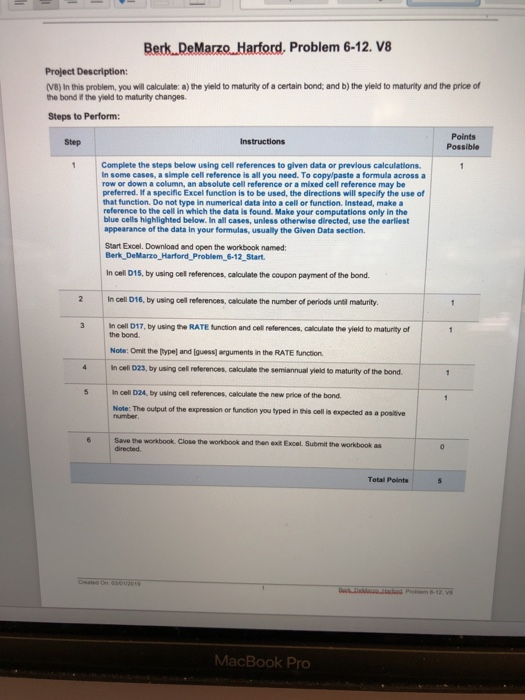
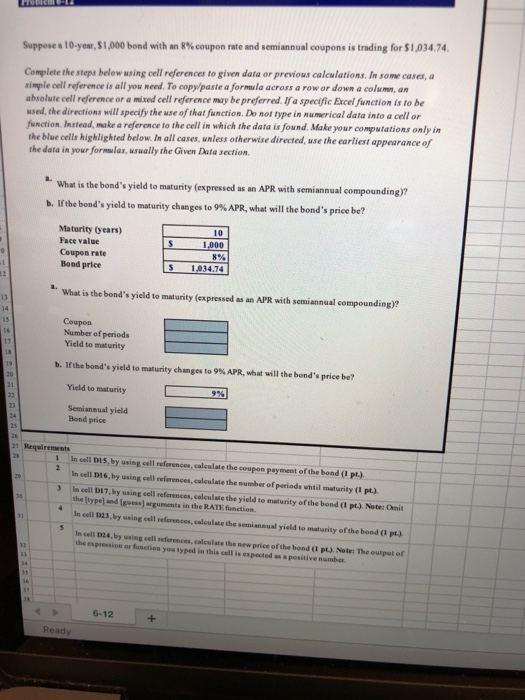
Berk.DeMarzo.Harford, Problem 6-12. V8 Project Description: (VB) In this problem, you will calculate: a) the yield to maturity of a certain bond, and b) the yield to maturity and the price of the bond i# the yield to maturity changes. Steps to Perform Points Possible Step 1 Complete the steps below using cell references to given data or previous calculations. In some cases, a simple cell reference is all you need. To copy/paste a formula across a row or down a column, an absolute cell reference or a mixed cell reference may be preferred. If a specific Excel function is to be used, the directions will specify the use of that function. Do not type in numerical data into a cell or function. Instead, make a reference to the cell in which the data is found. Make your computations only in the blue cells highlighted below. In all cases, unless otherwise directed, use the earliest appearance of the data in your formulas, usually the Given Data section Start Excel. Download and open the workbook named: Berk DeMarzo_Harford Problem 6-12 Start In cell D15, by using cell references, calculate the coupon payment of the bond. In cell D16, by using cell reflerences, calculate the number of periods unl maturity 3 In call D17, by using the RATE funcion and cel references, alculate the yeld to maturity of the bond Note: Omit the [typej and [guess] arguments in the RATE function In cell D23, by using cell references, calculate the semiannual yield to maturity of the bond. 5 In cell 024, by using cell references, calculate the new price of the bond. Note: The cutput of the expression or function you typed in this cell is expected as a positive Save the workbook. Close the workbook and then exit Excel. Submit the workbook as directed Total Polints MacBook Pro Suppose a 10-year, $1 ,000 bond with an 8% coupon rate and semiannual coupons is trading for $1,034.74 Complete the steps below using cell references to given data or previous calculations. In some cases, a simple cell reference is all you need. To copy/paste a formula across a row or down a columen, an absolute cell reference or a mixed cell reference may be preferred. If a specific Excel function is to be used, the directions will specify the use of that function. Do not type in numerical data into a cell or function Instead, make a reference to the cell in which the data is found. Make your computations only in the blue cells highlighted below. In all cases, unless otherwise directed, use the earliest appearance of the data in your formulas, usually the Given Data section What is the bond's yield to maturity (expressed as an APR with semiannual compounding)? b. If the bond's yield to maturity changes to 9% APR, what will the bond's price be? Maturity (gears) 10 Face value Coupon rate Bond price 8% 1.034.74 a. What is the bond's yield to maturity (expressed as an APR with semiannual compounding)? Coupon Number of periods Yield to maturity b. If the bond's yield to maturity changes to 9% APR, what will the bond's price be? Yield to maturity Semiannual yield Bond price 1 In cell DI5,by using cell references, calculate the coupon payment of the bond (I pt) In cell D16,by using cell references, calculate the sumber of periods whtil maturity (1 pt.) the [type) and (guess) arguments in the RATE function in cell 1D23, by using cell references,calculate the semiansual yiald to maturity ofthe bond ( pt.) S In cell D17,by using cell references, calculate the yield to maturity of the bond ( pt.). Note: Omit in cell D24, by using cell references,calculate the new price of the bond (t p.). Note: The output of espression or function you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number the 6-12 Read