Question
BASIC JAVA CODE JAVA JAVA complete a programming project that incorporates inheritance The International Building Code (IBC) requires that all buildings and structures must be
BASIC JAVA CODE
JAVA
JAVA
complete a programming project that incorporates inheritance
The International Building Code (IBC) requires that all buildings and structures must be classified by group and occupancy according to the follow specifications: 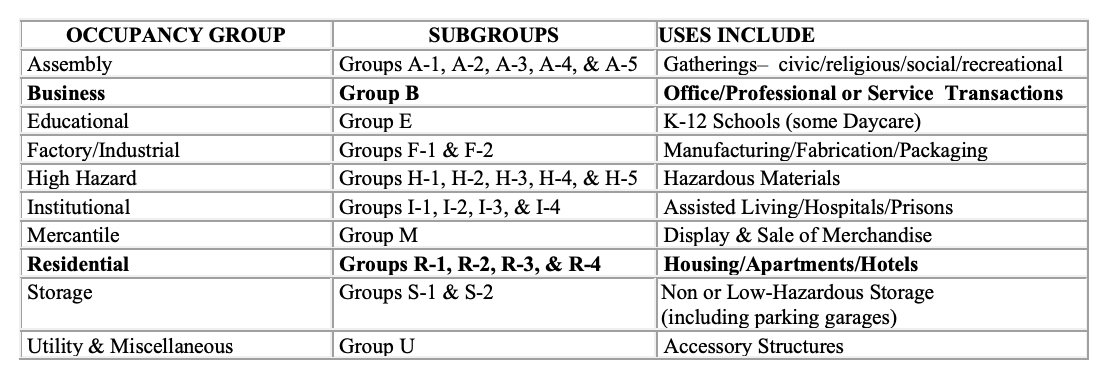
A local architecture firm has asked your company to develop a mapping application for all of its projects. Your Software Architecture Team has drafted the following UML Class Diagram with only two occupancy groups (Business and Residential) with which to get started.
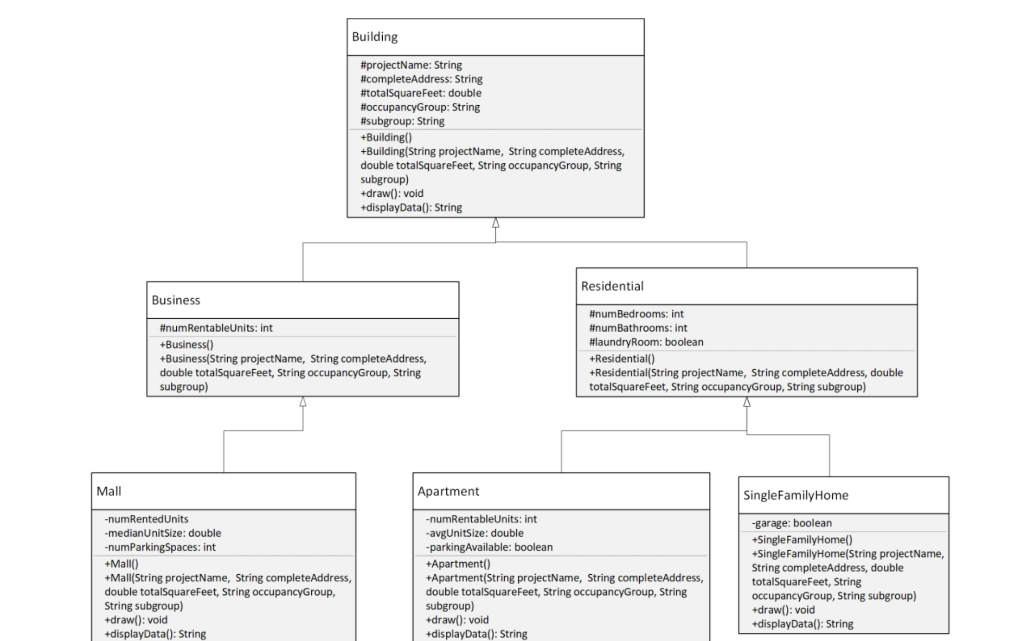
Using the UML Class Diagram write a prototype for the system with the following specifications: 1. Building class: this is the superclass for all objects in our system. It contains the following
instance members/constructors/methods:
-
projectName the name of the building project e.g. Smith House.
-
completeAddress the complete address of the project e.g. 123 Main Street,
St. Louis, Missouri 63116.
-
totalSquareFeet the square footage of the building (e.g. 2,500 square feet)
-
occupancyGroup group code according to Table 1.
-
subgroup subgroup code according to Table 1.
-
Constructors there are two constructors. An empty-argument constructor that
should set all instance fields to or 0.0 as appropriate. The preferred constructor
should support passing parameters for each instance field.
-
draw method eventually this will be used to draw the object to the screen. For
the prototype, it will simply print to the console: Drawing code for
Type>>. All of the draw methods in the subclasses will do the same.
-
displayData method will return a formatted String that contains all of the
information about the object.
2. Business class: this subclass of Building has the following instance members/constructors/methods:
-
numRentableUnits the number of units in the building that can be rented.
-
Constructors there are two constructors. An empty-argument constructor that should set all instance fields as appropriate for the data type. The preferred
constructor should support passing parameters for each instance field.
-
draw method eventually this will be used to draw the object to the screen. For the prototype, it will simply print to the console: Drawing code for
Type>>. All of the draw methods in the subclasses will do the same.
-
displayData method will return a formatted String that contains all of the
information about the object.
-
Mall class: this subclass of Business has the following instance members/constructors/methods:
-
numRentedUnits the number of units in the building that are currently being rented.
-
medianUnitSize the mall contains rentable units of different size. This instance member represents the median of all of the unit sizes.
-
numParkingSpaces the total number of parking spaces around the mall.
-
Constructors there are two constructors. An empty-argument constructor that should set all instance fields as appropriate for the data type. The preferred
constructor should support passing parameters for each instance field.
-
draw method eventually this will be used to draw the object to the screen. For the prototype, it will simply print to the console: Drawing code for
Type>>. All of the draw methods in the subclasses will do the same.
-
displayData method will return a formatted String that contains all of the
information about the object.
-
4. Residential class: this subclass of Building represents a building where people can live
(has bedrooms and bathrooms) and has the following instance members/constructors/methods:
-
numBedrooms the number of bedrooms in the building.
-
numBathrooms the number of bathrooms in the building.
-
laundryRoom whether or not the building has a laundry room.
-
Constructors there are two constructors. An empty-argument constructor that should set all instance fields as appropriate for the data type. The preferred constructor should support passing parameters for each instance field.
-
draw method eventually this will be used to draw the object to the screen. For the prototype, it will simply print to the console: Drawing code for >. All of the draw methods in the subclasses will do the same.
-
displayData method will return a formatted String that contains all of the information about the object.
-
Apartment class: this subclass of Residential represents a building where more than one family can live and has the following instance members/constructors/methods:
-
numRentableUnits the number of units that can be rented in the building.
-
avgUnitSize the average size of the apartments (square footage) in the building.
-
parkingAvailable a boolean value that indicates if onsite parking is available for
this building.
-
Constructors there are two constructors. An empty-argument constructor that
should set all instance fields as appropriate for the data type. The preferred
constructor should support passing parameters for each instance field.
-
draw method eventually this will be used to draw the object to the screen. For the prototype, it will simply print to the console: Drawing code for
Type>>. All of the draw methods in the subclasses will do the same.
-
displayData method will return a formatted String that contains all of the
information about the object.
-
-
SingleFamilyHome class: this subclass of Residential represents a building where a one family lives (has a limit on the number of people who can live there). This class has the following instance members/constructors/methods:
-
garage a boolean value that indicates whether or not the house has a garage.
-
Constructors there are two constructors. An empty-argument constructor that should set all instance fields as appropriate for the data type. The preferred
constructor should support passing parameters for each instance field.
-
draw method eventually this will be used to draw the object to the screen. For the prototype, it will simply print to the console: Drawing code for
Type>>. All of the draw methods in the subclasses will do the same.
-
displayData method will return a formatted String that contains all of the
information about the object.
-
-
Application class: After you have completed your inheritance hierarchy, write an Application class (not shown in the UML Class Diagram) to test every object. In your test, create an instance of every object and then write code to test every constructor/method/getter/setter/toString for the object. Start with the most generic object and move to the more specific object.
Notes:
-
Notice that every class has constructor that accepts the protected fields in Building (for consistency).
-
There is an empty-argument and a preferred constructor for each object. (Use the tools built into Eclipse to generate these)
-
Every object should have getters/setters for every instance field. (Use the tools built into Eclipse to generate these)
-
Every object should have a toString method (Use the tools built into Eclipse to generate these)
-
Ensure you follow the StyleGuide and fully comment/Javadoc the project.
-
Some objects have a displayData method. When that method is called it should return a
formatted string with all of the instance fields that the object can see. The format needs to be consistent from object to object, but you can choose the format. See below for examples:
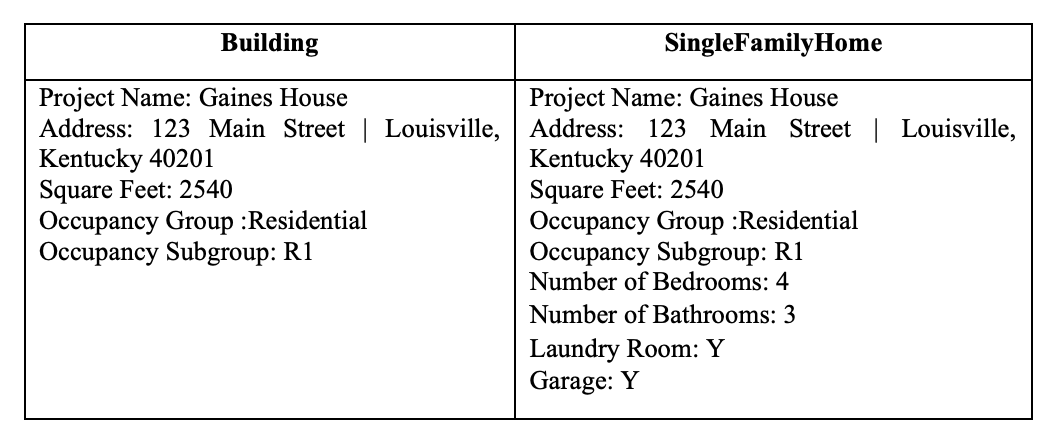
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


