Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
bundled with a / and a separate / and no and no / bundled with a / and a separate bundled with a / and
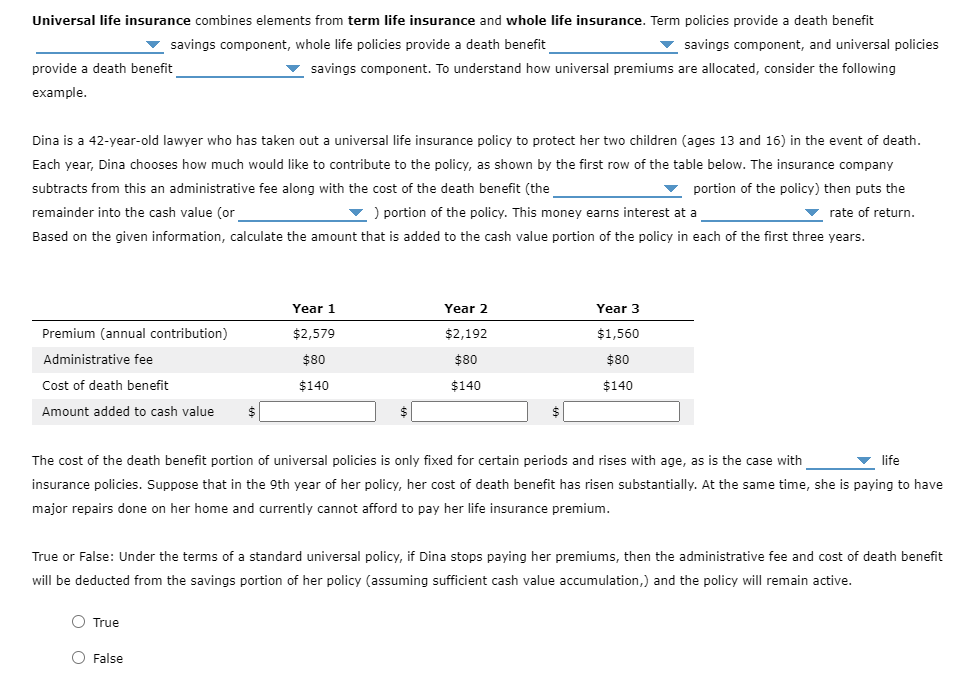
bundled with a / and a separate / and no
and no / bundled with a / and a separate
bundled with a / and no / and a separate
pure insurance / savings
pure insurance / savings
fixed / market based
term / whole
Universal life insurance combines elements from term life insurance and whole life insurance. Term policies provide a death benefit savings component, whole life policies provide a death benefit savings component, and universal policies provide a death benefit savings component. To understand how universal premiums are allocated, consider the following example. Dina is a 42-year-old lawyer who has taken out a universal life insurance policy to protect her two children (ages 13 and 16) in the event of death. Each year, Dina chooses how much would like to contribute to the policy, as shown by the first row of the table below. The insurance company subtracts from this an administrative fee along with the cost of the death benefit (the portion of the policy) then puts the remainder into the cash value (or portion of the policy. This money earns interest at a rate of return. Based on the given information, calculate the amount that is added to the cash value portion of the policy in each of the first three years. Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Premium (annual contribution) $2,579 $2,192 $1,560 Administrative fee $80 $80 $80 Cost of death benefit $140 $140 $140 Amount added to cash value $ $ The cost of the death benefit portion of universal policies is only fixed for certain periods and rises with age, as is the case with life insurance policies. Suppose that in the 9th year of her policy, her cost of death benefit has risen substantially. At the same time, she is paying to have major repairs done on her home and currently cannot afford to pay her life insurance premium. True or False: Under the terms of a standard universal policy, if Dina stops paying her premiums, then the administrative fee and cost of death benefit will be deducted from the savings portion of her policy (assuming sufficient cash value accumulation) and the policy will remain active. O True O False Universal life insurance combines elements from term life insurance and whole life insurance. Term policies provide a death benefit savings component, whole life policies provide a death benefit savings component, and universal policies provide a death benefit savings component. To understand how universal premiums are allocated, consider the following example. Dina is a 42-year-old lawyer who has taken out a universal life insurance policy to protect her two children (ages 13 and 16) in the event of death. Each year, Dina chooses how much would like to contribute to the policy, as shown by the first row of the table below. The insurance company subtracts from this an administrative fee along with the cost of the death benefit (the portion of the policy) then puts the remainder into the cash value (or portion of the policy. This money earns interest at a rate of return. Based on the given information, calculate the amount that is added to the cash value portion of the policy in each of the first three years. Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Premium (annual contribution) $2,579 $2,192 $1,560 Administrative fee $80 $80 $80 Cost of death benefit $140 $140 $140 Amount added to cash value $ $ The cost of the death benefit portion of universal policies is only fixed for certain periods and rises with age, as is the case with life insurance policies. Suppose that in the 9th year of her policy, her cost of death benefit has risen substantially. At the same time, she is paying to have major repairs done on her home and currently cannot afford to pay her life insurance premium. True or False: Under the terms of a standard universal policy, if Dina stops paying her premiums, then the administrative fee and cost of death benefit will be deducted from the savings portion of her policy (assuming sufficient cash value accumulation) and the policy will remain active. O True O FalseStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


