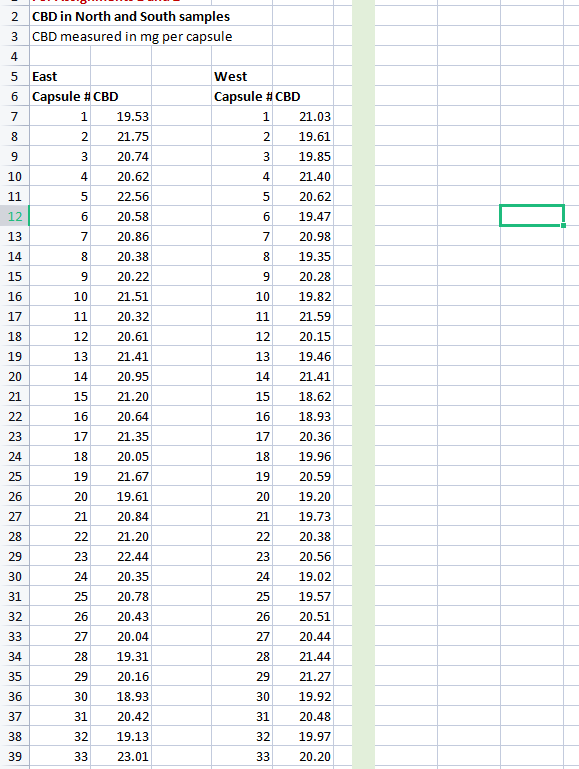
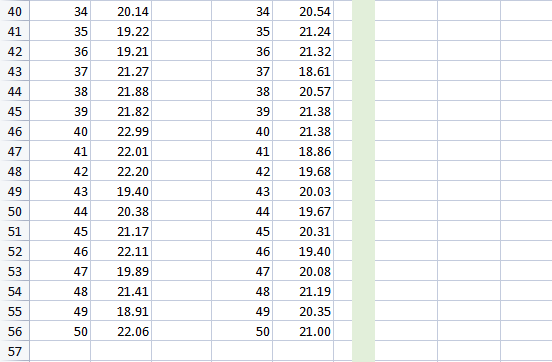



\begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|l|l|l|} \hline 40 & 34 & 20.14 & 34 & 20.54 \\ \hline 41 & 35 & 19.22 & 35 & 21.24 \\ \hline 42 & 36 & 19.21 & 36 & 21.32 \\ \hline 43 & 37 & 21.27 & 37 & 18.61 \\ \hline 44 & 38 & 21.88 & 38 & 20.57 \\ \hline 45 & 39 & 21.82 & 39 & 21.38 \\ \hline 46 & 40 & 22.99 & 40 & 21.38 \\ \hline 47 & 41 & 22.01 & 41 & 18.86 \\ \hline 48 & 42 & 22.20 & 42 & 19.68 \\ \hline 49 & 43 & 19.40 & 43 & 20.03 \\ \hline 50 & 44 & 20.38 & 44 & 19.67 \\ \hline 51 & 45 & 21.17 & 45 & 20.31 \\ \hline 52 & 46 & 22.11 & 46 & 19.40 \\ \hline 53 & 47 & 19.89 & 47 & 20.08 \\ \hline 54 & 48 & 21.41 & 48 & 21.19 \\ \hline 55 & 49 & 18.91 & 49 & 20.35 \\ \hline 56 & 50 & 22.06 & 50 & 21.00 \\ \hline 57 & & & & \\ \hline \end{tabular} For each assignment you will analyze data about a hypothetical company's products so as to understand how to improve its processes. Real life context In Canada, cannabis products are legally sold by provincially licensed retailers to adult consumers for recreational use, and by federally licensed producers to authorized patients for medical use. Many recreational consumers prefer products that contain lots of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the main chemical that makes users feel intoxicated or "high". By contrast, many medical patients want lots of CBD (cannabidiol), a chemical that might reduce inflammation. Furthermore, while recreational users tend to prefer smoking dried cannabis flower, medical users tend to prefer refined cannabis oils that they swallow or place under their tongues. Cannabis oil products are manufactured via the following steps. - Cannabis plants are grown in a controlled environment to maximize their chemical content and minimize contamination. - After the plants are harvested, raw oil is extracted from the flowers and leaves. - For some products, the oil is decarboxylated ("decarbed") by heating it. This converts the inactive chemical CBDA (cannabidiolic acid) into the active chemical CBD. - The oil is filtered, blended, and/or diluted to create the desired formulation. - The finished oil is placed into bottles, vape cartridges, gelatin capsules, etc. Opinions can vary widely among employees and managers regarding the "best" way to operate this process, because many cannabis companies are relatively new. Their employees also have varied backgrounds: some have horticultural experience, some worked in the pharmaceutical industry, and some came from the consumer packaged-goods sector. You are working for a licensed processor that makes cannabis products for the medical market. Your company buys dried cannabis plants from a licensed grower and gelatin powder from a food processor. It uses those raw materials to produce gelatin capsules ("gel caps") filled with cannabis oil for sale online to authorized medical patients. For its most popular product, the design specification states that the oil in each capsule should contain 20.00mg of CDB, but any amount between 18.50 and 21.50mg is medically acceptable. Capsules with CBD levels outside of those limits are discarded at a cost of $0.25 each. Your company makes this product at two production sites. Each site operates for 35 hours per week. One site serves customers from eastern Canada, where the demand averages 590,000 capsules per week. The other site serves customers in western Canada, where the demand averages 415,000 capsules per week. Each site can produce up to 20,000 capsules per hour. Your supervisor is concerned about the growing number of customer complaints about this product. She is also looking for ways to boost productivity. Consequently, you have been assigned to help the workers improve the gel cap production process. This assignment applies concepts from the Analyze phase of a Lean Six Sigma project. It again uses data from the first Cannabis Oil Data spreadsheet and from the Background Information document. The spreadsheet shows the milligrams of CBD in capsules from the east and west sites. Use this data to answer the following questions. Story Your initial investigation uncovered apparent differences between the east and west processes. You next need to determine whether the differences were due to actual differences between the processes, rather than to the randomness of the sampling procedure (i.e., were the capsules you chose just "lucky"). Questions 1. Draw 2 histograms to compare the "widths" of the two processes. In the first histogram show the distribution of CBD per cartridge for the east site. In the second histogram show the distribution for the west site. You can draw these using software or by hand. Use the same vertical and horizontal scales for both diagrams. You might need to try different "bin limits" to see what works best for the horizontal scales. Which process looks more consistent? 2. Perform a statistical test to compare the variability of the 2 processes. That is, do a 2-sample F-test to compare the CBD standard deviations of the east and west sites. Make sure the F calculated value is greater than 1. Do this test using software or by hand. For hand calculations you can use the Excel functions "finv()" or "f.inv()" to get the critical value and "fdist()" or "f.dist.rt()" to get the significance p. Is there a difference in variability? 3. Perform a statistical test to compare the typical output of the 2 processes. That is, do a 2 sample t-test to compare the mean of the east process to the mean of the west one, assuming unequal variances. Do this test using software and include the results table in your answer. Are the processes different on average? 4. Perform a statistical test to assess the accuracy of the west process only. That is, do a 1-sample t-test to compare the mean CBD of the west process to the design target for the product. Do this test by hand. You can use the Excel functions "tinv()" or "t.inv.2t()" to get the critical value and "tdist () " or "t.dist.2t()" to get the p. Does the output match the target? \begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|l|l|l|} \hline 40 & 34 & 20.14 & 34 & 20.54 \\ \hline 41 & 35 & 19.22 & 35 & 21.24 \\ \hline 42 & 36 & 19.21 & 36 & 21.32 \\ \hline 43 & 37 & 21.27 & 37 & 18.61 \\ \hline 44 & 38 & 21.88 & 38 & 20.57 \\ \hline 45 & 39 & 21.82 & 39 & 21.38 \\ \hline 46 & 40 & 22.99 & 40 & 21.38 \\ \hline 47 & 41 & 22.01 & 41 & 18.86 \\ \hline 48 & 42 & 22.20 & 42 & 19.68 \\ \hline 49 & 43 & 19.40 & 43 & 20.03 \\ \hline 50 & 44 & 20.38 & 44 & 19.67 \\ \hline 51 & 45 & 21.17 & 45 & 20.31 \\ \hline 52 & 46 & 22.11 & 46 & 19.40 \\ \hline 53 & 47 & 19.89 & 47 & 20.08 \\ \hline 54 & 48 & 21.41 & 48 & 21.19 \\ \hline 55 & 49 & 18.91 & 49 & 20.35 \\ \hline 56 & 50 & 22.06 & 50 & 21.00 \\ \hline 57 & & & & \\ \hline \end{tabular} For each assignment you will analyze data about a hypothetical company's products so as to understand how to improve its processes. Real life context In Canada, cannabis products are legally sold by provincially licensed retailers to adult consumers for recreational use, and by federally licensed producers to authorized patients for medical use. Many recreational consumers prefer products that contain lots of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the main chemical that makes users feel intoxicated or "high". By contrast, many medical patients want lots of CBD (cannabidiol), a chemical that might reduce inflammation. Furthermore, while recreational users tend to prefer smoking dried cannabis flower, medical users tend to prefer refined cannabis oils that they swallow or place under their tongues. Cannabis oil products are manufactured via the following steps. - Cannabis plants are grown in a controlled environment to maximize their chemical content and minimize contamination. - After the plants are harvested, raw oil is extracted from the flowers and leaves. - For some products, the oil is decarboxylated ("decarbed") by heating it. This converts the inactive chemical CBDA (cannabidiolic acid) into the active chemical CBD. - The oil is filtered, blended, and/or diluted to create the desired formulation. - The finished oil is placed into bottles, vape cartridges, gelatin capsules, etc. Opinions can vary widely among employees and managers regarding the "best" way to operate this process, because many cannabis companies are relatively new. Their employees also have varied backgrounds: some have horticultural experience, some worked in the pharmaceutical industry, and some came from the consumer packaged-goods sector. You are working for a licensed processor that makes cannabis products for the medical market. Your company buys dried cannabis plants from a licensed grower and gelatin powder from a food processor. It uses those raw materials to produce gelatin capsules ("gel caps") filled with cannabis oil for sale online to authorized medical patients. For its most popular product, the design specification states that the oil in each capsule should contain 20.00mg of CDB, but any amount between 18.50 and 21.50mg is medically acceptable. Capsules with CBD levels outside of those limits are discarded at a cost of $0.25 each. Your company makes this product at two production sites. Each site operates for 35 hours per week. One site serves customers from eastern Canada, where the demand averages 590,000 capsules per week. The other site serves customers in western Canada, where the demand averages 415,000 capsules per week. Each site can produce up to 20,000 capsules per hour. Your supervisor is concerned about the growing number of customer complaints about this product. She is also looking for ways to boost productivity. Consequently, you have been assigned to help the workers improve the gel cap production process. This assignment applies concepts from the Analyze phase of a Lean Six Sigma project. It again uses data from the first Cannabis Oil Data spreadsheet and from the Background Information document. The spreadsheet shows the milligrams of CBD in capsules from the east and west sites. Use this data to answer the following questions. Story Your initial investigation uncovered apparent differences between the east and west processes. You next need to determine whether the differences were due to actual differences between the processes, rather than to the randomness of the sampling procedure (i.e., were the capsules you chose just "lucky"). Questions 1. Draw 2 histograms to compare the "widths" of the two processes. In the first histogram show the distribution of CBD per cartridge for the east site. In the second histogram show the distribution for the west site. You can draw these using software or by hand. Use the same vertical and horizontal scales for both diagrams. You might need to try different "bin limits" to see what works best for the horizontal scales. Which process looks more consistent? 2. Perform a statistical test to compare the variability of the 2 processes. That is, do a 2-sample F-test to compare the CBD standard deviations of the east and west sites. Make sure the F calculated value is greater than 1. Do this test using software or by hand. For hand calculations you can use the Excel functions "finv()" or "f.inv()" to get the critical value and "fdist()" or "f.dist.rt()" to get the significance p. Is there a difference in variability? 3. Perform a statistical test to compare the typical output of the 2 processes. That is, do a 2 sample t-test to compare the mean of the east process to the mean of the west one, assuming unequal variances. Do this test using software and include the results table in your answer. Are the processes different on average? 4. Perform a statistical test to assess the accuracy of the west process only. That is, do a 1-sample t-test to compare the mean CBD of the west process to the design target for the product. Do this test by hand. You can use the Excel functions "tinv()" or "t.inv.2t()" to get the critical value and "tdist () " or "t.dist.2t()" to get the p. Does the output match the target











