sandwich Employees Payroll Tax: Direct Labor Cost per sandwich x Payroll Tax Rate = Payroll Tax per sandwich See problem 4. $0.00
















