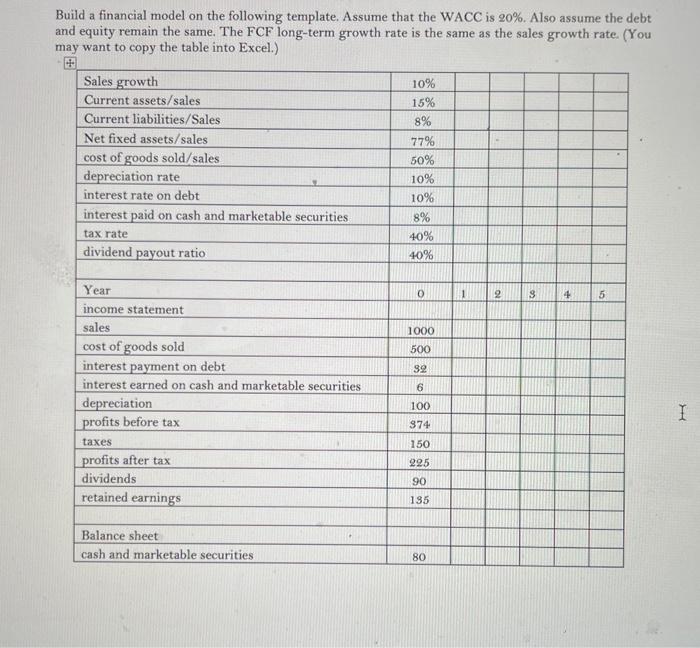
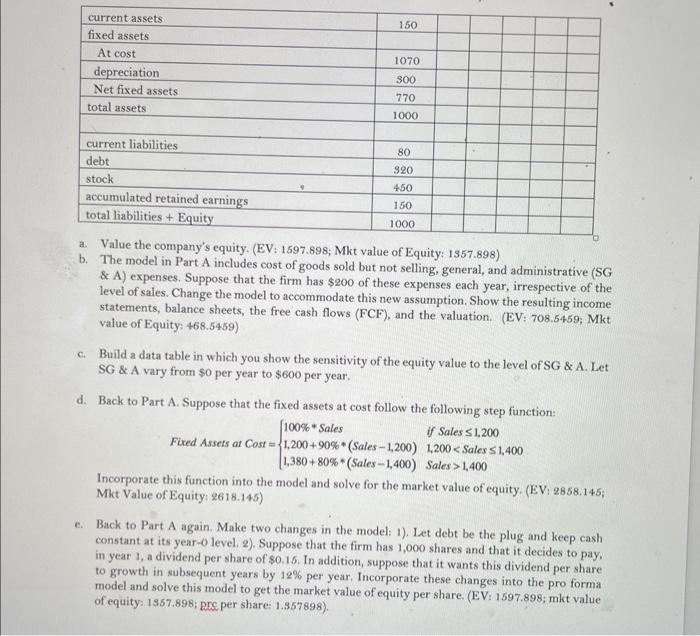
Build a financial model on the following template. Assume that the WACC is 20%. Also assume the debt and equity remain the same. The FCF long-term growth rate is the same as the sales growth rate. (You may want to copy the table into Excel.) a. Value the company's equity. (EV: 1597.898; Mkt value of Equity: 1557.898) b. The model in Part A includes cost of goods sold but not selling, general, and administrative (SG \& A) expenses. Suppose that the firm has $200 of these expenses each year, irrespective of the level of sales. Change the model to accommodate this new assumption. Show the resulting income statements, balance sheets, the free cash flows (FCF), and the valuation. (EV: 708.5459; Mkt value of Equity: 468.5459) c. Build a data table in which you show the sensitivity of the equity value to the level of SG \& A. Let SG \& A vary from $0 per year to $600 per year. d. Back to Part A. Suppose that the fixed assets at cost follow the following step function: FixedAssetsatCost=100%Sales1,200+90%(Sales-1,200)1,380+80%(Sales-1,400)ifSales1,2001,200
1,400 Incorporate this function into the model and solve for the market value of equity. (EV: 2858.145; Mkt Value of Equity: 2618.145 ) e. Back to Part A again. Make two changes in the model: 1). Let debt be the plug and keep cash constant at its year-0 level, 2). Suppose that the firm has 1,000 shares and that it decides to pay, in year 1, a dividend per share of $0.15. In addition, suppose that it wants this dividend per share to growth in subsequent years by 12% per year, Incorporate these changes into the pro forma model and solve this model to get the market value of equity per share. (EV: 1597.898; mkt value of equity: 1857.898; pre per share: 1.957898). Build a financial model on the following template. Assume that the WACC is 20%. Also assume the debt and equity remain the same. The FCF long-term growth rate is the same as the sales growth rate. (You may want to copy the table into Excel.) a. Value the company's equity. (EV: 1597.898; Mkt value of Equity: 1557.898) b. The model in Part A includes cost of goods sold but not selling, general, and administrative (SG \& A) expenses. Suppose that the firm has $200 of these expenses each year, irrespective of the level of sales. Change the model to accommodate this new assumption. Show the resulting income statements, balance sheets, the free cash flows (FCF), and the valuation. (EV: 708.5459; Mkt value of Equity: 468.5459) c. Build a data table in which you show the sensitivity of the equity value to the level of SG \& A. Let SG \& A vary from $0 per year to $600 per year. d. Back to Part A. Suppose that the fixed assets at cost follow the following step function: FixedAssetsatCost=100%Sales1,200+90%(Sales-1,200)1,380+80%(Sales-1,400)ifSales1,2001,2001,400 Incorporate this function into the model and solve for the market value of equity. (EV: 2858.145; Mkt Value of Equity: 2618.145 ) e. Back to Part A again. Make two changes in the model: 1). Let debt be the plug and keep cash constant at its year-0 level, 2). Suppose that the firm has 1,000 shares and that it decides to pay, in year 1, a dividend per share of $0.15. In addition, suppose that it wants this dividend per share to growth in subsequent years by 12% per year, Incorporate these changes into the pro forma model and solve this model to get the market value of equity per share. (EV: 1597.898; mkt value of equity: 1857.898; pre per share: 1.957898)