Question
Balance Sheet 2011 and 2012 1. You sold some fixed assets on January 1 for a gain of $80,000. The original basis of the assets
 Balance Sheet 2011 and 2012
Balance Sheet 2011 and 2012
1. You sold some fixed assets on January 1 for a gain of $80,000. The original basis of the assets sold was $4,500,000 and the accumulated depreciation was $1,125,000.
2. During 2011, you acquired a stake in one of your suppliers by investing $1 million in cash in their common stock. This investment gives you 20% of the company and two seats on their board of directors. The investment in Never Finished Corporation was made right at the end of 2011 and during 2012, NFC earned an after tax profit of $800,000. They also distributed a dividend to you of $40,000 in cash and $60,000 of additional stock.
3. You purchased additional fixed assets on June 30 for $750,000 using money you borrowed from the bank.
4. On December 31, 2012, you paid off $2,250,000 of your outstanding bank loans and made sure there was no interest payable balance at the end of the year.
5. You paid dividends to the shareholders during 2012 of $1,000,000.
6. To raise some additional funds, you sold common stock during the year. You sold 500,000 additional shares at an average price of $10 per share. You paid your attorneys and accountants a total of $800,000 for offering assistance.
7. You made income tax payments during the year and your effective tax rate is 40%.
8. You bought some more fixed assets on December 31, 2012 in exchange for a note payable to the seller of the fixed assets for a total purchase price of $2 million.
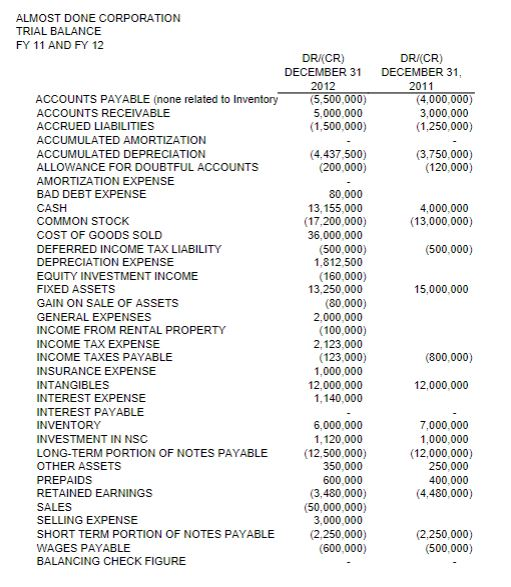
ALMOST DONE CORPORATION TRIAL BALANCE FY 11 AND FY 12 DR (CR) DECEMBER 31 2012 (5,500,000) 5.000.000 (1.500.000) DR (CR) DECEMBER 31, 2011 (4,000,000) 3,000,000 (1.250,000) (4.437 500) (200,000) (3,750,000) (120,000) 4,000,000 (13,000,000) (500,000) ACCOUNTS PAYABLE (none related to inventory ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE ACCRUED LIABILITIES ACCUMULATED AMORTIZATION ACCUMULATED DEPRECIATION ALLOWANCE FOR DOUBTFUL ACCOUNTS AMORTIZATION EXPENSE BAD DEBT EXPENSE CASH COMMON STOCK COST OF GOODS SOLD DEFERRED INCOME TAX LIABILITY DEPRECIATION EXPENSE EQUITY INVESTMENT INCOME FIXED ASSETS GAIN ON SALE OF ASSETS GENERAL EXPENSES INCOME FROM RENTAL PROPERTY INCOME TAX EXPENSE INCOME TAXES PAYABLE INSURANCE EXPENSE INTANGIBLES INTEREST EXPENSE INTEREST PAYABLE INVENTORY INVESTMENT IN NSC LONG-TERM PORTION OF NOTES PAYABLE OTHER ASSETS PREPAIDS RETAINED EARNINGS SALES SELLING EXPENSE SHORT TERM PORTION OF NOTES PAYABLE WAGES PAYABLE BALANCING CHECK FIGURE 80.000 13,155.000 (17,200,000) 36,000,000 (500.000) 1.812.500 (160.000) 13,250.000 (80.000) 2,000,000 (100,000) 2.123.000 (123.000) 1.000.000 12.000.000 1.140.000 15,000,000 (800,000) 12,000,000 6.000.000 1. 120.000 (12.500.000) 350.000 600.000 3.480.000 (50.000.000 3.000.000 2.250.000) (600.000) 7,000,000 1.000.000 (12,000,000) 250,000 400.000 (4.480,000) (2.250,000) (500.000)Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


