Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
BNL Stores: The 11 Ratios are are needed for Question 1 are: Gross Profit Margin, Net Profit Margin (ROS), Return on Equity, Return on Assets,
BNL Stores:

 The 11 Ratios are are needed for Question 1 are:
The 11 Ratios are are needed for Question 1 are:
Gross Profit Margin, Net Profit Margin (ROS), Return on Equity, Return on Assets, Inventory Turnover, Total Asset Turnover, Day Receivables, Current Ratio, Quick Ratio, Debt-to-Equity Ratio, Financial Leverage
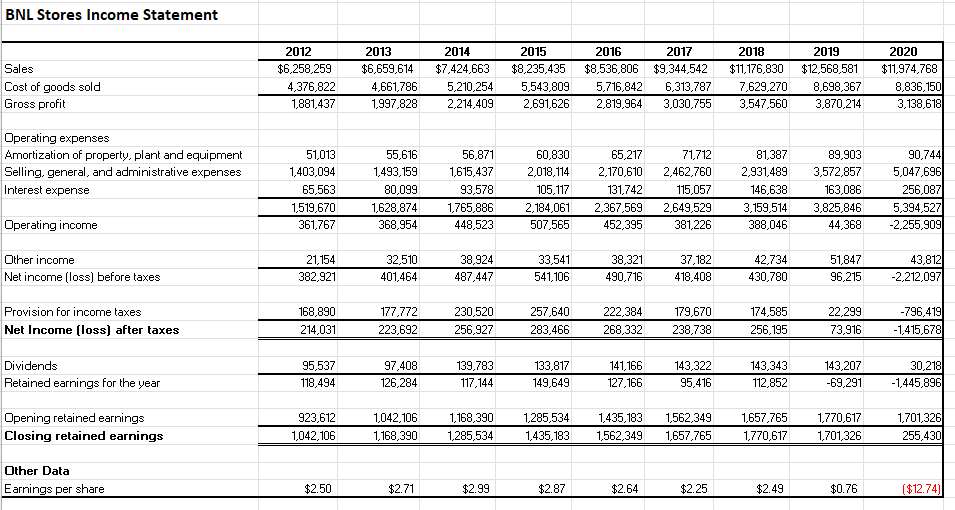
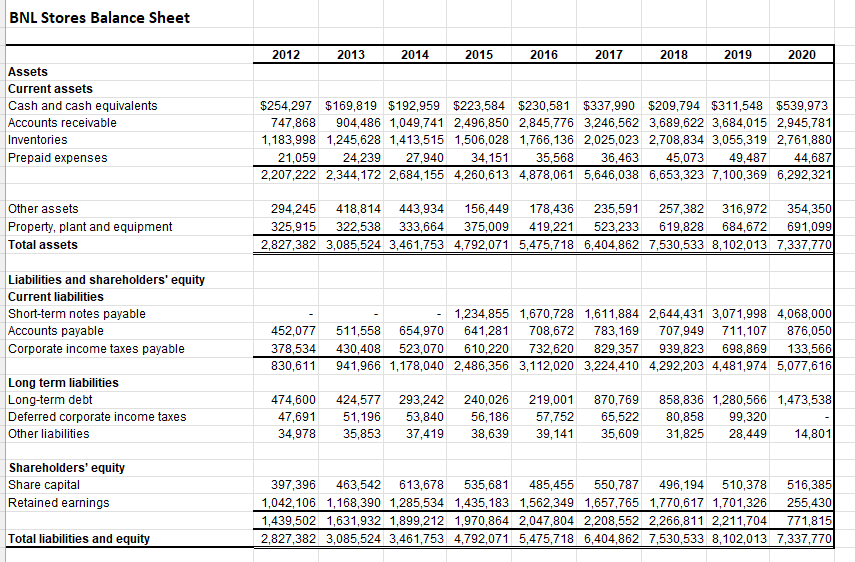
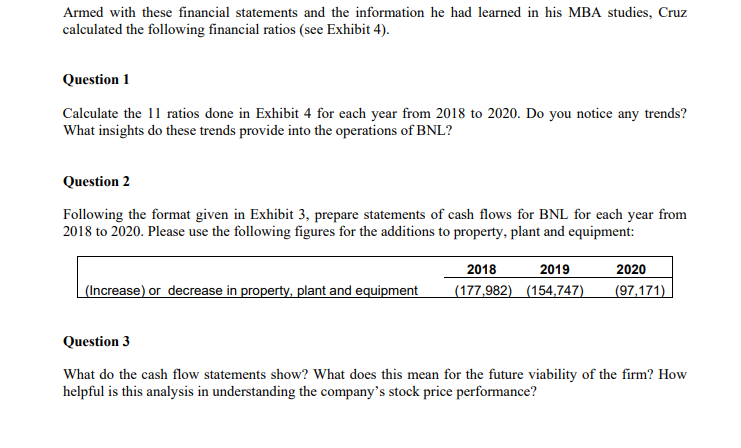
BNL Stores Income Statement Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit Dperating expenses Dther income Net income (loss) before taxes \begin{tabular}{rrrrrrrrr|r|} 221,154 & 32,510 & 38,924 & 33,541 & 38,321 & 37,182 & 42,734 & 51,847 & 43,812 \\ \hline 382,921 & 401,464 & 487,447 & 541,106 & 490,716 & 418,408 & 430,780 & 96,215 & 2,212,097 \\ \hline \end{tabular} Provision for income taxes Net Income [loss] after taxes \begin{tabular}{rrrrrrrrrr|r|} \hline 168,890 & 177,772 & 230,520 & 257,640 & 222,384 & 179,670 & 174,585 & 22,299 & 796,419 \\ \hline 214,031 & 223,692 & 256,927 & 283,466 & 268,332 & 238,738 & 256,195 & 73,916 & 1,415,678 \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} Dividends Retained earnings for the year \begin{tabular}{rrrrrrrrr|r|} \hline 95,537 & 97,408 & 139,783 & 133,817 & 141,166 & 143,322 & 143,343 & 143,207 & 30,218 \\ \hline 118,494 & 126,284 & 117,144 & 149,649 & 127,166 & 95,416 & 112,852 & 69,291 & 1,445,896 \\ \hline \end{tabular} Gpening retained earnings Closing retained earnings \begin{tabular}{rrrrrrrr|r|} \hline 923,612 & 1,042,106 & 1,168,390 & 1,285,534 & 1,435,183 & 1,562,349 & 1,657,765 & 1,770,617 & 1,701,326 \\ \hline 1,042,106 & 1,168,390 & 1,285,534 & 1,435,183 & 1,562,349 & 1,657,765 & 1,770,617 & 1,701,326 & 255,430 \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} Other Data Earnings per share $2.50 $2.71 $2.99$2.87 $2.64 $2.25 $2.49 $0.76 [$12.74) BNL Stores Balance Sheet In the spring of 2020, Paul Cruz was an analyst at an investment bank who had recently graduated from the Ivey Business School MBA program. As an initial assignment, his supervisor had given him the task of analyzing the financial position of BNL Stores. Cruz was interested in BNL Stores because it was one of his favorite places to shop. However, recently he had read in the business press that BNL's stock had fallen dramatically, dropping from a high of $160 per share to less than $8, despite the fact that the company was known to pay out relatively constant dividends to its shareholders. BNL was an established Midwestern retailer that had been in business for over 50 years. In recent times, management had undertaken a series of new business strategies, one of which was to expand the number of BNL's new supercenter stores, while phasing out the traditional discount stores. The supercenter stores carried a greater selection of durable goods, such as appliances and furniture. In order to entice customers to purchase these more expensive items, BNL had started offering store credit to its customers. Each individual store manager was responsible for authorizing the opening of store credit accounts and ultimately had the final say as to whether credit would be granted to a customer. Store managers were paid an annual bonus, based on net income for their respective store, and were known for being quite lenient in granting credit in order to increase net income for the year and, therefore, the size of their bonus. Cruz wondered whether these new strategies were responsible for the decline in BNL's share price, which he had read about. To collect the financial statement information that he required to complete his assignment, he went to a business reference library and obtained BNL's balance sheets, statements of income, and statements of cash flows for the fiscal years ending 2012 through 2017. However, for 2018 to 2020 , he was able to obtain income the balance sheets and statements of income, but not statements of cash flows (see Exhibits 1,2 and 3). Armed with these financial statements and the information he had learned in his MBA studies, Cruz calculated the following financial ratios (see Exhibit 4). Question 1 Calculate the 11 ratios done in Exhibit 4 for each year from 2018 to 2020. Do you notice any trends? What insights do these trends provide into the operations of BNL? Question 2 Following the format given in Exhibit 3, prepare statements of cash flows for BNL for each year from 2018 to 2020 . Please use the following figures for the additions to property, plant and equipment: Question 3 What do the cash flow statements show? What does this mean for the future viability of the firm? How helpful is this analysis in understanding the company's stock price performanceStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


