Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
break-even point with that in part (1). Why is it so different? PR 4-6A Contribution margin, break-even sales, cost-volume-profit chart, OBJ. 2, 3, 4, 5

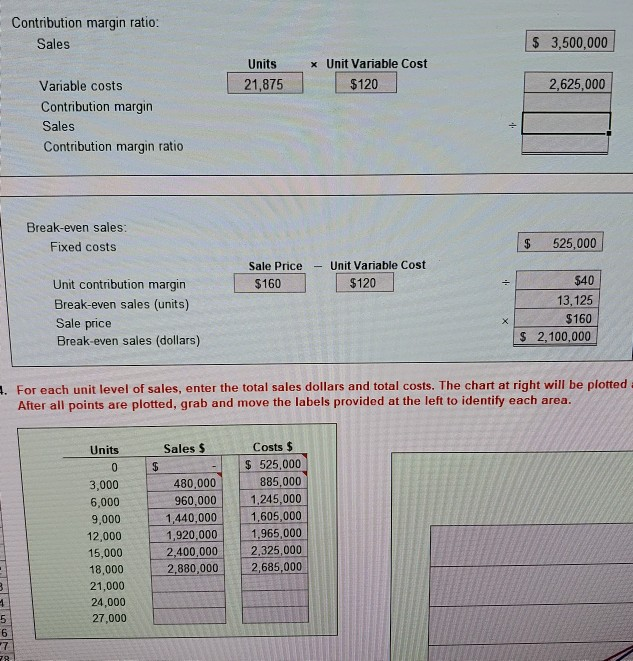
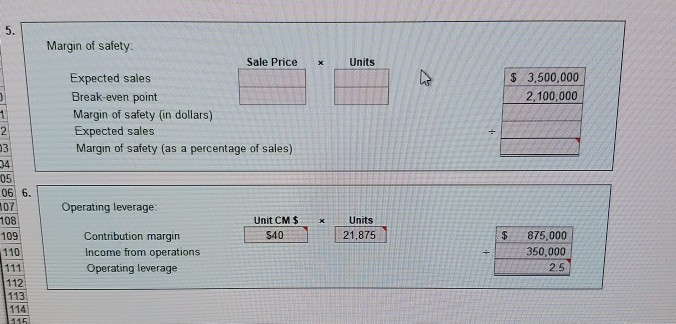
break-even point with that in part (1). Why is it so different? PR 4-6A Contribution margin, break-even sales, cost-volume-profit chart, OBJ. 2, 3, 4, 5 margin of safety, and operating leverage Wolsey Industries Inc. expects to maintain the same inventories at the end of 2016 as at the beginning of the year. The total of all production costs for the year is therefore assumed to be equal to the cost of goods sold. With this in mind, the various department heads were asked to submit estimates of the costs for their departments during the year. A summary report of these estimates is as follows: Estimated Estimated Variable Cost Fixed Cost (per unit sold) Production costs: Direct materials $ 46 Direct labor 40 Factory overhead. $200,000 20 Selling expenses: Sales salaries and commissions.. 110,000 Advertising 40,000 Travel 12,000 Miscellaneous selling expense 7,600 Administrative expenses: Office and officers' salaries 132,000 Supplies... 10,000 4 Miscellaneous administrative expense.. 13,400 1 Total $525,000 $120 001 - It is expected that 21,875 units will be sold at a price of $160 a unit. Maximum sales within the relevant range are 27,000 units. Instructions 1. Prepare an estimated income statement for 2016. 2. What is the expected contribution margin ratio? 3. Determine the break-even sales in units and dollars. 4. Construct a cost-volume-profit chart indicating the break-even sales. 5. What is the expected margin of safety in dollars and as a percentage of sales? 6. Determine the operating leverage. Contribution margin ratio: Sales $ 3,500,000 Units 21,875 x Unit Variable Cost $120 2,625,000 Variable costs Contribution margin Sales Contribution margin ratio Break-even sales: Fixed costs $ 525,000 Sale Price $160 Unit Variable Cost $120 Unit contribution margin Break-even sales (units) Sale price Break-even sales (dollars) $40 13,125 $160 $ 2,100,000 4. For each unit level of sales, enter the total sales dollars and total costs. The chart at right will be plotted After all points are plotted, grab and move the labels provided at the left to identify each area. Units Sales $ 0 $ 3,000 6,000 9,000 12,000 15,000 18,000 21,000 24,000 27,000 480,000 960,000 1,440,000 1,920,000 2,400,000 2.880,000 Costs $ $ 525,000 885,000 1,245,000 1,605,000 1.965,000 2.325,000 2,685,000 1 5 6 7 78 5. X Units Margin of safety Sale Price Expected sales Break-even point Margin of safety (in dollars) Expected sales Margin of safety (as a percentage of sales) $ 3,500,000 2,100,000 + Operating leverage x 2 03 34 05 06 6. 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 15 Unit CM $ $40 Units 21,875 $ Contribution margin Income from operations Operating leverage 875,000 350,000 2.5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


