Question: Base class: Wolf Constructor Variable: gender (public, string), age (public, int) Functions: void eat(), hunt() * Each function displays the behavior of the wolf

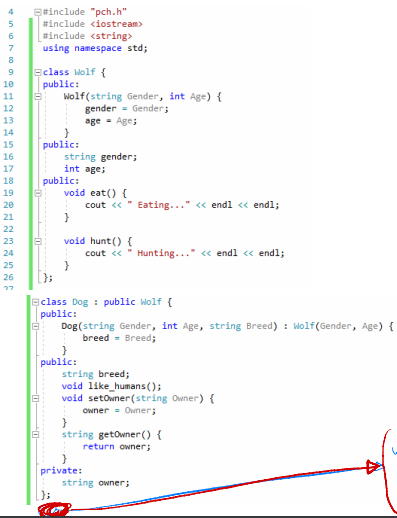

Base class: Wolf Constructor Variable: gender (public, string), age (public, int) Functions: void eat(), hunt() * Each function displays the behavior of the wolf (eating, hunting). * Functions are implemented inside the class. Derived class: Dog Constructor Variable: breed (public, string), owner (private, string) Functions: void like_humans(), set, get methods (for private variable, owner) * Each function displays the behavior of the wolf (like humans...). * The like_humans() is implemented outside of the class. Objects & Display Two object: wolf, puppy setOwner() for puppy => John Display: all of variables & functions TFCTBTOH=22982222 5 6 7 11 10 public: 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 23 24 #include "pch.h" #include #include using namespace std; 25 26 27 Eclass Wolf { Wolf (string Gender, int Age) { gender Gender; age = Age; public: string gender; int age; public: void eat() { D}; } void hunt() { cout < Add the code below: Void Dog :: like human () { Cart < < " like human"
Step by Step Solution
3.48 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
It seems you have a class diagram and a task to implement a simple objectoriented program in C The program describes a base class Wolf and a derived c... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


