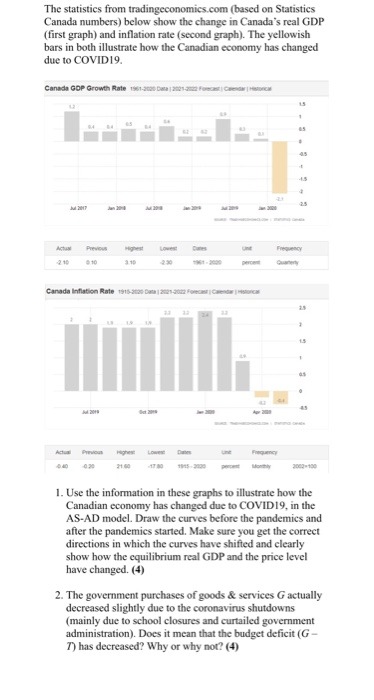
Question: Buinesss The statistics from tradingeconomics.com (based on Statistics Canada numbers) below show the change in Canada's real GDP (first graph) and inflation rate (second graph).



Buinesss
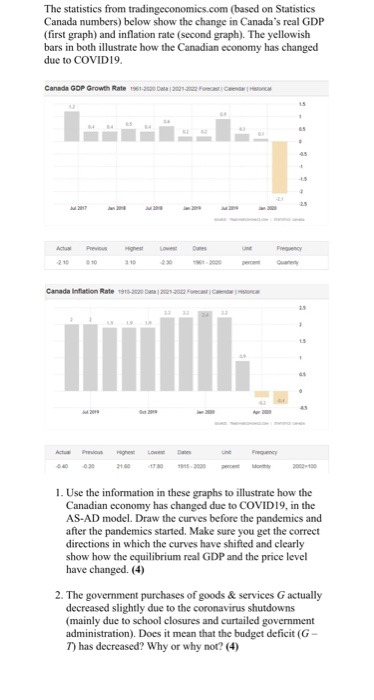



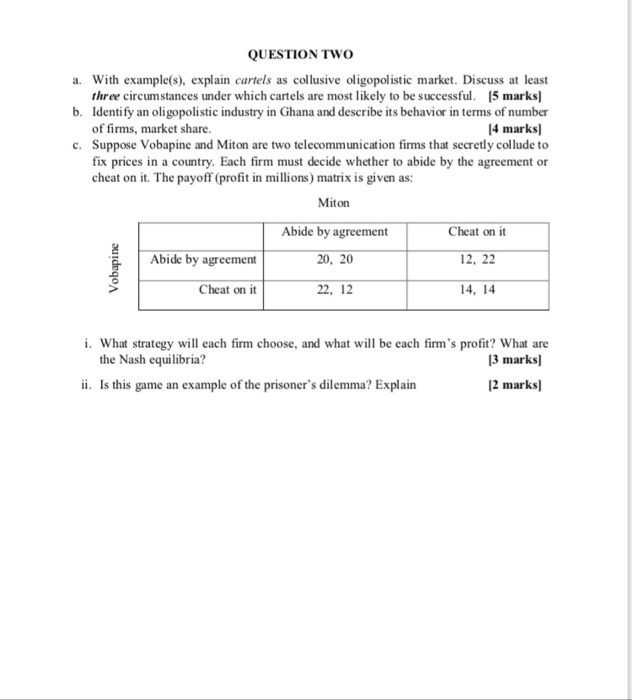
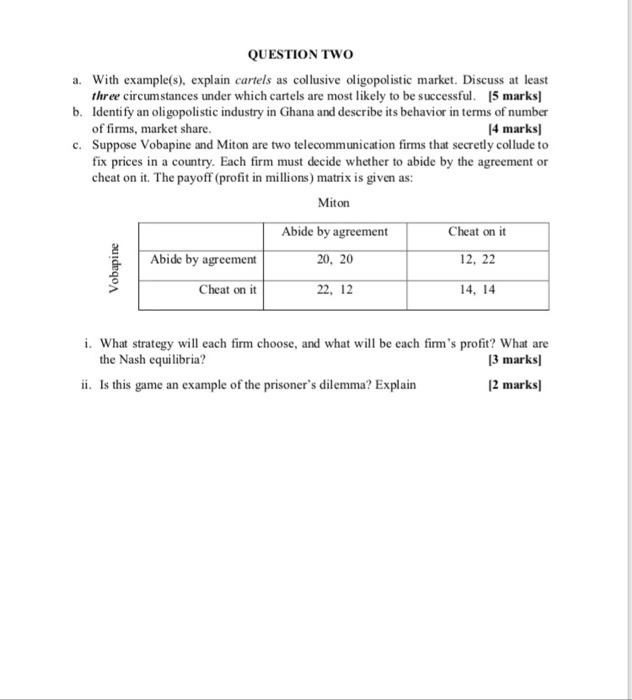
The statistics from tradingeconomics.com (based on Statistics Canada numbers) below show the change in Canada's real GDP (first graph) and inflation rate (second graph). The yellowish bars in both illustrate how the Canadian economy has changed due to COVID 19. Canada GOP Growth Rate Ti-and Day |20osama Fus 15 Previous Canada Inflation Rate the Shot Down join-dom forum Create | Ristic MEHI Actionil 1. Use the information in these graphs to illustrate how the Canadian economy has changed due to COVID19, in the AS-AD model. Draw the curves before the pandemics and after the pandemics started. Make sure you get the correct directions in which the curves have shifted and clearly show how the equilibrium real GDP and the price level have changed. (4) 2. The government purchases of goods & services G actually decreased slightly due to the coronavirus shutdowns (mainly due to school closures and curtailed government administration). Does it mean that the budget deficit (G - 7) has decreased? Why or why not? (4)The statistics from tradingeconomics.com (based on Statistics Canada numbers) below show the change in Canada's real GDP (first graph) and inflation rate (second graph). The yellowish bars in both illustrate how the Canadian economy has changed due to COVID 19. Canada GOP Growth Rate Ti-and Day |20osama Fus 15 Previous Canada Inflation Rate the Shot Down join-dom forum Create | Ristic MEHI Actionil 1. Use the information in these graphs to illustrate how the Canadian economy has changed due to COVID19, in the AS-AD model. Draw the curves before the pandemics and after the pandemics started. Make sure you get the correct directions in which the curves have shifted and clearly show how the equilibrium real GDP and the price level have changed. (4) 2. The government purchases of goods & services G actually decreased slightly due to the coronavirus shutdowns (mainly due to school closures and curtailed government administration). Does it mean that the budget deficit (G - 7) has decreased? Why or why not? (4)19. Suppose the parameters of the IS curve are a, = 0, b = 0.5, r = 3% and the real interest rate is initially R = 3%. (a) Is the economy in its long-term equilibrium? Explain. (b) Suppose the real interest rate falls to 2 percent; what happens to the short-run equilibrium, holding everything else constant? (c) What happens to the short-run equilibrium if a falls 3 percent, holding everything else constant? (d) What occurs if the marginal product of capital rises to 5%? What would cause this to happen?19. Suppose the parameters of the IS curve are a, = 0, b = 0.5, r = 3% and the real interest rate is initially R = 3%. (a) Is the economy in its long-term equilibrium? Explain. (b) Suppose the real interest rate falls to 2 percent; what happens to the short-run equilibrium, holding everything else constant? (c) What happens to the short-run equilibrium if a falls 3 percent, holding everything else constant? (d) What occurs if the marginal product of capital rises to 5%? What would cause this to happen?Problem 4 (40 points) (This is a somewhat mathematically involved problem. Please show your work, partial credit will be given) A firm has a Cobb-Douglas production function q = f(K, L) = Kall-a and faces wages, w, and rental rate of capital, r. 1. (3 points) Does this production function exhibit increasing, decreasing, or con- stant returns to scale? 2. (6 points) Find the short-run cost curve, C(q), as a function of q and the param- eters. 3. (6 points) For this subpart only, assume that K = 10, r = 1.5, w = 6, and o = 2/3. Derive expressions for MC, VC, FC, ATC, AVC, and AFC. Plot MC, ATC, AVC, and AFC, all on the same graph (using a graphing program -WolframAlpha, Mathematica, Matlab, etc.- is fine for this part). 4. (6 points) For this subpart only, assume that K = 10, r = 1.5, w = 6, and a = 2/3. Assume now that we know the market price is p = 18, which is fixed, and we are still operating in the short-run. What is the profit-maximizing choice of q? 5. (6 points) Solve for profits, a, as a function of market price, p (and the parameters w, r, K, a). Then, assume as we did in subpart 3 that K = 10, r = 1.5, w = 6, and a = 2/3, and continue to assume so until subpart 6 (included). Will profits ever be negative? If so, find the price range at which profits are negative. 6. (6 points) Is the firm better off shutting down (producing q = 0) at any positive low price? Explain. 7. (7 points) Going back to the original production function, let's think about the firm's problem in the long run. Find their optimal choices of inputs (as a function of q, w, r, a) and the resulting long-run cost function C(q). How does the firm's choice of L and K change if r goes up? What happens to costs?Problem 2 (16 points) A firm has a production function q = /(K, L) = K + 0.5L and face wages w and rental rate of capital r. Let w = 1,r = 1. For this problem, think about the long-run where capital is not fixed. 1. (8 points) Suppose the firm wants to produce q = 200. What is the combination of K and L that minimizes total cost? Draw the isoquant and isocost curves that correspond to the firm's optimal choice, with K in the y-axis and L in the x-axis. Explain. 2. (8 points) Suppose that the government wants to encourage the use of labor and decides to pay for 50% of the firm's wage costs for the first 100 units of labor used -i.e. the firm only pays 0.5w for the first 100 units of labor used. Again, assume that the firm wants to produce q = 200. What are all the possible combinations of K and L that minimize total cost? Draw the isoquant and isocost curves that correspond to the firm's optimal choice. Explain. Problem 3 (16 points) In the short run, a firm has fixed capital K. We know that its short-run cost function is CSR (q) = q' - 2q2 + 2q + 2. 1. (8 points) Plot the short-run marginal cost and average variable cost (as a function of q). What is the short-run supply curve? 2. (8 points) Suppose that the long-run cost curve is CLR (q) = =q'. Can you find the quantity q such that in the long-run the firm optimally chooses to use K units of capital to produce 4? (Hint: if you are having trouble finding the solution by hand, use a numerical solver; Wolfram Alpha is a great resource!)QUESTION TWO a. With example(s). explain cartels as collusive oligopolistic market. Discuss at least three circumstances under which cartels are most likely to be successful. [5 marks] b. Identify an oligopolistic industry in Ghana and describe its behavior in terms of number of firms, market share. [4 marks] c. Suppose Vobapine and Miton are two telecommunication firms that secretly collude to fix prices in a country. Each firm must decide whether to abide by the agreement or cheat on it. The payoff (profit in millions) matrix is given as: Miton Abide by agreement Cheat on it Abide by agreement 20, 20 12, 22 Vobapine Cheat on it 22, 12 14, 14 i. What strategy will each firm choose, and what will be each firm's profit? What are the Nash equilibria? [3 marks] ii. Is this game an example of the prisoner's dilemma? Explain [2 marks]QUESTION TWO a. With example(s). explain cartels as collusive oligopolistic market. Discuss at least three circumstances under which cartels are most likely to be successful. [5 marks] b. Identify an oligopolistic industry in Ghana and describe its behavior in terms of number of firms, market share. [4 marks] c. Suppose Vobapine and Miton are two telecommunication firms that secretly collude to fix prices in a country. Each firm must decide whether to abide by the agreement or cheat on it. The payoff (profit in millions) matrix is given as: Miton Abide by agreement Cheat on it Abide by agreement 20, 20 12, 22 Vobapine Cheat on it 22, 12 14, 14 i. What strategy will each firm choose, and what will be each firm's profit? What are the Nash equilibria? [3 marks] ii. Is this game an example of the prisoner's dilemma? Explain [2 marks]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


