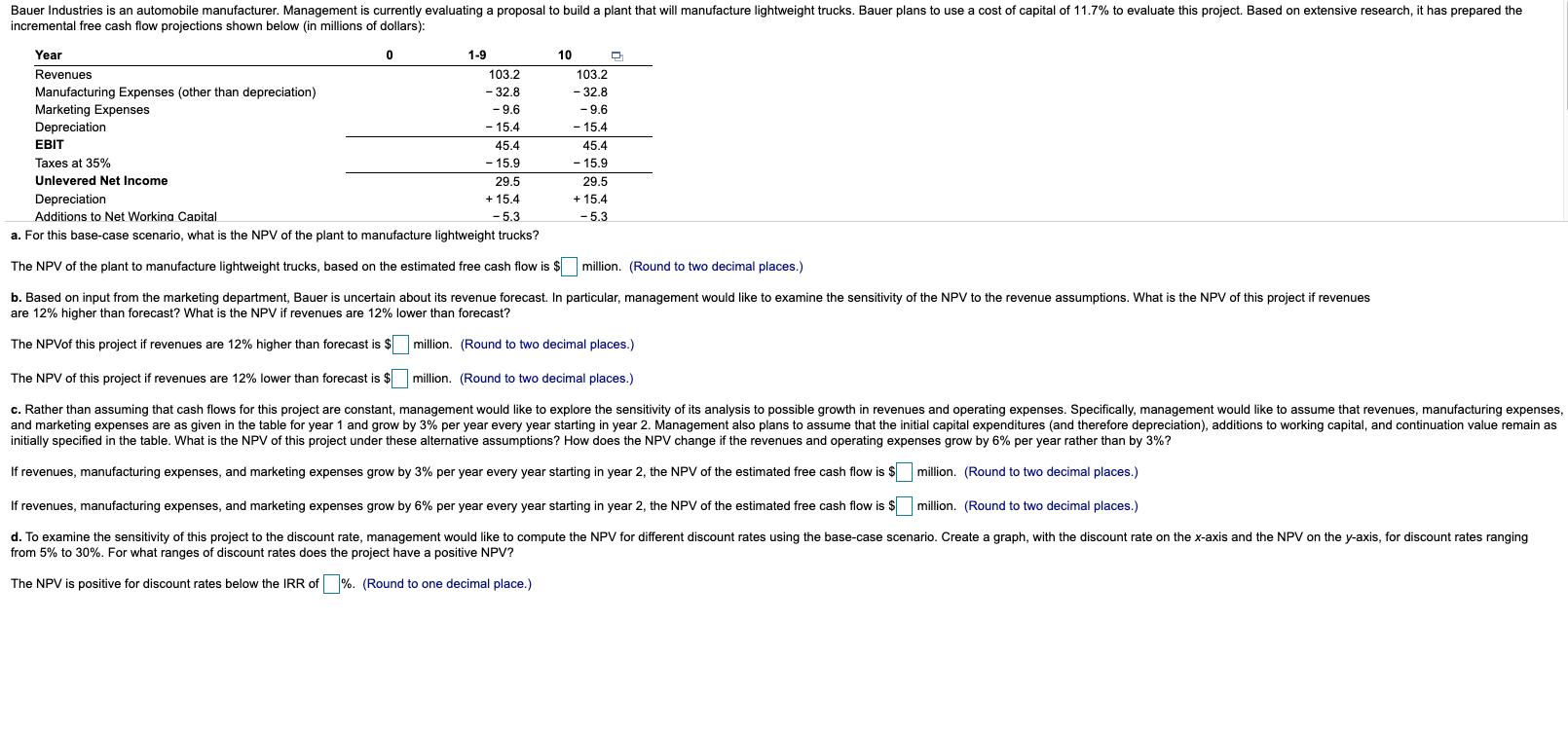
Bauer Industries is an automobile manufacturer. Management is currently evaluating a proposal to build a plant that will manufacture lightweight trucks. Bauer plans to use a cost of capital of 11.7% to evaluate this project. Based on extensive research, it has prepared the incremental free cash flow projections shown below (in millions of dollars): Year 1-9 Revenues 103.2 Manufacturing Expenses (other than depreciation) - 32.8 Marketing Expenses - 9.6 Depreciation - 15.4 EBIT 45.4 Taxes at 35% - 15.9 Unlevered Net Income 29.5 Depreciation + 15.4 Additions to Net Workina Capital -5.3 a. For this base-case scenario, what is the NPV of the plant to manufacture lightweight trucks? 100 103.2 - 32.8 - 9.6 - 15.4 45.4 - 15.9 29.5 + 15.4 -5.3 The NPV of the plant to manufacture lightweight trucks, based on the estimated free cash flow is $ million. (Round to two decimal places.) b. Based on input from the marketing department, Bauer is uncertain about its revenue forecast. In particular, management would like to examine the sensitivity of the NPV to the revenue assumptions. What is the NPV of this project if revenues are 12% higher than forecast? What is the NPV if revenues are 12% lower than forecast? The NPVof this project if revenues are 12% higher than forecast is $ million. (Round to two decimal places.) The NPV of this project if revenues are 12% lower than forecast is $ million. (Round to two decimal places.) c. Rather than assuming that cash flows for this project are constant, management would like to explore the sensitivity of its analysis to possible growth in revenues and operating expenses. Specifically, management would like to assume that revenues, manufacturing expenses, and marketing expenses are as given in the table for year 1 and grow by 3% per year every year starting in year 2. Management also plans to assume that the initial capital expenditures (and therefore depreciation), additions to working capital, and continuation value remain as initially specified in the table. What is the NPV of this project under these alternative assumptions? How does the NPV change if the revenues and operating expenses grow by 6% per year rather than by 3%? If revenues, manufacturing expenses, and marketing expenses grow by 3% per year every year starting in year 2, the NPV of the estimated free cash flow is $ million. (Round to two decimal places.) If revenues, manufacturing expenses, and marketing expenses grow by 6% per year every year starting in year 2, the NPV of the estimated free cash flow is $ million. (Round to two decimal places.) d. To examine the sensitivity of this project to the discount rate, management would like to compute the NPV for different discount rates using the base-case scenario. Create a graph, with the discount rate on the x-axis and the NPV on the y-axis, for discount rates ranging from 5% to 30%. For what ranges of discount rates does the project have a positive NPV? The NPV is positive for discount rates below the IRR of %. (Round to one decimal place.) Bauer Industries is an automobile manufacturer. Management is currently evaluating a proposal to build a plant that will manufacture lightweight trucks. Bauer plans to use a cost of capital of 11.7% to evaluate this project. Based on extensive research, it has prepared the incremental free cash flow projections shown below (in millions of dollars): Year 1-9 Revenues 103.2 Manufacturing Expenses (other than depreciation) - 32.8 Marketing Expenses - 9.6 Depreciation - 15.4 EBIT 45.4 Taxes at 35% - 15.9 Unlevered Net Income 29.5 Depreciation + 15.4 Additions to Net Workina Capital -5.3 a. For this base-case scenario, what is the NPV of the plant to manufacture lightweight trucks? 100 103.2 - 32.8 - 9.6 - 15.4 45.4 - 15.9 29.5 + 15.4 -5.3 The NPV of the plant to manufacture lightweight trucks, based on the estimated free cash flow is $ million. (Round to two decimal places.) b. Based on input from the marketing department, Bauer is uncertain about its revenue forecast. In particular, management would like to examine the sensitivity of the NPV to the revenue assumptions. What is the NPV of this project if revenues are 12% higher than forecast? What is the NPV if revenues are 12% lower than forecast? The NPVof this project if revenues are 12% higher than forecast is $ million. (Round to two decimal places.) The NPV of this project if revenues are 12% lower than forecast is $ million. (Round to two decimal places.) c. Rather than assuming that cash flows for this project are constant, management would like to explore the sensitivity of its analysis to possible growth in revenues and operating expenses. Specifically, management would like to assume that revenues, manufacturing expenses, and marketing expenses are as given in the table for year 1 and grow by 3% per year every year starting in year 2. Management also plans to assume that the initial capital expenditures (and therefore depreciation), additions to working capital, and continuation value remain as initially specified in the table. What is the NPV of this project under these alternative assumptions? How does the NPV change if the revenues and operating expenses grow by 6% per year rather than by 3%? If revenues, manufacturing expenses, and marketing expenses grow by 3% per year every year starting in year 2, the NPV of the estimated free cash flow is $ million. (Round to two decimal places.) If revenues, manufacturing expenses, and marketing expenses grow by 6% per year every year starting in year 2, the NPV of the estimated free cash flow is $ million. (Round to two decimal places.) d. To examine the sensitivity of this project to the discount rate, management would like to compute the NPV for different discount rates using the base-case scenario. Create a graph, with the discount rate on the x-axis and the NPV on the y-axis, for discount rates ranging from 5% to 30%. For what ranges of discount rates does the project have a positive NPV? The NPV is positive for discount rates below the IRR of %. (Round to one decimal place.)







