Question
BuildDLL.java public class BuildDLL { DoubleLinkedNode front, rear; private static char[] letters = new char[] {'K', 'T', 'E', 'N', 'P', 'A',


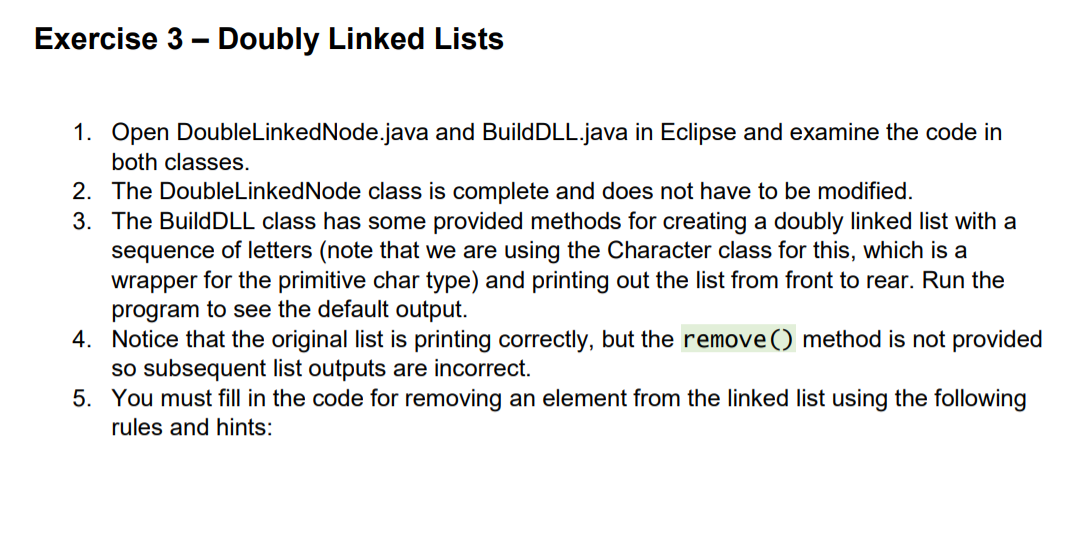

BuildDLL.java
public class BuildDLL {
DoubleLinkedNode
private static char[] letters = new char[] {'K', 'T', 'E', 'N', 'P', 'A', 'L'};
public BuildDLL () {
build();
}
public void remove (Character elem) {
// Add code in here to remove the node with the given value.
}
private void build () {
DoubleLinkedNode
node = new DoubleLinkedNode
pnode = front = node;
for (int i = 1; i < 7; i++) {
node = new DoubleLinkedNode
pnode.setNext(node);
node.setPrevious(pnode);
pnode = node;
}
rear = node;
}
public DoubleLinkedNode
return front;
}
public DoubleLinkedNode
return rear;
}
public void printF (DoubleLinkedNode
DoubleLinkedNode
while (curr != null) {
System.out.print(curr.getElement() + " ");
curr = curr.getNext();
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
BuildDLL dll = new BuildDLL();
System.out.println("Original List:");
dll.printF(dll.getFront());
System.out.println("***");
System.out.println("Removing an internal node:");
dll.remove('N');
dll.printF(dll.getFront());
System.out.println("***");
System.out.println("Removing the front node:");
dll.remove('K');
dll.printF(dll.getFront());
System.out.println("***");
System.out.println("Removing the rear node:");
dll.remove('L');
dll.printF(dll.getFront());
System.out.println("***");
}
}
BuildLinkedList.java
/**
* Build a linked list of integers from 1 to 10
*
* @author CS1027
*/
public class BuildLinkedList {
/*
* Print the information stored in all the nodes of the list whose first node is
* referenced by front
*/
private static void printList(LinearNode
LinearNode
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println(current.getElement());
current = current.getNext();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a linked list that holds 1, 2, ..., 10
// by starting at 10 and adding each node at head of list
LinearNode
LinearNode
for (int i = 10; i >= 1; i--) {
// create a new node for i
intNode = new LinearNode
// add it at the head of the linked list
intNode.setNext(front);
front = intNode;
}
printList(front);
}
}
DoubleLinkedNode.java
public class DoubleLinkedNode
private DoubleLinkedNode
private DoubleLinkedNode
private E element;
public DoubleLinkedNode(){
next = null;
previous = null;
element = null;
}
public DoubleLinkedNode (E elem){
next = null;
previous = null;
element = elem;
}
public DoubleLinkedNode
return next;
}
public DoubleLinkedNode
return previous;
}
public void setNext (DoubleLinkedNode
next = node;
}
public void setPrevious (DoubleLinkedNode
previous = node;
}
public E getElement(){
return element;
}
public void setElement (E elem){
element = elem;
}
}
LinearNode.java
/**
* LinearNode represents a node in a linked list.
*
* @author Dr. Lewis
* @author Dr. Chase
* @version 1.0, 08/13/08
*/
public class LinearNode
{
private LinearNode
private E element;
/**
* Creates an empty node.
*/
public LinearNode()
{
next = null;
element = null;
}
/**
* Creates a node storing the specified element.
*
* @param elem the element to be stored within the new node
*/
public LinearNode (E elem)
{
next = null;
element = elem;
}
/**
* Returns the node that follows this one.
*
* @return the node that follows the current one
*/
public LinearNode
{
return next;
}
/**
* Sets the node that follows this one.
*
* @param node the node to be set to follow the current one
*/
public void setNext (LinearNode
{
next = node;
}
/**
* Returns the element stored in this node.
*
* @return the element stored in this node
*/
public E getElement()
{
return element;
}
/**
* Sets the element stored in this node.
*
* @param elem the element to be stored in this node
*/
public void setElement (E elem)
{
element = elem;
}
}
Person.java
/**
* Class that represents a person with attributes name, email address
* @author CS1027
*
*/
public class Person {
/* Attribute declarations */
private String lastName; // last name
private String firstName; // first name
/**
* Constructor initializes the person's name and email address
*/
public Person(String firstName, String lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
/**
* getName method returns the person's full name
* @return first name followed by last name, blank separated
*/
public String getName () {
return firstName + " " + lastName;
}
/**
* toString method returns a string representation of the person
* @return string with first name and last name, email address
*/
public String toString() {
String s = firstName + " " + lastName;
return s;
}
}
TestReverse.java
public class TestReverse {
public static void main (String[] args) {
String[] arr1 = new String[] {"atom", "breeze", "clock", "daydream", "energy"};
ReversibleArray
System.out.println(revArr1.toString());
revArr1.reverse();
System.out.println(revArr1.toString());
Integer[] arr2 = new Integer[] {11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77};
ReversibleArray
System.out.println(revArr2.toString());
revArr2.reverse();
System.out.println(revArr2.toString());
Person p1 = new Person("Jerry", "Seinfeld");
Person p2 = new Person("Salma", "Hayek");
Person p3 = new Person("Reese", "Witherspoon");
Person p4 = new Person("Vince", "Vaughn");
Person[] arr3 = new Person[] {p1, p2, p3, p4};
ReversibleArray
System.out.println(revArr3.toString());
revArr3.reverse();
System.out.println(revArr3.toString());
}
}
Exercise 1 - Creating a class with generics 1. Create a new class called ReversibleArray. 2. In the class header, add the code immediately to the right of the class name. 3. Give this class two private instance variables: T array and int count 4. Create a constructor which takes in one parameter of type T[] and assign that parameter's value into this. array. Set count as the length of the array. 5. Add a toString() method that outputs the array values in the format: elem0, elem1, elem2, etc. (hint: add the comma and space only if you are not on the final iteration of the loop). 6. Create the most important function in this class: public void reverse () { } a. This method must swap elements within the array, without making a new array or other collection. b. The swaps should be made symmetrically about the middle of the array. This means array[0] swaps with array[n-1], array[1] swaps with array[n-2], etc. c. Use a temp variable to help with these swaps. What variable type should this temp variable be? d. How many swaps must be made to correctly reverse the array? 7. Open TestReverse.java and read over the code in its main() function.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


