Question: Briefly explain the selected trend TREND SUMMARY In a time of constant tech disruption, earning trust is a 360-degree challenge-and opportunity. Develop an approach to
Briefly explain the selected trend
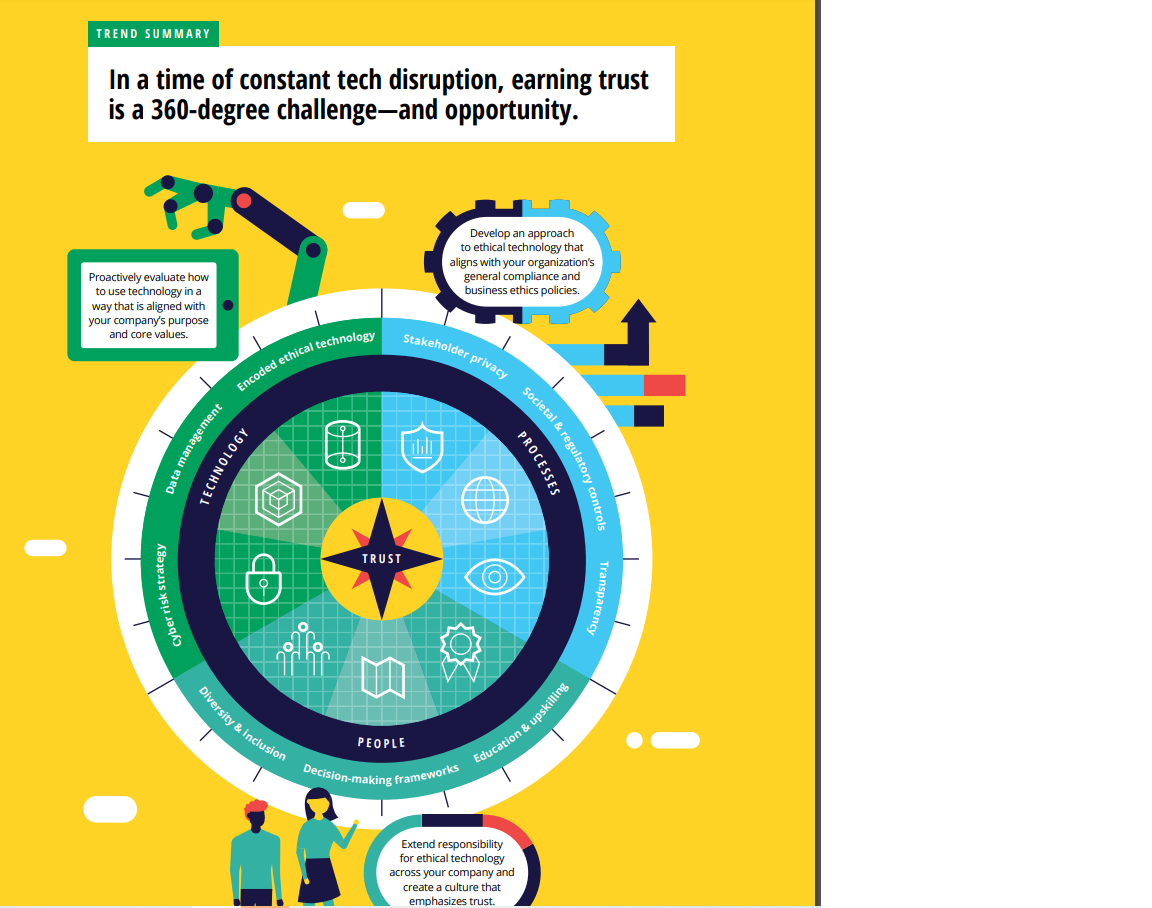










TREND SUMMARY In a time of constant tech disruption, earning trust is a 360-degree challenge-and opportunity. Develop an approach to ethical technology that aligns with your organization's Proactively evaluate how general compliance and to use technology in a business ethics policies way that is aligned with your company's purpose and core values. Encoded ethical technology Stakeholder privacy Data management Societal & regulatory controls TECHNOLOGY PROCESSES TRUST O Cyber risk strategy Transparency iversity & inclusion Education & upskilling PEOPLE Decision-making frameworks Extend responsibility for ethical technology across your company and create a culture that emphasizes trust.Ethical technology and trust the person who wears it, accesses it, or lives with it Ultimately, Brotz says, data-enabled technologies inside their body. And that means we must protect that help people live better lives are an extension it-securely and responsibly." of the lifesaving products and services that patients Abbott also relies on a strong external ecosystem to "We know that when we maintain patient trust. Independent third parties and research groups test Abbott's products and build technology, we are services and assess their vulnerabilities on an ongoing basis. For example, the company is part doing so on behalf of of the # WeHeartHackers initiative, a collaboration the person who wears between the medical device and security research communities that seeks to improve medical device it, accesses it, or lives security. At a recent event, Abbott teamed with with it inside their body. university researchers to build a mock immersive hospital that enabled researchers to practice And that means we cybersecurity defense techniques. 30 must protect it-securely Rounding out Abbott's trust ecosystem are patients and responsibly." and care providers themselves. To learn what concepts such as trust, security, and privacy mean and their care providers have trusted for 130 years. to the different users of its products and services, "Patients place the highest levels of trust in us, and the company regularly holds focus groups with we take it very seriously," she says. "It's part of our them and produces educational material to raise DNA. Our greatest responsibility is to keep them awareness of these issues. and their data safe and secure." Rebuilding security from the ground up to maintain customer trust ECAUSE A COMPANY'S approach to A decade ago, as Google moved internal applications and resources to the cloud, its security trust in its brand, businesses that are perimeter was constantly expanding and changing, leveraging advanced technologies can benefit from complicating the defense of its network perimeter. considering the technologies' impact on ecosystem At the same time, companies were seeing more partners, employees, customers, and other sophisticated attacks by nation-state-sponsored key stakeholders. Strong security controls and hackers, testing the limits of the perimeter-based practices are foundational elements for building model of security. Hence, Google decided to and maintaining stakeholder trust. Recognizing completely overhaul its security approach and the impact of security breaches on customer trust, implement a new security model that turned Google went beyond the expected table stakes the existing industry standard on its head, says by completely redesigning its security model to Sampath Srinivas, Google product management protect enterprise systems and data. director for information security.3Tech Trends 2020 Google security experts could no longer assume encrypts traffic to protect data in transmission, that walling off the network would provide the and acts as a sophisticated rules engine that security required to maintain system integrity determines access rights based on the user and and customer trust. They sought to reinvent the device's context, such as whether it is fully patched. company's existing security architecture, since Every access request is subject to authentication, the traditional castle-and-moat model-based authorization, and encryption. To protect against on a secure network perimeter with VPN-based phishing, the company-working with the industry employee access to internal applications-was in the FIDO Alliance standards organization- no longer adequate. The goal: to ensure that developed and deployed a new form of employees could use any corporate application cryptographic hardware two-factor authentication from any location on any device as easily as if they called Security Keys.3 were using Gmail and as safely as if they were in a Google office. Today, Google's user- and device-centric security workflow allows authorized users to securely work Google embraced the zero-trust concept, an from an untrusted network without the use of a innovative security model that eliminates network- VPN. The user experiences internal applications based trust, Srinivas says, instead applying access as if they were directly on the internet. Employees, controls to applications based on user identity contractors, and other users can have a seamless and the status of their devices, regardless of their user-access experience from any location by network location. simply typing in a web address-a process that dramatically reduces support burden. "To deliver Google's zero-trust security strategy treats every on our goal of maintaining customer privacy single network request as if it came from the and trust, we had to look beyond the status quo internet. It applies context-aware access policies solutions, innovate, and take risks," Srinivas says. to clues such as user identity, device attributes, "When we broke with tradition and changed the session information, IP address, and context of way we thought about our security infrastructure, the access request itself, collected in real time by it allowed us to develop a more effective way to a device inventory service. A globally distributed protect data and systems." reverse proxy server protects the target server,/ ley-!47-2 Ethical technology technology An overarching set of values and trust that direct an organization's approach to its use of technologies as a whole and Applying your company's the ways in which they are deployed to drive business. values to technology, people, and processes BY THE NUMBERS COMMON REFRAIN in Deloitte's Tech Trends reports is that every company is now a technology company. With the advent of digital technology, businesses have been asking customers to trust them in new and deeper ways, from asking for 55% personal information to tracking online behavior through digital breadcrumbs. At the same time, headlines regularly chronicle technology-based issues such as security hacks, inappropriate or illegal surveillance, misuse of personal data, spread of misinformation, algorithmic bias, and lack of transparency. The of respondents in a Deloitte distrust these incidents breed in stakeholders-whether customers, study from high-growth employees, partners, investors, or regulators-can significantly companies are highly damage an organization's reputation.' Indeed, consumer trust in concerned about the ethical commercial enterprises is declining, citizens are becoming wary of ramifications of technologies, public institutions, and workers are asking employers to explicitly compared to only 27% of state their core values." low-growth companies. In what we recognize as an emerging trend, some companies are approaching trust not as a compliance or public relations TREND BREAKDOWN issue but as a business-critical goal to be pursued-one that can differentiate them in an increasingly complex and overfilled market. As discussed in Deloitte's 2020 Global Marketing Trends report, brand trust is more important than ever for businesses- and it's all-encompassing. Customers, regulators, and the media Risk expect brands to be open, honest, and consistent across all aspects of their business, from products and promotions to workforce culture and partner relationships." Business of Digital technology experience Every aspect of a company that is disrupted by technology represents an opportunity to gain or lose trust with customers, employees, partners, investors, and/or regulators. Leaders who embed organizational values and the principles of ethical technology across their organizations are demonstrating a "Timothy Murphy et al., Ethical technology use in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, 25 Deloitte Insights, July 15, 2019.Tech Trends 2020 commitment to "doing good" that can build a organization's leaders spend enough time thinking long-term foundation of trust with stakeholders. In about and communicating the impact of digital this light, trust becomes a 360-degree undertaking initiatives on society. While respondents from to help ensure that an organization's technology, digitally maturing companies are the most likely processes, and people are working in concert to to say their leaders are doing enough, even then, maintain that foundation. the percentage barely breaks into a majority, at 57 percent.s As the adage reminds us, trust is hard to gain and easy to lose. These findings suggest that organizations still have significant room to step into the lead. Those companies that develop an ethical technology The ethical technology terrain mindset-demonstrating a commitment to ethical decision-making and promoting a culture that The term ethical technology refers to an supports it-have an opportunity to earn the trust overarching set of values that is not limited of their stakeholders. to or focused on any one technology, instead addressing the organization's approach to its use of technologies as a whole and the ways in In pursuit of trust which they are deployed to drive business strategy and operations.* Companies should consider In the digital era, trust is a complex issue fraught proactively evaluating how they can use technology with myriad existential threats to the enterprise. in ways that are aligned with their fundamental And while disruptive technologies are often viewed purpose and core values. as vehicles for exponential growth, tech alone can't build long-term trust. For this reason, leading Ethical technology policies do not replace general organizations are taking a 360-degree approach to compliance or business ethics, but they should all maintain the high level of trust their stakeholders connect in some way. Just as your approach to expect. cybersecurity hasn't taken the place of your company's more general privacy policies, your IN TECHNOLOGY WE TRUST ethical technology approach should complement Artificial intelligence (AD), machine learning, your overall approach to ethics and serve as its blockchain, digital reality, and other emerging logical extension in the digital realm. Some technologies are integrating into our everyday lives companies are expanding the mission of existing more quickly and deeply than ever. How can ethics, learning, and inclusion to include ethical businesses create trust with the technologies their technology, while maintaining separate technology customers, partners, and employees are using? ethics programs. Doing so helps keep technology ethics top of mind across the organization and . Encode your company's values. With encourages executives to consider the distinctions technology ingrained in the business and between technology-related ethical issues and machine learning driving business decisions broader corporate and professional ethics and actions, an organization's values should be concerns. encoded and measured within its technology solutions. Digital systems can be designed to The fifth annual study of digital business by MIT reduce bias and enable organizations to operate Sloan Management Review and Deloitte found in line with their principles." For instance, a that just 35 percent of respondents believe their city government worked with policy institutesto develop an algorithm toolkit intended to of time focusing on cyber issues, and rightly identify ways to minimize unintended harm to so. Cyber defenses represent your commitment constituents by limiting biases in the criminal to protect your customers, employees, and justice system and other institutions. business partners from those who do not share their values-or yours. Cyber risk strategy Safeguards can promote stakeholder welfare should be built and managed from the ground by helping prevent users from engaging with up, embedded in the business mindset, technology in unhealthy or irresponsible ways. strategy, and policies, not only within IT. Examples include a company that imposes time Business leaders can collaborate with IT to and spending limits on habit-forming games, create a comprehensive cyber risk strategy- a content aggregator that prompts users to be encompassing security, privacy, integrity, and skeptical about the veracity of crowdsourced confidentiality-to help build stakeholder trust information, and cloud computing providers and drive competitive advantage. This requires that automatically issue alerts before customers considering the organization's risk tolerance, go over budget. identifying the most vulnerable gaps as well as the most valuable data and systems, then Explainable AI technologies can clarify how devising plans for mitigation and recovery. Al-driven decisions are made. For instance, to enhance confidence in Al-supported WHAT'S IN A PROCESS medical diagnoses, health care companies are A strong foundation for ethical technology and developing solutions that assign each diagnosis trust will be shaped by the principles of an a confidence score that explains the probability organization's leaders and realized in business and contribution of each patient symptom processes. (vital signs, signals from medical reports, lifestyle traits, etc.) to that diagnosis. Clinical Respect stakeholder privacy. One of professionals can see why the conclusion was technology disruption's most overarching made and make a different one if required.? effects has been to accelerate the collection, analysis, and dissemination of information. . Build a strong data foundation. Without Not so long ago, the transactional details of methodically and consistently tracking what our lives were kept in physical file cabinets, data you have, where it lives, and who can pulled out and referenced for specific needs. access it, you cannot create an environment Today, systems routinely collect these details of trust. A strong data foundation unifies and combine them with our purchase histories, stakeholders around a single vision of posts on social media, online searches, and data accountability and delivers on secure even the route we drive to work each day. " If technology that supports effective data consumers have reason to believe their data management." Leaders should aim to give is being used in ways they don't approve of, stakeholders some control over how their reactions can include calls for boycotts, public data will be used and delete data on demand inquiries, and even severe penalties under strict unless it's necessary to keep it for legal or regulations, such as the European Union's regulatory purposes. General Data Protection Regulation and California's Consumer Privacy Act. Companies . Harden your defenses. Deloitte's 2019 should create data privacy policies that build, Future of Cyber Survey reveals that executives rather than erode, public trust. A natural first are increasingly spending significant amounts step can be to ensure the data usage alignswith the company mission." For instance, cooperation with law with law enforcement is routine in JD Wetherspoon, a pub company servicing many countries but perhaps unwise in places the United Kingdom and Ireland, recently with rampant corruption or lack of protection deleted more than 656,ooo customer email for political or religious rights. Some countries addresses, since it perceived the emails as an have very specific regulations around gaining intrusive approach to customer interaction explicit customer consent to data usage; other that provides little value."This case highlights municipalities are passing legislation, such the importance of not only aligning data as banning facial recognition technology, collection and usage to a company's values but, that can conflict with other rulings. Effective by extension, supporting the company's trust governance of emerging technologies requires relationship with the customer. all relevant stakeholders-industry, consumers, businesses, governments, academia, and Be transparent. Companies can build society-to work together. Businesses can trust with stakeholders by proactively and play a key role in helping governments as they transparently demonstrating good behavior. develop laws and standards that increase the "Transparency becomes vital and important," reliability of emerging technologies"-frank, says AI Global executive director Ashley candid discourse about new technologies, for Casovan.'3 "Whether or not people are example, could lead to new rules and guidance interested in seeing the resources and data concerning matters of privacy, transparency, behind it doesn't really matter. Simply knowing inclusivity, accessibility, inequality, and more." that companies have transparent policies provides more confidence that they are doing EMPOWER THE PEOPLE the right thing." Transparency extends beyond Since technology is arguably used by most if not all policies explaining data collection and usage individuals within an organization, ethical tech- practices. For instance, rather than masquerade nology and trust is a topic that touches everyone. as humans, intelligent agents or chatbots should identify themselves as such. Companies . Deploy the power of all. Companies can should disclose the use of automated waste time and money creating something decision systems that affect customers" and that excludes a customer group or providing a should stay focused on the customer when service with undesirable side effects. Perhaps problems occur, providing both speed and even worse, they may build solutions that quality in response. The fallout from negative undermine customer trust. Often, design incidents need not include customer loss or dilemmas begin with a homogeneous group reputation-damaging headlines.' of people designing products, processes, or services without thinking through how other . Respect differing cultural norms. An groups of people might be affected. Leading organization's overall approach to building companies are changing this dynamic by trust is informed by interests, experiences, creating teams and roles that reflect their and professional standards as well as societal diverse customer base and bringing in multiple norms and government controls. It can be viewpoints from different industries, economic challenging to serve a global market in which backgrounds, educational experiences, genders, expectations on government surveillance or and ethnic backgrounds." A 2013 Harvard law enforcement cooperation vary widely. For survey revealed that organizations with example, what is expected surveillance in some leadership teams that have a combination of at countries might seem outrageous elsewhere; least three inherent (ones you are born with)and three acquired (ones you gain through 360 degrees of opportunity experience) diversity traits out-innovate and outperform the others; these organizations Companies that don't consider technology to be are 45 percent more likely to report growth their core business may assume that these in market share and 70 percent more likely to considerations are largely irrelevant. In truth, no report capturing a new market." matter the industry or geography, most organizations are increasingly reliant on advanced Teach them to fish. Training technologists digital and physical technologies to run their to recognize their own biases, and to eliminate day-to-day operations. bias in the products they create is an important step toward creating a culture that emphasizes While there is so much emphasis on the challenges trust. But it is only one step. Building awareness disruptive technologies bring and the existential of how technology affects stakeholder trust in threats to an organization's reputation when those not directly involved or responsible for technology isn't handled correctly-whether technology and creating associated decision- through misfeasance or malfeasance-these same making frameworks are additional steps disruptive technologies can be used to increase organizations should consider. This is especially transparency, harden security, boost data privacy, important in non-digital native organizations, and ultimately bolster an organization's position where the ripple effects of day-to-day uses of trust. of technology may be less obvious to leaders and teams. Companies should consider For example, organizations can pivot what resources may be needed to help their personalization algorithms to provide relevant employees recognize ethical dilemmas, evaluate recommendations based on circumstance-for alternatives, and make (and test) ethical example, offer an umbrella on a rainy day rather technology decisions." than an umbrella after someone buys a raincoat. By focusing on relevance rather than personalization, Give employees a reason to trust. Al recommendations are likely to seem more Much of the anxiety over AI and other helpful than invasive.*3 advanced technologies stems from the fear of the displacement of labor. From an ethical Deloitte surveys have found a positive correlation perspective, this presents business leaders between organizations that strongly consider the with a challenge: balancing the best interests ethics of Industry 4.0 technologies and company of the business, the employees, and the wider growth rates. For instance, in organizations that community and society. It's a task made are witnessing low growth (up to 5 percent), only more complex by the fact that advanced 27 percent of the respondents indicated that they technology systems are not self-sufficient. are strongly considering the ethical ramifications of While AI can replace some jobs, for example, these technologies. By contrast, 55 percent of the it creates others that often require specialized respondents from companies growing at a rate of skills and training."Companies can build 10 percent or more are highly concerned about trust with employees by advising them how ethical considerations.34 technology may affect their jobs in the future. This could include retraining workers whose After all, the pursuit of trust is not just a roles may evolve and who will likely work with 360-degree challenge. It is also a 360-degree automated systems." opportunity.LESSONS FROM THE FRONT LINES A healthy foundation for trust ISRUPTIONS IN THE health care industry- patients at scale," he says. "But it also has the C including new care delivery models, potential to cause damage at scale." consumer demand for digital experiences, declining reimbursements, and growing For example, data analytics, AI, and machine regulatory pressures-are driving many health learning can help researchers and clinicians care organizations to use technology to improve predict chronic disease risk and arrange early efficiency, cut costs, and improve patient care. And interventions, monitor patient symptoms and there could be an inadvertent benefit: Technology receive alerts if interventions are needed, estimate could help health care systems build trust with patient costs more accurately, reduce unnecessary patients and providers. care, and allocate personnel and resources more efficiently. When patients understand Providence St. Joseph Health (PS.JH) is leveraging these benefits, they're generally willing to share technology to adhere to its mission of improving their personal and health information with care the health of underprivileged and underserved providers. But their trust could diminish-or populations, says B.J. Moore, CIO of PS.JH. vanish-if weak data security or governance Technology is helping the Catholic not-for-profit protocols were to result in a data breach or health system simplify complex experiences unauthorized use of private health information. to enhance caregiver and patient interactions, This could cause patients to conceal information modernize the operating environment and business from care professionals, lose confidence in processes, and innovate with cloud, data analytics, diagnoses, or ignore treatment recommendations. Al, and other technologies to help improve patient care. Technological breakthroughs In the process, PSJH is building trust. For example, the organization is collaborating with can increase trust-but technology partners to standardize cloud platforms careless deployment and and productivity and collaboration tools across its 51 hospitals and 1,085 clinics, a move that negligence can quickly will improve provider and patient engagement erode it. and enable data-driven clinical and operational decision-making. It also aims to develop the first blockchain-powered integrated provider-payer A number of industry regulations help ensure claims processing system. Such technological patient privacy and safety, and PSJH has another breakthroughs can increase trust-but careless effective governance and oversight mechanism: deployment and negligence can quickly erode a council of sponsors, consisting of clergy and it. That's why Moore has doubled down on laypeople, that holds moral accountability for establishing and maintaining a solid technology PS.JH's actions in service of its mission. Sponsors foundation for innovation and, by extension, trust. help develop guidelines that ensure adherence to "Technology holds so much promise for helping mission and values and advise the organization's 30Ethical technology and tru executive leadership and board of trustees on trust- says. "Educating and communicating with patients, related technology matters, such as the ethical use care professionals, regulatory bodies, and other key of data and the impact of technology on employees stakeholders can help prevent potential barriers and caregivers. to rapid experimentation and innovation and allow us-and our patients-to fully experience the "We're continuously working to raise awareness benefits of technology." of technology's role in improving health," Moore Do what's right: CIBC's strategic approach to building trust and engagement IBC IS USING technology to understand With the strategy in place, the next step was to and anticipate individual client needs with build an AI governance process to ensure that the goal of delivering highly personalized new technology projects comply with the strategy experiences-an initiative they call Clientnomics Th. and guiding principles. When a new project is Terry Hickey," CIBC's chief analytics officer, proposed, stakeholders answer a series of questions recognized that Al-based algorithms could deliver that help them plan and document what they want the client insights required to drive Clientnomics to accomplish. These questions cover a broad range but that to be successful, leaders needed to of ethical considerations, including project goals, understand and share with employees how AI will possible inherent biases, and client permissions. complement and support the work they're doing. Approved project documents are stored in a versus replacing their jobs. The bank also needed centralized library that regulators, internal to maintain clients' trust by protecting their data auditors, and other reviewers can reference to and governing its use. explain the thought process behind the algorithm or model. In early 2019, leaders from the bank's analytics, risk, and corporate strategy teams collaborated to CIBC has also developed advanced analytic develop an organizationwide AI strategy, which techniques to help govern its use of data-for CIBC's senior executive committee and board of instance, encoding client data in a way that it directors approved. At the heart of the strategy are cannot be reverse-engineered to identify an guiding principles that address questions such as: individual. The analytics team also devised a way to When will we use the technology? When will we assign a data veracity score-based on data quality not use it? How do we ensure that that we have and integrity, possible bias, ambiguity, timeliness, our clients' permission? and relevance-to each piece of information that could be used by an algorithm. The algorithmic To reinforce employee trust, the strategic plan models are designed to recognize and treat the data stated that a primary purpose of AI would be veracity appropriately, supporting more reliable, to augment employees' capabilities to achieve trustworthy, and engaging interactions. company goals. Leaders agreed to focus on funding AI use cases that support employees in their roles As the analytics team launches Clientnomics, and improve practices that aren't currently members are focused on developing customized optimized. Al-supported client experiences rather thanTech Trends 2020 large-scale technology projects. So far, they have "In my previous role," Hickey says, "I spent a accumulated 147 use cases, completing 40 in the lot of time with organizations around the world. first year. Everyone talked about the benefits and future potential of AI, and some completed proofs-of- For example, when a client calls CIBC's contact concept, but few were able to implement them, center, a predictive model dynamically configures especially in banking and finance. By proactively the interactive voice response menu based on the addressing how we will-and will not-use client's recent transactions and offers the most technology, CIBC has embraced the positive relevant information at the top of the menu. The benefits it can deliver to employees and clients. bank aims to cement client relationships over All of this in less than a year." time with a continuous string of personalized interactions. Trust encoded in Abbott's DNA N THE HEALTH care industry, trust is a primary diagnose heart attacks." To safeguard patient driver of patient behavior: Trusted organizations data and privacy-a core facet of trust-Abbott have an edge in influencing behaviors that has enacted a number of enterprisewide policies, can create more positive health outcomes. For procedures, and annual employee training and 130-year-old global health care company Abbott, certification programs related to data handling and trust is top of mind as it evolves and expands its protection and compliance with national and global portfolio of diagnostic products, medical devices, regulatory mandates. Leaders have also made nutritionals, and branded generic medicines, says significant investments in cybersecurity capabilities CMO Melissa Brotz."7 and controls embedded into product designs, which is increasingly critical for a company such With technology-driven products such as sensor- as Abbott, with products and services that are based glucose monitoring systems, smartphone- heavily connected and integrated-often with other connected insertable cardiac monitors, and products, systems, and apps. cloud-connected implantable defibrillators and pacemakers, Abbott takes a multifaceted approach In addition, ensuring patient trust is a to trust, adds CIO Mark Murphy. Across the responsibility that falls to each of Abbott's 103,000 enterprise and its connected technologies, this employees, from the board of directors and C-suite includes comprehensive data protection policies, leadership to researchers, product designers, and employee training programs, and an external engineers. Company leadership, for instance, is ecosystem of trust-based partners, and other involved in data and product security oversight components. groups and board subcommittees, while employees participate in rigorous education programs on For example, Abbott is exploring multiple data- the implications of data privacy, security, and enabled opportunities to improve health care, transparency. "Abbott is focused on helping people such as a machine learning solution that combines live better, healthier lives," Murphy notes. "Often, performance data from the company's diagnostics technology is the enabler to help us do that, but it platforms with global clinical and patient always starts with the patient. We know that when demographic data to help health care providers we build technology, we are doing so on behalf of
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


