Based on the output images attached answer the following questions
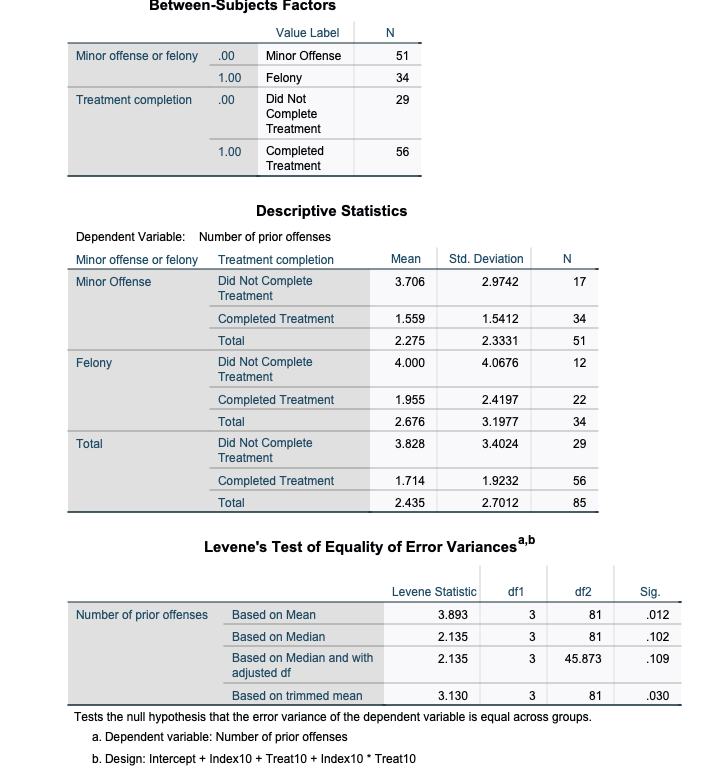
- Which group had the largest sample size (biggestN)?
a.adolescents who committed a FELONY & COMPLETED TREATMENT
b.adolescents who committed a FELONY & DID NOT complete TREATMENT
c.adolescents who committed a MINOR OFFENSE & DID NOT complete TREATMENT
d.adolescents who committed a MINOR OFFENSE & COMPLETED TREATMENT
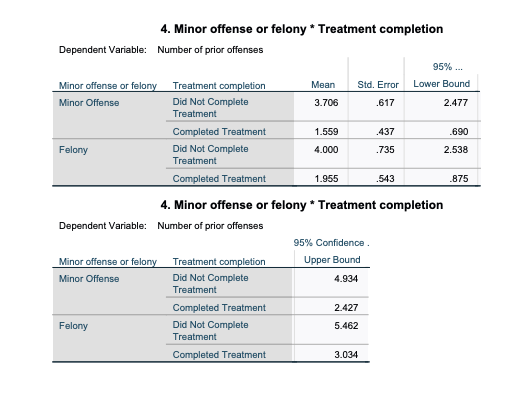
2.How many PRIOR OFFENSES did adolescents who committed a MINOR OFFENSE & DID NOT COMPLETE TREATMENT?
3.How many PRIOR OFFENSES did adolescents who committed a FELONY & DID COMPLETE TREATMENT?
a.3.71
b.12.50
c.1.56
d.4.00
e.1.96
4.Using a 2 x 2 (Type [minor offense, felony] by Treatment Completion [Did Not Complete, Complete]) Factorial ANOVA, assess which condition of juvenile offenders had the most number of prior offenses with the law.
Question: Which is the correct APA statistical sentence for Levene's Test?
a.F (3.893) = 81, p = .109
b.F(1, 81) = 12.50, p = .001
c.F(3, 81) = 3.89, p = .012
d.F(81, 3) = .012, p = 3.89
e.F(1, 81) = .338, p = .562
5.USING THE STANDARD ALPHA LEVEL (.05): How would you interpret this Levene's test?
Select one:
a.Reject the null hypothesis: DO NOT assume equal variances
b.Fail to Reject the null hypothesis: assume equal variances
c.Reject the null hypothesis: assume equal variances
d.Fail to Reject the null hypothesis: DO NOT assume equal variances
e.not enough information to tell
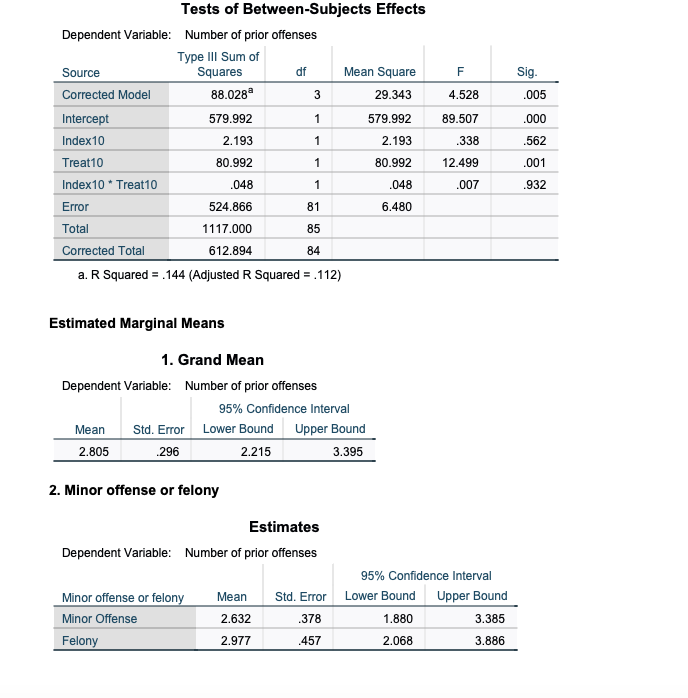
6.REGARDLESS OF THE ASSUMPTION CHECK, just proceed:
Which of the main effects were significant, if any?
Select one:
a.Index10
b.Treat10
c.Treat10*Index10
d.There are no significant effects in this analysis
7.REGARDLESS OF THE ASSUMPTION CHECK, just proceed:
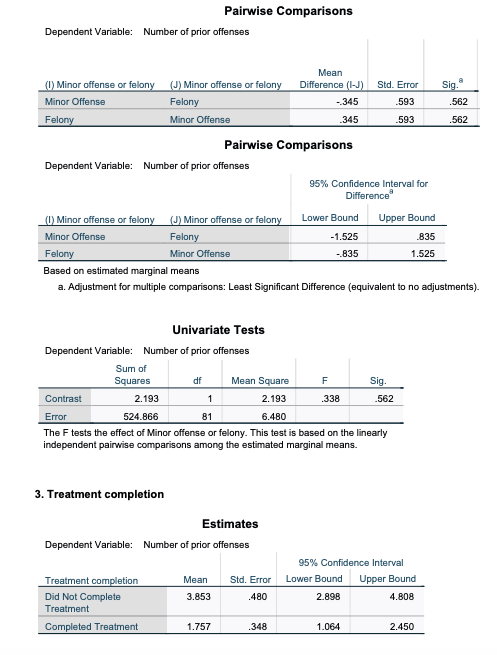
Youth who committed a felony hadSIGNIFICANTLY MOREprior offenses than Youth who only committed a misdemeanor (minor offense). True/False
Select one:
True
False
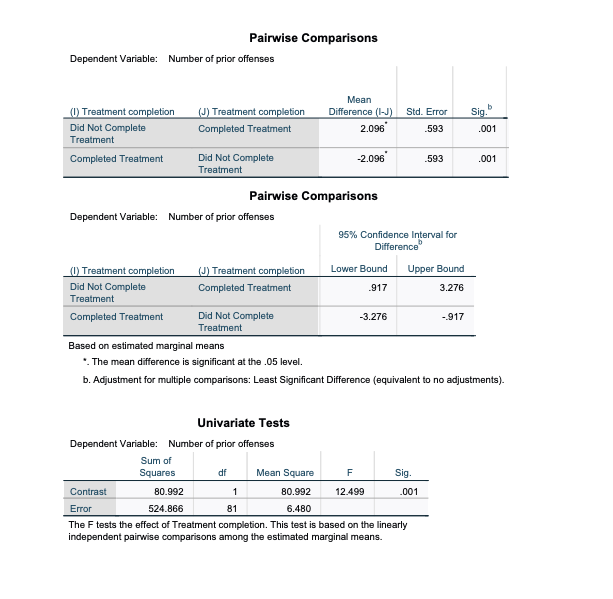
8REGARDLESS OF THE ASSUMPTION CHECK, just proceed:
Youth who completed treatment hadSIGNIFICANTLY LESSPRIOR OFFENSES than Youth who DID NOT complete treatment (treat10). True/False
Select one:
True
False
9.REGARDLESS OF THE ASSUMPTION CHECK, just proceed:
Which is the correctly written APA main effect for the significant effect, if any?
Select one:
a.F(3, 85) = 12.50,p= .001
b.F(1, 81) = 12.50,p= .001
c.F(1, 81) = 0.34,p= .562
d.There were no significant effects
e.F(1, 81) = 0.01,p= .932
10.
Which of the following is the statistical sentence for the interaction effect?
Select one:
a.F(1, 81) = 0.34, p = .562
b.F(1, 81) = 0.01, p = .932
c.F(1, 81) = 12.50, p = .001
d.F(3, 81) = 4.53, p = .005
Between-Subjects Factors Value Label N Minor offense or felony .00 Minor Offense 51 1.00 Felony 34 Treatment completion .00 Did Not 29 Complete Treatment 1.00 Completed 56 Treatment Descriptive Statistics Dependent Variable: Number of prior offenses Minor offense or felony Treatment completion Mean Std. Deviation N Minor Offense Did Not Complete 3.706 2.9742 17 Treatment Completed Treatment 1.559 1.5412 34 Total 2.275 2.3331 51 Felony Did Not Complete 4.000 4.0676 12 Treatment Completed Treatment 1.955 2.4197 22 Total 2.676 3.1977 34 Total Did Not Complete 3.828 3.4024 29 Treatment Completed Treatment 1.714 1.9232 56 Total 2.435 2.7012 85 Levene's Test of Equality of Error Variances a,b Levene Statistic df1 df2 Sig. Number of prior offenses Based on Mean 3.893 81 012 Based on Median 2.135 31 102 Based on Median and with 2.135 3 45.873 .109 adjusted of Based on trimmed mean 3.130 3 81 030 Tests the null hypothesis that the error variance of the dependent variable is equal across groups. a. Dependent variable: Number of prior offenses b. Design: Intercept + Index10 + Treat10 + Index10 * Treat10Tests of Between-Subjects Effects Dependent Variable: Number of prior offenses Type Ill Sum of Source Squares df Mean Square F Sig. Corrected Model 88.028 3 29.343 4.528 .005 Intercept 579.992 579.992 89.507 .000 Index10 2.193 2.193 338 562 Treat10 80.992 80.992 12.499 001 Index10 * Treat10 048 1 048 007 932 Error 524.866 81 6.480 Total 1117.000 85 Corrected Total 612.894 84 a. R Squared = .144 (Adjusted R Squared = .112) Estimated Marginal Means 1. Grand Mean Dependent Variable: Number of prior offenses 95% Confidence Interval Mean Std. Error Lower Bound Upper Bound 2.805 296 2.215 3.395 2. Minor offense or felony Estimates Dependent Variable: Number of prior offenses 95% Confidence Interval Minor offense or felony Mean Std. Error Lower Bound Upper Bound Minor Offense 2.632 378 1.880 3.385 Felony 2.977 457 2.068 3.886Pairwise Comparisons Dependent Variable: Number of prior offenses Mean (!) Minor offense or felony (J) Minor offense or felony Difference (I-J) Std. Error Sig. Minor Offense Felony -.345 593 562 Felony Minor Offense 345 593 .562 Pairwise Comparisons Dependent Variable: Number of prior offenses 95% Confidence Interval for Difference (1) Minor offense or felony (J) Minor offense or felony Lower Bound Upper Bound Minor Offense Felony -1.525 835 Felony Minor Offense .835 1.525 Based on estimated marginal means a. Adjustment for multiple comparisons: Least Significant Difference (equivalent to no adjustments). Univariate Tests Dependent Variable: Number of prior offenses Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig. Contrast 2.193 1 2.193 338 .562 Error 524.866 81 6.480 The F tests the effect of Minor offense or felony. This test is based on the linearly independent pairwise comparisons among the estimated marginal means. 3. Treatment completion Estimates Dependent Variable: Number of prior offenses 95% Confidence Interval Treatment completion Mean Std. Error Lower Bound Upper Bound Did Not Complete 3.853 480 2.898 4.808 Treatment Completed Treatment 1.757 348 1.064 2.450Pairwise Comparisons Dependent Variable: Number of prior offenses Mean (0) Treatment completion (J) Treatment completion Difference (I-J) Std. Error Sig. Did Not Complete Completed Treatment 2.096 593 001 Treatment Completed Treatment Did Not Complete -2.096 593 001 Treatment Pairwise Comparisons Dependent Variable: Number of prior offenses 95% Confidence Interval for Difference" (0) Treatment completion (J) Treatment completion Lower Bound Upper Bound Did Not Complete Completed Treatment 917 3.276 Treatment Completed Treatment Did Not Complete -3.276 -.917 Treatment Based on estimated marginal means *. The mean difference is significant at the .05 level. b. Adjustment for multiple comparisons: Least Significant Difference (equivalent to no adjustments)- Univariate Tests Dependent Variable: Number of prior offenses Sum of Squares df Mean Square sig. Contrast 80.992 80.992 12.499 001 Error 24.866 81 6.480 The F tests the effect of Treatment completion. This test is based on the linearly independent pairwise comparisons among the estimated marginal means.4. Minor offense or felony * Treatment completion Dependent Variable: Number of prior offenses 95% ... Minor offense or felony Treatment completion Mean Std. Error Lower Bound Minor Offense Did Not Complete 3.706 617 2.477 Treatment Completed Treatment 1.559 .437 690 Felony Did Not Complete 4.000 735 2.538 Treatment Completed Treatment 1.955 .543 .875 4. Minor offense or felony * Treatment completion Dependent Variable: Number of prior offenses 95% Confidence . Minor offense or felony Treatment completion Upper Bound Minor Offense Did Not Complete 4.934 Treatment Completed Treatment 2.427 Felony Did Not Complete 5.462 Treatment Completed Treatment 3.034