Business information system:
1) In the case, what problems did the police department have with data?
2) How is a DBMS expected to help the police department compared to work with files such as Excel files? Relate both to the problems explicitly mentioned in the case with respect to data, and other issues you can identify by relating to the processes mentioned in the case



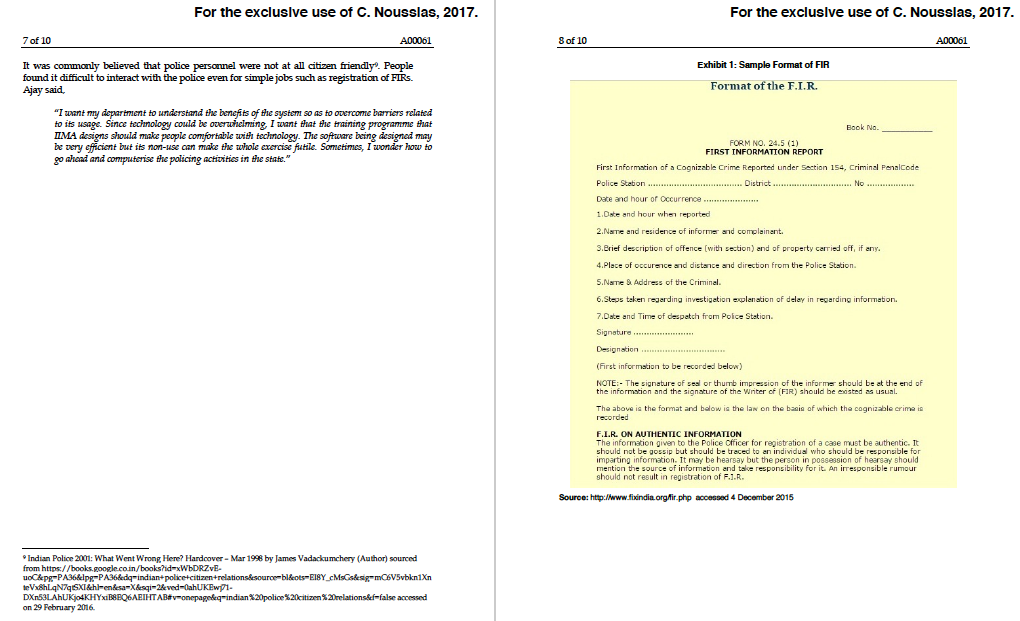
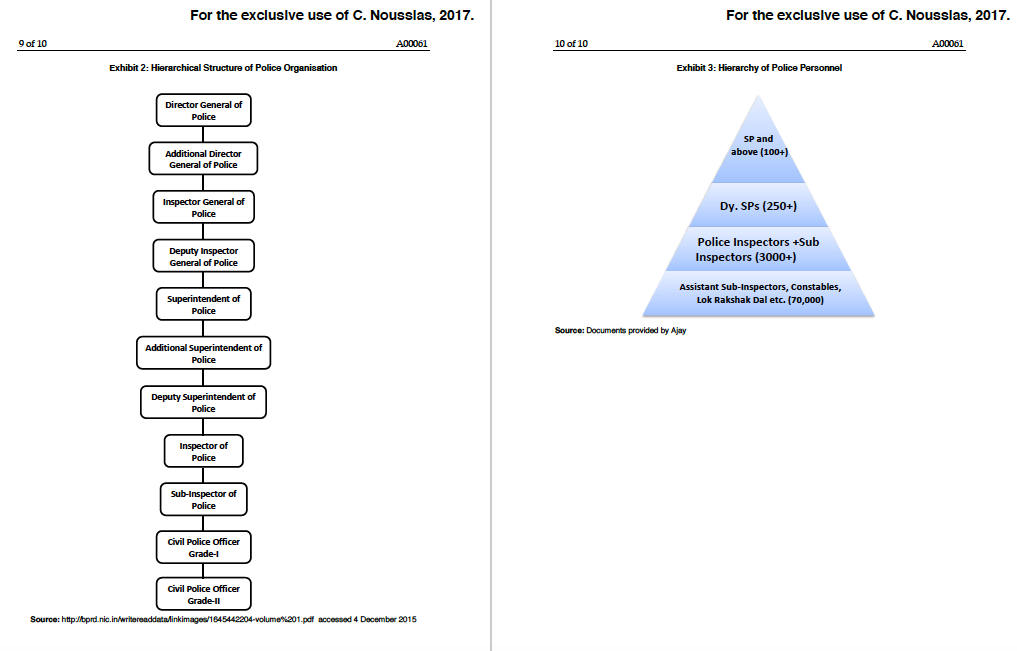
. For the excluslve use of C. Nousslas, 2017 For the excluslve use of C. Nousslas, 2017 2 of 10 A00061 The interaction of the case author with various police officers indicated that this need towards was not a arious attenmpts had been made to Indian Institute of Management Ahmedabad A00061 Mareh 17,2016 the police department in different states. While some states had made reasonably good progress, others had not. This curent attempt at the computerisation of a Police Department in ASWI was the third one of its kind. According to Ajay. this time, it had seen some suocess, albeit not full in sowing the seeds of computerisation However, it was st "Miles to go before we sleep Computerisation of a Police Department in ASWI The govermment is keen touurds computerisation; houer, since the number of people in th department is so lge, I amm confused up ho wich level of the hiearchy to target and what modules of the softwmare shoula be impiemen tod at the beginning. Also, the kind of taining that BACKGROUND OF THE COMPUTERISATION PROJECT has to be imparted and gee content of e traning programme are difficult to determine." ln 1919, the National Police Commission which was set up by the Govemment of India recoummended the creatian of a nodal agency. which would suggest standard formats for maintenance of crime-criminal records at all the police stations in the country. The same commmon format could also be utilised to created shareable databases at Police Stations, and District, State and National Levels. Based on this Bureau (NCRB) was established in 1986 with the amalgamation of the Directorate of Coordination Police Computers Central Fnger Frint Bureau Data Section of Coordination Division of Central Bureau of Investigation and Statistical Sectian of the Bureau of Police Research and Development The National Crime-Criminal Infomation System (NCCIS) was conceived as part of the police computerisation plan approved with the objective of managing the hieh volume of crime and ciminal-related information geopraphically dispersed all over the Mr. Ajay Vasav. Inspector General of Police of ASWI (A state in Western India) he shared his apprehensions about the cououterisation process in the state. This initiative was beine taken when the Govemment of India had envisaged a centralised crime and criminal tracking system he National Crime Records to hamess the power of information technology According to Ajay, policing is ane of the most difficult jobs in the govemment as it requires 52 x 7 x 24 vigil (52 weeks in a year seven days a week, and 24 hours a day). Any improper action whether taken before time or delayed may hurt the case. There were many duties that the police had to peform, which ranged from maintaining law and order, monitoring anti-natianal activities, controlling crime, providing protection and so on The geographic span in whuch the country and facilitating the real-time on-line sharing of the information through integrated networking department worked was vast. Ajay shared In 1093, the Natianal Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), New Dellhi linked the State Crime Records Bureau (SCRB) at the state capital with the Crime and Criinal Information System (CCIS). According to the NCRB website, CCis was implemented in 35 States and UTs (Union Territories).727 police districts and at the national level using standard software and hardware. It was envisioned that more than 15,000 police stations and more than one lalth police posts in the country would come anto this network once the computerisation exercise was over. The application had been designed and Y2K problem the system was migrated from UNDX to a Windows platform The application was uperaded to support various Indian languages such as Gijarati Marathi Taml, Gurunukhi, and Kannada besides Hindi and English Also, the queries and reports were made web enabled NCRB had prepared formats for registering a Frst Information Report (FIR) arrests, and other crimes so that access to records and data became easier. Inutially. the FIR was to be in the recommended format and after feeding data it could be stored directly in the computers in poice stations. Networkine between the police stations was to be done after feeding the old records and data However, there were gaps between vision and implementation The project did not get completed as envisaged NCRB was in the process of implementing CCINS(Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems). CCTNS would be a country-wide network of crimes and criminals, and would help in tracking criminals A rual police shation may have scores of villages undcr its jurisdiction. Wnle cach police station and police-chowkey has limated authority, the criinas and ofenders do not work in limitod arcas Their domain overlaps various police teihorics. Effective policing raquires interactions and sharing of information at tice-choukey, police station, diserict, inter- district, inter-shate and intermational level. In such conditions, it is crucial that police personnd exchange information which comes to gnir notice. In ogers words, to bc ewery police personnei should e the right information available to thenm oake he nghe under UND CS using INGRES RDBMS Post the using ctie decisions at the rioht timc. Ajay shared that till umtl recently. the information system in the police had been manual quite archaic and did not make use of available or latest technologymphasis was the recording of facts than on dissemination and use of information The officials of the police department understood that it was time to adopt tedhnology and replace manual records and dissemination of information with electroric records and dissemination Poice cheorkey is Hindi for police outpost Prepared by Professor Sarjay Vema India Inctitute of Management,Ahmedabad The author is thankful to M. Priyanka Sharma, Research Associate, for hes support Cases of the Indian Inctitute of Management Ahmedabad are prepared as a basis of dassroom discussian. They are not designed to present ilustrations of eithes correct or incorrect handling of admiristraive probles. The history of computerisation is abstracted from http:/crbnic in accessed on 4 December 215. Y2K or Year 2000 was a bug in software developed before 2000 where the six digit format of date was used instrad of eight digit format 2015 by he Indian Inctihate of Manapemnt, Ahmedabad. . For the excluslve use of C. Nousslas, 2017 For the excluslve use of C. Nousslas, 2017 2 of 10 A00061 The interaction of the case author with various police officers indicated that this need towards was not a arious attenmpts had been made to Indian Institute of Management Ahmedabad A00061 Mareh 17,2016 the police department in different states. While some states had made reasonably good progress, others had not. This curent attempt at the computerisation of a Police Department in ASWI was the third one of its kind. According to Ajay. this time, it had seen some suocess, albeit not full in sowing the seeds of computerisation However, it was st "Miles to go before we sleep Computerisation of a Police Department in ASWI The govermment is keen touurds computerisation; houer, since the number of people in th department is so lge, I amm confused up ho wich level of the hiearchy to target and what modules of the softwmare shoula be impiemen tod at the beginning. Also, the kind of taining that BACKGROUND OF THE COMPUTERISATION PROJECT has to be imparted and gee content of e traning programme are difficult to determine." ln 1919, the National Police Commission which was set up by the Govemment of India recoummended the creatian of a nodal agency. which would suggest standard formats for maintenance of crime-criminal records at all the police stations in the country. The same commmon format could also be utilised to created shareable databases at Police Stations, and District, State and National Levels. Based on this Bureau (NCRB) was established in 1986 with the amalgamation of the Directorate of Coordination Police Computers Central Fnger Frint Bureau Data Section of Coordination Division of Central Bureau of Investigation and Statistical Sectian of the Bureau of Police Research and Development The National Crime-Criminal Infomation System (NCCIS) was conceived as part of the police computerisation plan approved with the objective of managing the hieh volume of crime and ciminal-related information geopraphically dispersed all over the Mr. Ajay Vasav. Inspector General of Police of ASWI (A state in Western India) he shared his apprehensions about the cououterisation process in the state. This initiative was beine taken when the Govemment of India had envisaged a centralised crime and criminal tracking system he National Crime Records to hamess the power of information technology According to Ajay, policing is ane of the most difficult jobs in the govemment as it requires 52 x 7 x 24 vigil (52 weeks in a year seven days a week, and 24 hours a day). Any improper action whether taken before time or delayed may hurt the case. There were many duties that the police had to peform, which ranged from maintaining law and order, monitoring anti-natianal activities, controlling crime, providing protection and so on The geographic span in whuch the country and facilitating the real-time on-line sharing of the information through integrated networking department worked was vast. Ajay shared In 1093, the Natianal Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), New Dellhi linked the State Crime Records Bureau (SCRB) at the state capital with the Crime and Criinal Information System (CCIS). According to the NCRB website, CCis was implemented in 35 States and UTs (Union Territories).727 police districts and at the national level using standard software and hardware. It was envisioned that more than 15,000 police stations and more than one lalth police posts in the country would come anto this network once the computerisation exercise was over. The application had been designed and Y2K problem the system was migrated from UNDX to a Windows platform The application was uperaded to support various Indian languages such as Gijarati Marathi Taml, Gurunukhi, and Kannada besides Hindi and English Also, the queries and reports were made web enabled NCRB had prepared formats for registering a Frst Information Report (FIR) arrests, and other crimes so that access to records and data became easier. Inutially. the FIR was to be in the recommended format and after feeding data it could be stored directly in the computers in poice stations. Networkine between the police stations was to be done after feeding the old records and data However, there were gaps between vision and implementation The project did not get completed as envisaged NCRB was in the process of implementing CCINS(Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems). CCTNS would be a country-wide network of crimes and criminals, and would help in tracking criminals A rual police shation may have scores of villages undcr its jurisdiction. Wnle cach police station and police-chowkey has limated authority, the criinas and ofenders do not work in limitod arcas Their domain overlaps various police teihorics. Effective policing raquires interactions and sharing of information at tice-choukey, police station, diserict, inter- district, inter-shate and intermational level. In such conditions, it is crucial that police personnd exchange information which comes to gnir notice. In ogers words, to bc ewery police personnei should e the right information available to thenm oake he nghe under UND CS using INGRES RDBMS Post the using ctie decisions at the rioht timc. Ajay shared that till umtl recently. the information system in the police had been manual quite archaic and did not make use of available or latest technologymphasis was the recording of facts than on dissemination and use of information The officials of the police department understood that it was time to adopt tedhnology and replace manual records and dissemination of information with electroric records and dissemination Poice cheorkey is Hindi for police outpost Prepared by Professor Sarjay Vema India Inctitute of Management,Ahmedabad The author is thankful to M. Priyanka Sharma, Research Associate, for hes support Cases of the Indian Inctitute of Management Ahmedabad are prepared as a basis of dassroom discussian. They are not designed to present ilustrations of eithes correct or incorrect handling of admiristraive probles. The history of computerisation is abstracted from http:/crbnic in accessed on 4 December 215. Y2K or Year 2000 was a bug in software developed before 2000 where the six digit format of date was used instrad of eight digit format 2015 by he Indian Inctihate of Manapemnt, Ahmedabad











